2022 Ransomware Trends Review
The original report is in Chinese, and this version is an AI-translated edition.
1.Overview
Ransomware is a type of highly destructive computer Trojan program. In recent years, ransomware has become one of the main cybersecurity threats faced by global companies and organizations. It is a criminal tool used by attackers to obtain illegal economic benefits. Once attacked by ransomware, the normal operation of companies and organizations will be seriously affected, often resulting in business interruption, data encryption and theft. Attackers threaten victim companies and organizations with data recovery, data exposure and other forms and extort ransom. Data forms include documents, emails, databases, source code and other formats; ransom forms include real currency, Bitcoin and other virtual currencies. Attackers usually set a time limit for ransom payment, and the ransom amount will increase over time. Sometimes, even if the victim companies and organizations pay the ransom to the attackers, the encrypted files cannot be recovered. In 2022, the global manufacturing, medical, construction, energy, financial and government agencies were frequently attacked by ransomware, which caused serious losses to the global industrial output value.
Antiy CERT has sorted out the popular ransomware in 2022 and formed a family overview information table, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Active ransomware families and related attacks in 2022
| Number | Family (alphabetical order) | Victims of the business and organization | Attack time | Influence |
| 1 | AvosLocker | Christus Health | May 2022 | More than 600 devices were affected by the attack, system data was stolen, and approximately 15,000 people were affected |
| 2 | Black Basta | German building materials group Knauf | June 2022 | Forced its global IT team to shut down all IT systems to isolate the negative impact |
| 3 | BlackCat | Creos Luxembourg SA , operator of the Luxembourg gas pipeline and electricity network | July 2022 | Some portals are unavailable and about 150GB of files have been stolen |
| 4 | Clop | UK Water Suppliers South Staffordshire Water | August 2022 | Some of the company’s IT systems were interrupted and about 5TB of files were stolen |
| 5 | Conti | Delta Electronics | January 2022 | About 1,500 servers and 12,000 PCs were encrypted, and a ransom of $15 million was demanded. |
| 6 | Cuba | Montenegro National Government | August 2022 | 150 workstations of 10 government agencies were encrypted, and a ransom of $10 million was demanded |
| 7 | Hive | Costa Rican Public Health Service | May 2022 | Multiple computers in the network environment cannot work properly, and data on the victim system is stolen |
| 8 | LockBit | Bridgestone Americas | February 2022 | The company suspended some operations and the victim system data was stolen |
| 9 | LV | German semiconductor manufacturer Semikron | August 2022 | Some files in the IT system were encrypted, and about 2 TB of data was stolen from the victim system |
| 1 0 | Vice Society | Palermo, Italy | June 2022 | A large number of Internet services have been suspended, and citizens and tourists are unable to handle related business |
2.Ransomware Behavior Classification
There are four main types of ransomware activities active in 2022:
1.Impact on user systems
This type of ransomware can prevent users from using their computers normally by modifying the disk MBR or setting a lock screen program. (For example, MBR Locker and WhisperGate)
2.Destroy data
This type of ransomware does not encrypt files, but instead overwrites files with characters or damages files in other ways, permanently destroying user data. Some ransomware will also demand a ransom after destroying the data. (For example, Hermetic Ransom and Onyx ransomware)
3.Encrypt files
This type of ransomware uses a combination of specific encryption algorithms (such as AES, RSA, ChaCha20 and Salsa20 , etc.) to encrypt files. Most victim files cannot be decrypted temporarily without the corresponding key decryption tool. Only a small number of victim files can be decrypted due to algorithmic logic errors in the ransomware. (For example, Coffee [1] and P hobos ransomware)
4.Steal files + encrypt files
This type of ransomware will reside in the victim system for a period of time before launching a ransomware attack, during which time it steals data files. After the theft is completed, it will launch a ransomware attack, encrypt the files in the system, and notify the victim that the files have been stolen. If the ransom is not paid on time, the stolen data files will be made public to put pressure on the victim, thus forcing the victim to pay the ransom as soon as possible. (For example, Pandora [2] , LockBit and Conti [3] ransomware)
3.2022 Ransomware Families Review
Looking back at the ransomware attacks that occurred in 2022, this article takes stock of popular ransomware families, including basic family information, family overview and typical cases, sorted by the first letter of the family name, in no particular order.
3.1 AvosLocker
AvosLocker ransomware was discovered in July 2021. The attack organization behind it uses the Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model to operate, adopts a dual extortion strategy of “threatening to expose corporate data + encrypting data for ransom”, and is good at launching ransomware attacks by exploiting vulnerabilities related to Microsoft Exchange Server and Log4j. In October 2021, it began to use Linux system attack payloads and has the ability to attack the ESXi platform. After successfully invading the victim system network environment, the attacker used the remote desktop software AnyDesk to connect to the victim host and carry out subsequent malicious behaviors. Security researchers found that the ransomware can run in safe mode, and some of its technical features are related to the REvil ( Sodinokibi) ransomware [4] .
3.1.1 Family Overview
| Family name | AvosLocker |
| Appearance time | July 2021 |
| Typical propagation methods (except phishing attacks) | Exploits |
| Typical encryption suffixes | .avos |
| Decryption tool | No public decryption tool has been found yet |
| Encryption system | Windows, Linux |
| Attack mode | There are cases of targeted attacks |
| Common industries | Medical, finance, IT, education |
| Common countries/regions | United States, Canada, India, Philippines |
| Is it double extortion? | Yes |
| Ransom note | 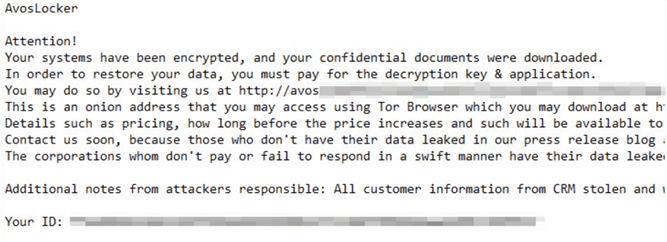 |
3.1.2 Typical Cases
1.McKenzie Health in Michigan, USA, suffered from AvosLocker attack
March 10 , 2022, McKenzie Health, a medical institution in Michigan, USA, suffered a cyber attack[5]. The attack caused some IT systems to stop operating and some patient information to be deleted. Subsequently, the attack organization behind the AvosLocker ransomware claimed responsibility for the incident and stole some data.
2.Christus Health, a nonprofit health system in Texas, USA , suffered an AvosLocker attack
Christus Health, a nonprofit health system in Texas, was attacked by the AvosLocker ransomware in May[6]. Subsequently, the attack group behind the AvosLocker ransomware claimed responsibility for the incident and stole some data.
3.2 Black Basta
Black Basta ransomware was discovered in April 2022. The attack organization behind it uses the RaaS model to operate, adopting a dual ransom strategy of “threatening to expose corporate data + encrypting data for ransom”. It has attack payloads for Windows and Linux systems, and mainly spreads through obtaining access credentials from third parties, exploiting vulnerabilities, and carrying other malware. After invading any host in the victim’s network environment, it uses a combination of multiple tools to achieve lateral movement within the intranet. The attack organization behind this ransomware once posted on underground forums seeking corporate network access credentials and promised to provide a portion of the profits obtained from the attack as a reward. Security researchers speculate that Black Basta may be a branch or renamed organization of the Conti ransomware organization [7] .
3.2.1 Family Overview
| Family name | Black Basta |
| Appearance time | April 2022 |
| Typical propagation methods (except phishing attacks) | Third-party access to credentials, exploits, and other malware |
| Typical encryption suffixes | .basta |
| Decryption tool | No public decryption tool has been found yet |
| Encryption system | Windows, Linux |
| Attack mode | There are cases of targeted attacks |
| Common industries | Construction, finance, medical care, energy |
| Common countries/regions | United States, Germany, Canada, France |
| Is it double extortion? | Yes |
| Ransom note | 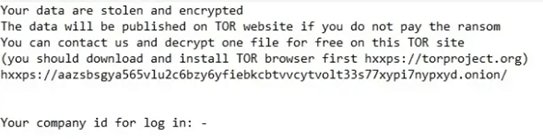 |
3.2.2 ypical Cases
1.American Dental Association under attack from Black Basta
In April 2022, the American Dental Association (ADA ) was attacked by the Black Basta ransomware[8], which caused the destruction of multiple online services, telephone systems, and email systems. Online service systems in multiple regions were also affected, such as New York, Virginia, and Florida. Subsequently, the attack organization behind the Black Basta ransomware claimed responsibility for the incident and disclosed about 2.8GB of data stolen from the victim system on its data leakage platform, indicating that this was only 30% of the total stolen data.
2.German wind turbine provider Deutsche Windtechnik hit by Black Batta attack
German wind turbine service provider Deutsche Windtechnik suffered a cyberattack around April 11[9] , which forced the company to shut down remote data monitoring connections to its wind turbines. The group behind the Black Basta ransomware subsequently claimed responsibility for the incident.
3.US defense firm Elbit hit by Black Basta attack
On June 8, the US subsidiary of Israeli defense company Elbit Systems suffered a cyberattack[10]. The company provides solutions related to defense, commercial aviation, homeland security, and medical equipment. The incident affected 369 people. The company provided 12 months of free identity protection and credit monitoring services to affected customers. Subsequently, the attack group behind the Black Basta ransomware released information about Elbit and stolen data on its data leakage platform in September, including payrolls, audit reports, and confidentiality agreements.
4.German building materials company Knauf Group suffered Black Basta attack
June 29, Knauf Group released a statement saying that it had suffered a cyber attack[11], which disrupted its business operations and forced its global IT team to shut down all IT systems to isolate the negative impact. Knauf is a multinational manufacturer of building systems and building materials headquartered in Germany, accounting for approximately 81% of the global wall panel market. Subsequently, the attack group behind the Black Basta ransomware released relevant data about the Knauf Group on its data leakage platform on July 16, including emails, internal production materials and employee information.
3.3 BlackCat
BlackCat ransomware, also known as ALPHV or Noberus, was discovered in November 2021. The attack organization behind it uses the RaaS model to operate, using Exmatter as a data theft tool, and adopts a double extortion strategy of “threatening to expose corporate data + encrypting data for extortion”. On this basis, it adds DDoS attack threats to constitute a triple extortion. It is the first ransomware organization to write a ransomware executable in Rust language, with Windows and Linux system attack payloads. It is mainly spread by obtaining access credentials from third parties, exploiting vulnerabilities, and carrying other malware, and uses the PsExec tool to spread in the victim’s intranet system.
3.3.1 Family Overview
| Family name | BlackCat |
| Appearance time | November 2021 |
| Typical propagation methods (except phishing attacks) | Third-party access to credentials, exploits, and other malware |
| Typical encryption suffixes | 7-digit personal ID with random combination of letters and numbers |
| Decryption tool | No public decryption tool has been found yet |
| Encryption system | Windows, Linux |
| Attack mode | There are cases of targeted attacks |
| Common industries | Energy, education, finance, manufacturing |
| Common countries/regions | United States, Australia, India, Indonesia |
| Is it double extortion? | Yes |
| Ransom note |  |
3.3.2 Typical Cases
1.Swissport International suffered BlackCat attack
In 2022, Swissport International Airport Services Co., Ltd. suffered a ransomware attack [12] , which caused 22 flight delays and a large number of network services to be interrupted. Subsequently, the attack organization behind the BlackCat ransomware claimed responsibility for the incident and leaked some of the data stolen from the incident.
2.Luxembourg gas pipeline and electricity network operator hit by BlackCat attack
Creos Luxembourg SA, the operator of Luxembourg’s natural gas pipeline and electricity network, issued a statement saying that it suffered a cyber attack from July 22 to 23[13]. The attack caused some of its portals to be unavailable and some data was stolen from the victim’s system. Subsequently, the attack group behind the BlackCat ransomware claimed responsibility for the incident and threatened to release 180,000 stolen files totaling 150GB in size, including contracts, passports, bills, and emails.
3.Columbian energy company EPM hit by BlackCat attack
Colombian energy company EPM was attacked by BlackCat ransomware[14], which is affiliated with the Medellín City Government. The incident caused the company’s operations and online services to be interrupted, more than 4,000 employees were unable to work on-site, and the attackers stole a large amount of data from the victim’s system.
3.4 Clop
Clop ransomware, also known as Cl0p , was discovered in February 2019. It evolved from Crypto Mix ransomware. The attack organization behind it uses the RaaS model to operate. In March 2020, the Clop ransomware organization enabled a leaked data site on the dark web for the first time, using a double extortion strategy of “threatening to expose corporate data + encrypting data for ransom.” After being attacked by this ransomware, it will deploy tools such as lateral penetration and remote control in the victim system to penetrate the target intranet and infect more machines. It is mainly spread through phishing, vulnerability exploitation, or remote desktop protocol (RDP) brute force cracking. According to security researchers, hacker groups TA505 and FIN11 have used Clop ransomware for network attacks [15] .
3.4.1 Family Overview
| Family name | Clop |
| Appearance time | February 2019 |
| Typical propagation methods (except phishing attacks) | Third-party access credentials, vulnerability exploits, and RDP brute force |
| Typical encryption suffixes | .clop |
| Decryption tool | No public decryption tool has been found yet |
| Encryption system | Windows |
| Attack mode | There are cases of targeted attacks |
| Common industries | Education, Energy, Government |
| Common countries/regions | United States, United Kingdom, Canada |
| Is it double extortion? | Yes |
| Ransom note | 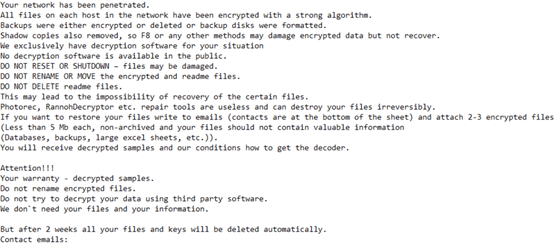 |
3.4.2 Typical Cases
1.UK water supplier South Staffordshire Water hit by Clop attack
In August 2022, the British water supplier South Staffordshire Water suffered a Clop ransomware attack[16]. The attack caused some of the company’s IT systems to be interrupted. The attacker stole 5 TB of data from the victim system and disclosed part of it on its data leakage platform, including SCADA system files, ID cards and other personal information.
2.US IT service company Softeq suffered from Clop attack
On November 5, Clop listed Softeq as a victim on its data breach platform [17] . Softeq provides IT services to many large organizations, including Microsoft, HP, Lenovo, Coca-Cola, Samsung, NVIDIA, and Disney.
3.5 Conti
The Conti ransomware family was discovered in December 2019. The attack organization behind it uses the Raas model to operate. Since May 2020, the attack activities have gradually increased. In July 2020, it used anonymized Tor to establish a ransom payment and data leakage platform, and adopted a double extortion strategy of “threatening to expose corporate data + encrypting data for ransom”. It mainly spreads by carrying other malware, vulnerability exploits, and RDP brute force cracking, and combines multiple tools to achieve lateral movement in the intranet. After the Log4j vulnerability (CVE-2021-44228) was exposed in December 2021, the Conti ransomware operator began to use VMware vCenter with Log4j vulnerabilities for lateral movement. The Conti ransomware organization was the first ransomware-related attack organization to express its political stance during the Russian-Ukrainian conflict, but this move was met with dissatisfaction from some members of its gang. A member who was allegedly Ukrainian made public the organization’s internal chat records and ransomware builders and other information online. Conti announced the cessation of operations in May 2022 , and shut down all public network infrastructure, including data leakage platforms and ransom negotiation platforms, in June. It is speculated that the organization may end its ransomware career or change its name to other ransomware to avoid government tracking [18] .
3.5.1 Family Overview
| Family name | Conti |
| Appearance time | December 2019 |
| Typical propagation methods (except phishing attacks) | Piggybacking of other malware, exploits, and RDP brute force |
| Typical encryption suffixes | .conti |
| Decryption tool | No public decryption tool has been found yet |
| Encryption system | Windows, Linux |
| Attack mode | There are cases of targeted attacks |
| Common industries | Manufacturing, services, finance, healthcare, government |
| Common countries/regions | United States, Italy, United Kingdom, Germany |
| Is it double extortion? | Yes |
| Ransom note | 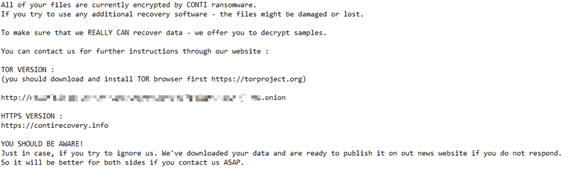 |
3.5.2 Typical Cases
1.China’s Delta Electronics hit by Conti attack
On January 18, 2022, China ‘s Delta Electronics Corporation was attacked by the Conti ransomware[19]. According to negotiations between the Conti ransomware organization and Delta, the attack organization claimed to have encrypted approximately 1,500 servers and 12,000 computers within Delta’s network environment and demanded a ransom of US$15 million.
2.Wind turbine group Nordex hit by Conti attack
On March 31, wind turbine group Nordex was attacked by the Conti ransomware[20]. Nordex Group IT Security detected that the company was affected by a cybersecurity incident. As a precautionary measure, the company decided to shut down IT systems in multiple locations and business units. Subsequently, the Conti ransomware group claimed responsibility for the incident.
3.Costa Rican government under attack from Conti
The Costa Rican government was attacked by the Conti ransomware[21]. The attack entry point was a system belonging to the Costa Rican Ministry of Finance. The attackers invaded from this system and carried out subsequent attacks. This incident affected multiple government agencies in Costa Rica. Subsequently, the Conti ransomware organization claimed responsibility for the incident and stole about 700GB of data from the victim system. It initially demanded a ransom of US$10 million. After the deadline for paying the ransom expired, the ransom was increased to US$20 million.
3.6 Cuba
The Cuba ransomware was first discovered in December 2019. The attack organization behind it uses the RaaS model to operate, adopting a dual extortion strategy of “threatening to expose corporate data + encrypting data for ransom”. It is mainly spread through phishing, vulnerability exploitation, and other malware. It often uses Microsoft Exchange Server -related vulnerabilities to carry out ransomware attacks. After invading a host in the victim’s network environment, it combines multiple tools to achieve lateral movement in the intranet. According to a joint report released by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) in December 2022, as of August 2022, the Cuba ransomware organization has damaged more than 100 entities worldwide, demanded more than $145 million in ransom, and received more than $60 million in ransom [22] .
3.6.1 Family Overview
| Family name | Cuba |
| Appearance time | December 2019 |
| Typical propagation methods (except phishing attacks) | Vulnerability exploits, other malware |
| Typical encryption suffixes | .cuba |
| Decryption tool | No public decryption tool has been found yet |
| Encryption system | Windows |
| Attack mode | There are cases of targeted attacks |
| Common industries | Medical, government, finance, IT |
| Common countries/regions | United States, Australia, Canada, France |
| Is it double extortion? | Yes |
| Ransom note | 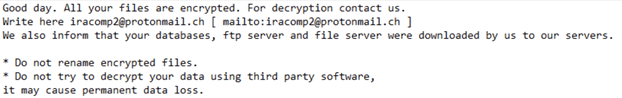 |
3.6.2 Typical Cases
1.Montenegro’s national government hit by Cuba attack
The Montenegrin government suffered a cyber attack on August 19, 2022 [23] , which infected approximately 150 workstations in 10 government agencies with malware. The Cuba ransomware group subsequently claimed responsibility for the incident and claimed to have stolen financial documents, bank correspondence, balance sheets, tax documents, compensation, source code and other data, and demanded a ransom of US$10 million to redeem these stolen files.
2.Ukrainian state organization hit by Cuban attack
In October, the Computer Emergency Response Team of Ukraine (CERT-UA) issued a warning about a Cuba ransomware campaign targeting the country. [24] The attackers delivered phishing emails disguised as being from the Ukrainian Armed Forces, thereby tricking victims into viewing and downloading the ransomware payload.
3.7 Hive
Hive ransomware was discovered in June 2021. The attack organization behind it uses the RaaS model to operate, adopting a dual extortion strategy of “threatening to expose corporate data + encrypting data for ransom”. It is mainly spread through third-party access credentials, vulnerability exploitation, and RDP brute force cracking. It has the ability to spread within the intranet and often exploits Microsoft Exchange Server -related vulnerabilities to carry out ransomware attacks. It has attack payloads for Windows and Linux systems. In March 2022 , it began to use the Rust language to write the ransomware executable, and set the data leakage platform to the account password login method, intending to restrict security researchers from analyzing it. The U.S. Department of Justice issued a statement on January 26, 2023, saying that its joint crackdown on the Hive ransomware organization with relevant law enforcement units in Germany, the Netherlands and Europe has achieved results, and has controlled the servers and websites used by the Hive ransomware organization for attacks and sent the decryption key to the victims [25] .
3.7.1 Family Overview
| Family name | Hive |
| Appearance time | June 2021 |
| Typical propagation methods (except phishing attacks) | Third-party access credentials, vulnerability exploits, and RDP brute force |
| Typical encryption suffixes | . hive |
| Decryption tool | Law enforcement sends decryption keys to victims |
| Encryption system | Windows, Linux, Free BSD |
| Attack mode | There are cases of targeted attacks |
| Common industries | Medical, energy, manufacturing, IT |
| Common countries/regions | United States, United Kingdom, Germany |
| Is it double extortion? | Yes |
| Ransom note | 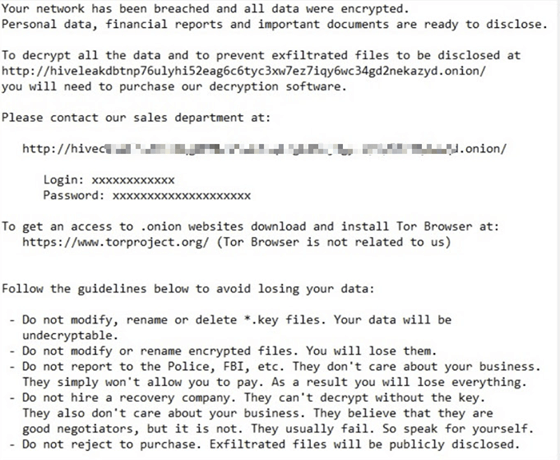 |
3.7.2 Typical Cases
1.Costa Rican public health agency hit by Hive attack
Costa Rica’s public health service agency, the Costa Rican Social Security Fund (CCSS) , was attacked by the Hive ransomware on May 31, 2022[26]. The attack caused a large number of computer systems in the agency’s network environment to fail to work properly, and the attackers stole some data from the victim systems.
2.Argentinian multimedia company Artear hit by Hive attack
On June 1, Argentinian multimedia company Artear was attacked by the Hive ransomware[27] . The attackers stole more than 1.4TB of data files from the victim system , including contracts, confidentiality agreements, and employee personal information.
3.Indian power company Tata Power hit by Hive attack
Tata Power is a subsidiary of the multinational Tata Group and the largest integrated power company in India. It was attacked by the Hive ransomware on October 3[28]. On October 25, the Hive ransomware organization published the data files stolen from Tata Power on its data leakage platform.
3.8 LockBit
The LockBit ransomware was discovered in September 2019. The attack organization behind it used the RaaS model to operate. In June 2021, it released version 2.0 and a dedicated data stealing tool, Steal Bit, using a dual extortion strategy of “threatening to expose corporate data + encrypting data for extortion”. On this basis, in August 2021, it added a DDoS attack threat, forming a triple extortion. In June 2022, LockBit launched version 3.0. The current version is mainly spread through obtaining access credentials from third parties, exploiting vulnerabilities, and carrying other malware. It has the ability to spread within the intranet and has attack payloads for Windows and Linux systems. Victims can choose to pay the ransom through Bitcoin , Monero, and Zcash. The organization also launched a vulnerability bounty program, which has become a new trick for ransomware to cause harm for a long time. The vulnerability bounty program instigates hackers to submit vulnerability reports and become accomplices in its extortion attacks in exchange for rewards ranging from US$ 1,000 to US$1 million [29] .
3.8.1 Family Overview
| Family name | LockBit |
| Appearance time | September 2019 |
| Typical propagation methods (except phishing attacks) | Third-party access to credentials, exploits, and other malware |
| Typical encryption suffixes | 9-digit personal ID with random combination of letters and numbers |
| Decryption tool | No public decryption tool has been found yet |
| Encryption system | Windows, Linux |
| Attack mode | There are cases of targeted attacks |
| Common industries | Finance, services, construction, education, IT , manufacturing |
| Common countries/regions | United States, United Kingdom, Germany, Canada |
| Is it double extortion? | Yes |
| Ransom note |  |
3.8.2 Typical Cases
1.Bridgestone Americas hit by LockBit attack
In February 2022, the American branch of Bridgestone, a world-renowned tire manufacturer, suffered a LockBit ransomware attack [30] . The attack caused the company to suspend some of its operations, and the attackers stole some important data from the victim system. Before and after this incident, there were a number of ransomware attacks targeting the automotive industry, including Swiss car dealer Emil Frey being attacked by Hive ransomware on January 11, Denso (automotive parts and system supplier) being attacked by Pandora ransomware on March 10, and Snap-on (automotive tool manufacturer) and Empire Electronics (automotive lighting component supplier) being attacked by Conti ransomware on March 16.
2.US security firm Entrust hit by LockBit attack
In July 2022, the US security company Entrust issued a statement saying that it had suffered a cyber attack on June 18. Subsequently, the LockBit ransomware organization claimed responsibility for the attack [31] and released relevant information about Entrust on its data leakage platform.
3.9 LV
The LV ransomware was discovered in December 2020. The attack organization behind it uses the RaaS model to operate, adopting a dual extortion strategy of “threatening to expose corporate data + encrypting data for ransom”. Some code segments are developed based on the REvil ransomware. It is mainly spread through third-party access credentials, vulnerability exploits, and other malware. It often uses Microsoft Exchange Server-related vulnerabilities to implement ransomware attacks. After invading any host in the victim’s network environment, it combines multiple tools to achieve lateral movement in the intranet. In December 2021, the LV ransomware organization posted on an underground forum seeking corporate network access credentials, claiming to operate the LV ransomware and seeking network access agents, expressing interest in obtaining network access rights for entities in Canada, Europe, and the United States, and then profiting from it by deploying ransomware[32] .
3.9.1 Family Overview
| Family name | LV |
| Appearance time | December 2020 |
| Typical propagation methods (except phishing attacks) | Third-party access to credentials, exploits, and other malware |
| Typical encryption suffixes | 5-10 digits of random combination of letters and numbers |
| Decryption tool | No public decryption tool has been found yet |
| Encryption system | Windows |
| Attack mode | There are cases of targeted attacks |
| Common industries | Manufacturing, education, finance |
| Common countries/regions | United States, Germany, Mexico |
| Is it double extortion? | Yes |
| Ransom note | 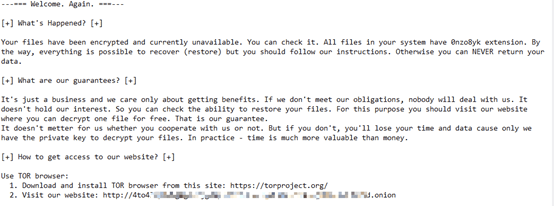 |
3.9.2 Typical Cases
1.German semiconductor manufacturer Semikron hit by LV attack
German semiconductor manufacturer Semikron issued a statement on August 1, 2022, saying that it had suffered a cyberattack[33] , which resulted in the encryption of IT systems and some files. Subsequently, the LV ransomware organization claimed responsibility for the incident and stated on its data leakage platform that 2 TB of files had been stolen .
2.Mexican car company UnitedAuto hit by LV
On November 19, LV added Mexican car company UnitedAuto to its data breach platform[34] , claimingto have stolen more than 2TB of personal information. The attackers slammed the victim, UnitedAuto, saying that ” UnitedAuto did not have any basic protection for its systems. The company did not even bother to install antivirus software on their systems while still processing customers’ personal data. In addition, UnitedAuto had many vulnerabilities on its network, which allowed us to download all the critical data.”
3.10 Vice Society
The Vice Society ransomware organization was discovered in June 2021. Its ransomware includes Hello Kitty (also known as Five Hands ) , Red Alert and Zeppelin. It operates in a RaaS model and adopts a double ransomware strategy of “threatening to expose corporate data + encrypting data for ransom”. It has Windows and Linux system attack payloads and is mainly spread through third parties obtaining access credentials and exploiting vulnerabilities.
In September 2022, the US FBI and CISA issued an alert [35] stating that Vice The Society ransomware group is targeting the education sector. When the FBI and CISA issued the alert, the Los Angeles Unified School District (LAUSD) stated that they had been attacked by the Vice Society ransomware group [36] , which seriously affected some of their information systems. The district is the second largest school district in the United States, with more than 640,000 students.
3.10.1 Family Overview
| Family name | Vice Society ( including Hello Kitty and Zeppelin) |
| Appearance time | June 2021 |
| Typical propagation methods (except phishing attacks) | Third-party access credentials and vulnerability exploits |
| Typical encryption suffixes | .v-society. <personal ID > |
| Decryption tool | No public decryption tool has been found yet |
| Encryption system | Windows, Linux |
| Attack mode | There are cases of targeted attacks |
| Common industries | Education, government, healthcare, manufacturing |
| Common countries/regions | United States, United Kingdom, Spain, France |
| Is it double extortion? | Yes |
| Ransom note | 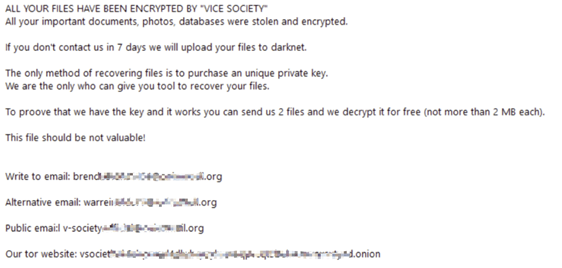 |
3.10.2 Typical Cases
1.Vice Society attacks Palermo, Italy
The Italian city of Palermo suffered a cyber attack in early June 2022[37], which caused a large number of Internet services to be unavailable. Subsequently, the Vice Society ransomware organization claimed responsibility for the incident and publicly threatened on its data leakage platform that all stolen data would be made public if the ransom was not paid.
2.FMC Services, a medical institution in Texas, USA, was attacked by Vice Society
On July 26, FMC Services, a medical institution in Texas, USA, was attacked by the Vice Society ransomware organization [38] , affecting more than 230,000 patients.
3.Los Angeles Unified School District under attack from Vice Society
The Los Angeles Unified School District suffered a cyberattack in September, and the Vice Society ransomware group subsequently claimed responsibility for the incident [39] and stated that 500GB of data was stolen from the victim systems.
Appendix 1: References
[1] Coffee ransomware continues to be active, Antiy releases decryption tool
https://www.antiy.cn/research/notice&report/research_report/20220222.html
[2] Pandora Ransomware Analysis Report
https://www.antiy.cn/research/notice&report/research_report/20220323.html
[3] Conti Ransomware Analysis Report
https://www.antiy.cn/research/notice&report/research_report/20211220.html
[4] Ransomware Spotlight AvosLocker
[5] Notice of Data Security Incident
https://www.mckenziehealth.org/notice-of-data-security-incident/
[6] AvosLocker Claims Responsibility For Christus Health Ransomware Attack
[7] Ransomware Spotlight Black Basta
[8] American Dental Association hit by new Black Basta ransomware
[9] Ransomware attack hits Deutsche Windtechniks
https://securereading.com/ransomware-attack-hits-deutsche-windtechnik/
[10] Defense Giant Elbit Confirms Data Breach After Ransomware Gang Claims Hack
[11] Building materials giant Knauf hit by Black Basta ransomware gang
[12] BlackCat (ALPHV) claims Swissport ransomware attack, leaks data
[13] BlackCat ransomware claims attack on European gas pipeline
[14] Colombian energy supplier EPM hit by BlackCat ransomware attack
[15] Ransomware Spotlight Clop
https://www.trendmicro.com/vinfo/us/security/news/ransomware-spotlight/ransomware-spotlight-clop
[16] Clop gang targeted UK drinking water supplier South Staffordshire Water
https://securityaffairs.co/134450/cyber-crime/south-staffordshire-water-cyberattack.html
[17] Inside the World of Initial Access Broker (IAB): Insights and Trends
https://www.cyfirma.com/outofband/inside-the-world-of-initial-access-broker-iab-insights-and-trends/
[18] Conti ransomware shuts down operation, rebrands into smaller units
[19] Taiwanese Apple and Tesla contractor hit by Conti ransomware
[20] Wind turbine firm Nordex hit by Conti ransomware attack
[21] Costa Rica declares national emergency after Conti ransomware attacks
[22] Ransomware Spotlight C uba
https://www.trendmicro.com/vinfo/be/security/news/ransomware-spotlight/ransomware-spotlight-cuba
[23] Montenegro hit by ransomware attack, hackers demand $10 million
[24] Kiberataka na Derezhavnī Oregano України з використанням skhidlivo Programma RomCom . Mozhliva причетність Cuba Ransomware aka Tropical Scorpius aka UNC2596 (CERT-UA#5509)
https://cert.gov.ua/article/2394117
[25] US Department of Justice Disrupts Hive Ransomware Variant
https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/us-department-justice-disrupts-hive-ransomware-variant
[26] Costa Rica’s public health agency hit by Hive ransomware
[27] SCOOP: Hive claims responsibility for attack on Artear , the Argentinian multimedia giant
[28] Hive claims ransomware attack on Tata Power, begins leaking data
[29] LockBit 3.0 introduces the first ransomware bug bounty program
[30] Bridgestone Americas confirms ransomware attack, LockBit leaks data
[31 ]LockBit claims ransomware attack on security giant Entrust, leaks data
[32] LV Ransomware Exploits ProxyShell in Attack on a Jordan-based Company
https://www.trendmicro.com/en_hk/research/22/j/lv-ransomware-exploits-proxyshell-in-attack.html
[33] Semiconductor manufacturer Semikron hit by LV ransomware attack
[34] Bits ‘n Pieces ( Trozos y Piezas )
https://www.databreaches.net/bits-n-pieces-trozos-y-piezas-17/
[35] #StopRansomware: Vice Society
https://www.cisa.gov/uscert/ncas/alerts/aa22-249a
[36] AN IN-DEPTH LOOK AT VICE SOCIETY RANSOMWARE
https://www.avertium.com/resources/threat-reports/an-in-depth-look-at-vice-society-ransomware
[37] Vice Society ransomware claims attack on Italian city of Palermo
[38] FMC Services, LLC Announces Data Breach Affecting More than 230k People’s Sensitive Information
https://www.jdsupra.com/legalnews/fmc-services-llc-announces-data-breach-6165700/
[39] Vice Society claims LAUSD ransomware attack, theft of 500GB of data
Appendix 2: About Antiy
Antiy is committed to enhancing the network security defense capabilities of its customers and effectively responding to security threats. Through more than 20 years of independent research and development, Antiy has developed technological leadership in areas such as threat detection engines, advanced threat countermeasures, and large-scale threat automation analysis.
Antiy has developed IEP (Intelligent Endpoint Protection System) security product family for PC, server and other system environments, as well as UWP (Unified Workload Protect) security products for cloud hosts, container and other system environments, providing system security capabilities including endpoint antivirus, endpoint protection (EPP), endpoint detection and response (EDR), and Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) , etc. Antiy has established a closed-loop product system of threat countermeasures based on its threat intelligence and threat detection capabilities, achieving perception, retardation, blocking and presentation of the advanced threats through products such as the Persistent Threat Detection System (PTD), Persistent Threat Analysis System (PTA), Attack Capture System (ACS), and TDS. For web and business security scenarios, Antiy has launched the PTF Next-generation Web Application and API Protection System (WAAP) and SCS Code Security Detection System to help customers shift their security capabilities to the left in the DevOps process. At the same time, it has developed four major kinds of security service: network attack and defense logic deduction, in-depth threat hunting, security threat inspection, and regular security operations. Through the Threat Confrontation Operation Platform (XDR), multiple security products and services are integrated to effectively support the upgrade of comprehensive threat confrontation capabilities.
Antiy provides comprehensive security solutions for clients with high security requirements, including network and information authorities, military forces, ministries, confidential industries, and critical information infrastructure. Antiy has participated in the security work of major national political and social events since 2005 and has won honors such as the Outstanding Contribution Award and Advanced Security Group. Since 2015, Antiy’s products and services have provided security support for major spaceflight missions including manned spaceflight, lunar exploration, and space station docking, as well as significant missions such as the maiden flight of large aircraft, escort of main force ships, and Antarctic scientific research. We have received several thank-you letters from relevant departments.
Antiy is a core enabler of the global fundamental security supply chain. Nearly a hundred of the world’s leading security and IT enterprises have chosen Antiy as their partner of detection capability. At present, Antiy’s threat detection engine provides security detection capabilities for over 1.3 million network devices and over 3 billion smart terminal devices worldwide, which has become a “national-level” engine. As of now, Antiy has filed 1,877 patents in the field of cybersecurity and obtained 936 patents. It has been awarded the title of National Intellectual Property Advantage Enterprise and the 17th (2015) China Patent Excellence Award.
Antiy is an important enterprise node in China emergency response system and has provided early warning and comprehensive emergency response in major security threats and virus outbreaks such as “Code Red”, “Dvldr”, “Heartbleed”, “Bash Shellcode” and “WannaCry”. Antiy conducts continuous monitoring and in-depth analysis against dozens of advanced cyberspce threat actors (APT groups) such as “Equation”, “White Elephant”, “Lotus” and “Greenspot” and their attack actions, assisting customers to form effective protection when the enemy situation is accurately predicted.


