Monographic analysis report on the Natrix Group
1、Overview
The Natrix Group has been active since the second half of 2022, launching a multitude of attack campaigns against domestic users. The Natrix Group spreads a wide variety of malware variants, rapidly updates its evasion techniques, frequently changes its infrastructure, and targets a wide range of industries. Thereby it has garnered significant attention from the domestic cybersecurity industry this year.
The Natrix Group spreads malicious programs through instant messaging software, malicious promotions on search engines, and phishing emails, utilizing techniques such as “DLL Hijacking”, “In-memory execution of Shellcode” and “In-memory decryption of Payload” to ultimately implant remote control Trojans into victims’ computers. After gaining control of the victim’s computer, the group primarily uses the victim’s WeChat for subsequent attack activities to gain profits. On one hand, they utilize the victim’s WeChat to send malicious programs to their friends or groups, thereby further expanding the infection range. On the other hand, they control the victim’s WeChat, committing fraud through identity impersonation or malicious group creation to illicitly obtain economic benefits.
Antiy CERT continuously monitors and tracks the Natrix Group, discovering the operating model of groups led by Natrix. Based on sample analysis, it generalizes the attack methods and technical characteristics of the group, reveals the common fraud routines used by the group, and summarizes effective protection suggestions. This is to help users understand and identify the common tactics of the group, avoid being harmed by their remote control Trojans, and prevent economic losses caused by the group’s fraud.
For detailed information about the group, please refer to the Antiy Virus Encyclopedia.
Long-press to recognize the QR code to view detailed information about the Natrix Group.
After verification, the Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection system (EDR) can effectively detect and eliminate this remote control Trojan.

Antiy security threat investigation tools can identify systems infected with Natrix Trojan
2、Attack Methods
groups primarily spread malicious programs through instant messaging (IM) software, search engine malicious promotion, phishing emails, and similar methods. The initial malicious program is typically a malicious downloader, which, when executed, accesses trusted websites or the attacker’s server to obtain malicious payload files hosted there. These files are loaded, executed, and combined using techniques such as “DLL Hijacking”, “In-memory execution of Shellcode”, “In-memory decryption of Payload” and more to evade antivirus detection. Finally, the Gh0st remote control Trojan is executed in memory, and it usually achieves persistence to remain on the victim’s host for an extended period.
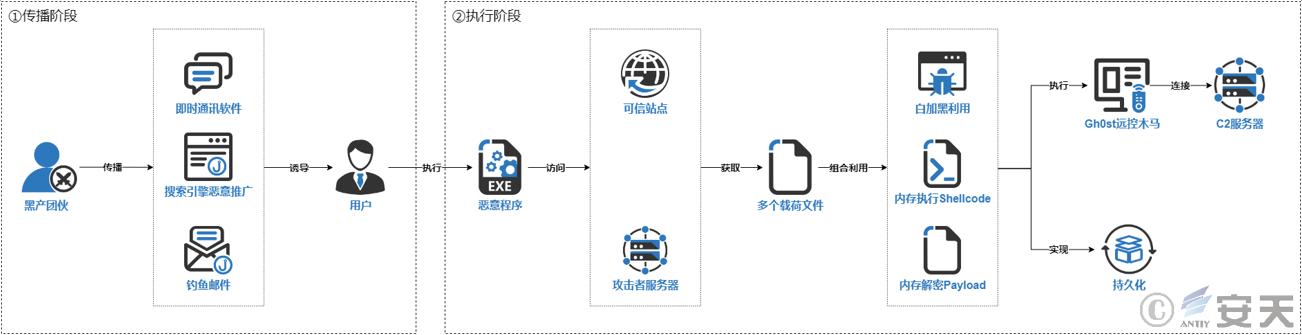
Figure 2-1 typical attack process of groups
2.1 Propagation Of Malware
Natrix Group primarily spreads malware through instant messaging (IM) software, malicious promotion through search engines, phishing emails, and similar methods.
2.1.1 Instant Messaging (IM)
In the article titled “Analysis of the Activities of the Natrix Group Using WeChat to Spread Malicious Code” [1], Antiy CERT provides a detailed overview of the operational model employed by groups to propagate malicious programs on a large scale by recruiting “agents” to assist them. Additionally, Antiy CERT has identified specific behavioral patterns exhibited by malware distributed through instant messaging software after execution, categorizing them into three classes: Double-click type, Jump-image type, and Damage type.
Double-click type
After the execution of double-click type malware, the mouse cursor often visibly spins for several seconds. Attackers induce users to execute the malicious program through instant messaging software and determine whether the malicious program has been executed based on user feedback (text, screenshots, or screen recordings).
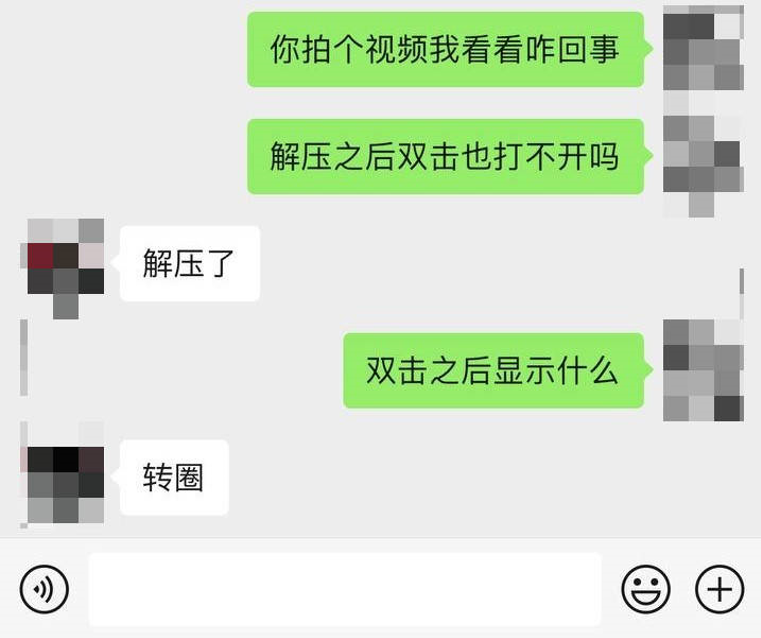
Figure 2-2 Chat history related to double-click type
Jump-image type
Jump-image type malicious programs, in addition to obtaining the necessary payload files from the C2 server, also fetch an image file and open it. This approach serves to confuse users, and attackers can determine whether the malicious program has been executed based on user feedback regarding the appearance of the popped-up image.
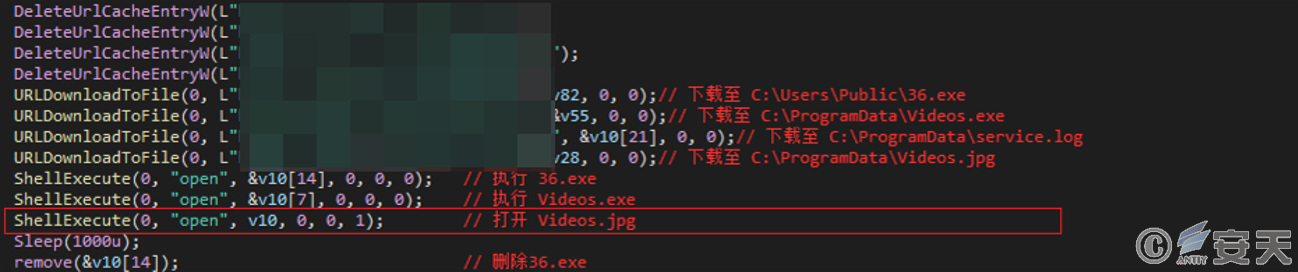
Figure 2-3 Download and open the image
Damage type
Damage type malicious programs, after obtaining and executing the necessary malicious payload files, display a carefully crafted error message pop-up. Typically, this message includes the phrase “File has been damaged,” along with the machine’s GUID and the current time.

Figure 2-4 Error message pop-up carefully crafted
When a victim user executes malicious programs and encounters error pop-up windows, they often believe that the file is damaged and proactively send screenshots to the attacker for inquiries. This allows the attacker to determine that the malicious program has been executed.
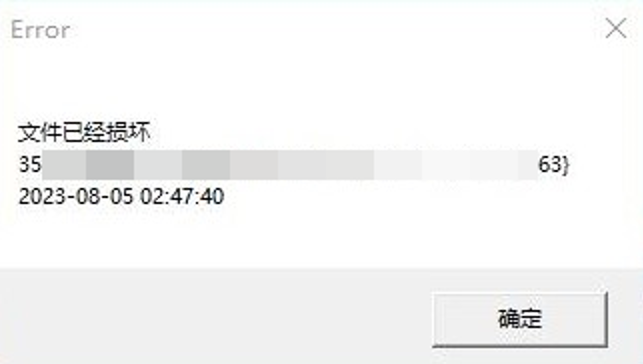
Figure 2-5 Error message pop-up
2.1.2 Search Engine Malicious Advertising
groups forge download pages for commonly used applications such as WeChat, DingTalk, WPS, PDF converters, and others. They then purchase advertising space on popular domestic search engines to maliciously promote these fake download sites, thereby enticing users to download and execute malicious programs.
Figure 2-6 Website forged by Natrix Group
2.1.3 Phishing Emails
When delivering malicious programs through phishing emails, groups often send phishing emails with subjects and content related to “invoices” or “summons”. These emails typically contain hyperlinks.
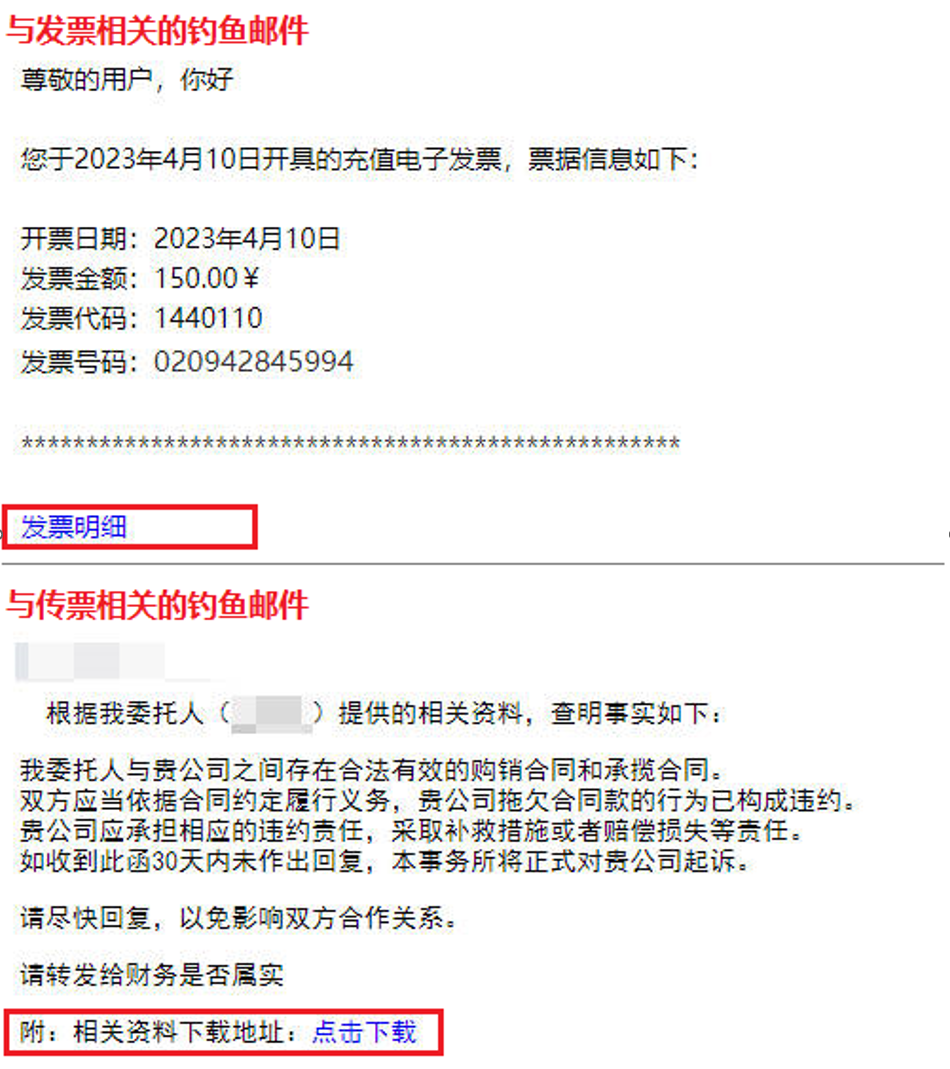
Figure 2-7 Example for invoice and summon
After users click on the links, they are redirected to phishing websites disguised as providers of invoice services or as tax authorities. groups use phishing emails and phishing websites related to invoices to entice users to download and execute malicious programs.
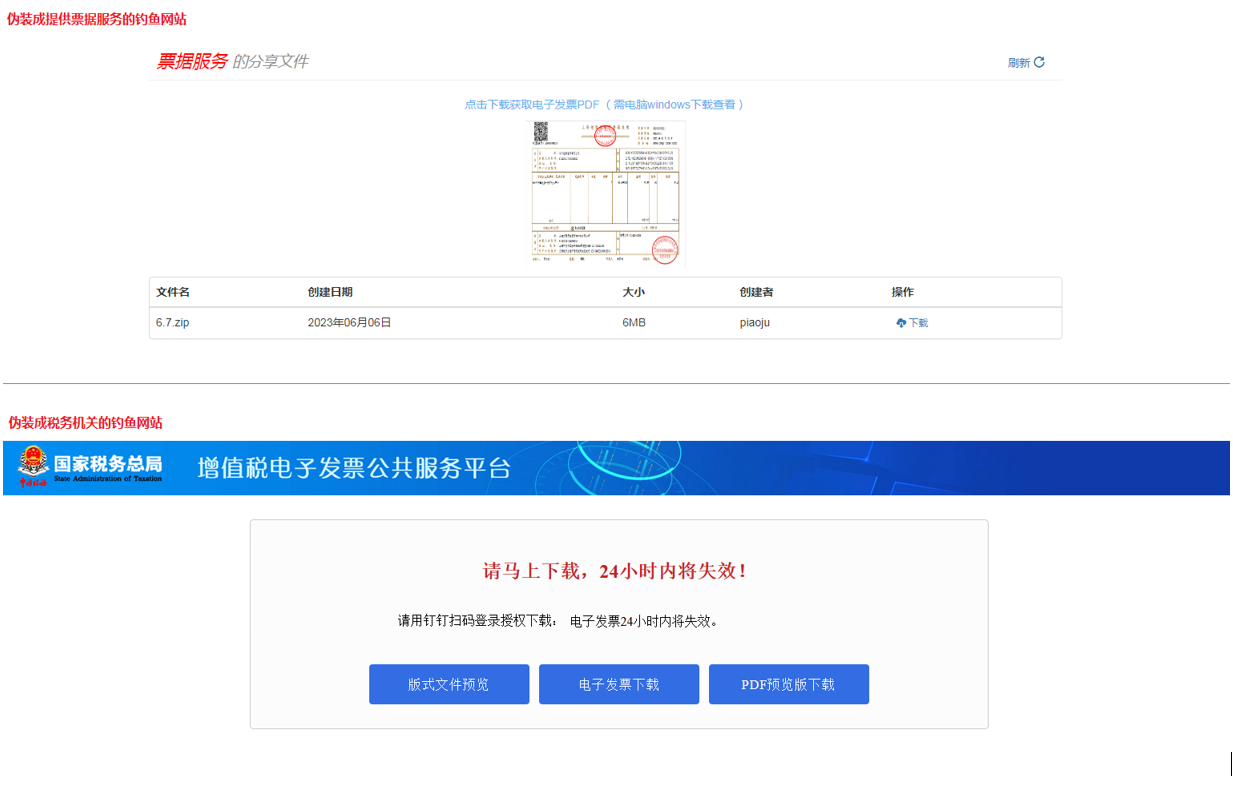
Figure 2-8 Phishing Website
2.2 Execution Of Malware
The initial malicious program is typically a malicious downloader, which, when executed, accesses trusted websites or the attacker’s server to obtain malicious payload files hosted there. These files are loaded, executed, and combined using techniques such as “DLL Hijacking”, “in-memory execution of Shellcode”, “in-memory decryption of Payload” and more to evade antivirus detection. Finally, the Gh0st remote control Trojan is executed in memory.
2.2.1 Hosting Malicious Payload
Trusted website
In the article titled “Analysis of Attack Activities Using Cloud Note Platforms for Delivering Remote Control Trojans” [2], Antiy CERT discusses the activities of groups that utilize cloud note platforms to deliver remote control Trojans. Attackers package malicious payload files into compressed archives and host them within created cloud note shares. The purpose of this is to utilize trusted websites to evade detection by security products on the traffic side. After the execution of the distributed malicious program, it retrieves the malicious payload files from the shared links to complete the subsequent attack process. Multiple cloud notes shares have been observed being used for attack activities, with the earliest creation date being in January 2022.
Table 2-1 Cloud note sharing for hosting malicious payloads
|
User ID |
Share folder name |
|
vip0418123000 |
签名正版 |
|
quanshiyu2022 |
GUDUO |
|
quanshiyu2022 |
XSD |
|
Ireallycanth |
Endless sea of |
|
m15529105475 |
wx |
|
m15529105475 |
kky |
Infrastructure for groups
When groups host malicious payloads on their self-built infrastructure, such as HFS servers or FTP servers, they make every effort to evade antivirus detection. In addition to encrypting the payload files, they may also remove or encrypt the file headers of PE (Portable Executable) files and split the payload files further. These actions are taken to avoid detection by security products.
2.2.2 Loading Malicious Payload
During the malicious payload loading phase, groups commonly employ techniques such as “DLL Hijacking”, “in-memory execution of Shellcode”, “in-memory decryption of Payload” and they often combine these methods.
DLL Hijacking: groups exploit vulnerabilities in certain legitimate programs where strict validation is lacking when calling necessary modules or script code. They construct malicious DLL files or add malicious script code, thereby leveraging these vulnerabilities to execute malicious code within the context of the normal program.
In the article titled “Analysis of Large-Scale Attack Activities Targeting Domestic Users by the Natrix Group” [3], Antiy CERT describes the method used by groups to attack using the NetSarang series of tools’ update program. This program loads a dat file with the same name from the same directory and parses script code within it when executed. Attackers take advantage of this behavior by adding malicious code to the original script, thus executing malicious Shellcode. It has been observed that black-hat groups have employed this technique to implant remote control Trojans in multiple attack campaigns.
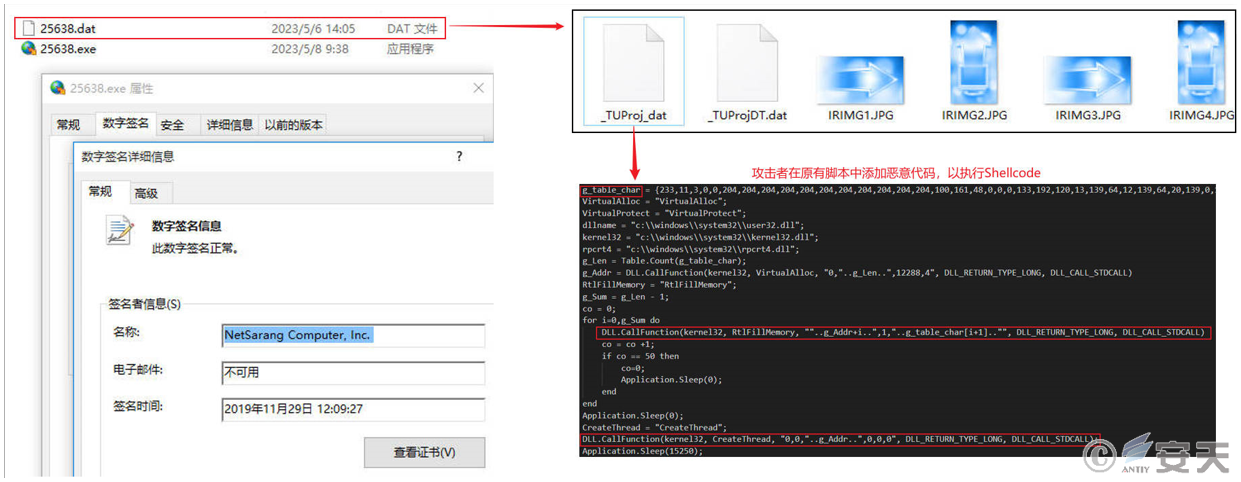
Figure 2-9 Malicious Shellcode Execution with NetSarang Series Tool Updater
In-memory execution of Shellcode: groups typically store pre-written Shellcode in text files. They use loaders to read the content from these files and execute the Shellcode in memory. The Shellcode crafted by groups falls into two main categories: one is used to check for the presence of security products on the system and create scheduled tasks for the loader to achieve persistence on the victim’s host. The other type is designed to acquire and decrypt remote control Trojans and load and execute them.
In-memory decryption of Payload: groups typically perform pre-encryption of remote control Trojan payloads and use corresponding decryption algorithms during execution to decrypt them. This process allows them to load and execute the final remote control Trojan in memory.
2.2.3 Release Gh0st Remote Control Trojan
The Gh0st remote control Trojan consists of two parts: the controlled end and the control end. The controlled end, which is implanted into the victim’s host, collects various types of information from the host, including basic system information, window information, antivirus product information, and more. It then constructs an online package and sends it to the C2 server, establishing communication with the control end. Custom algorithms are used to encrypt and decrypt the communication content.
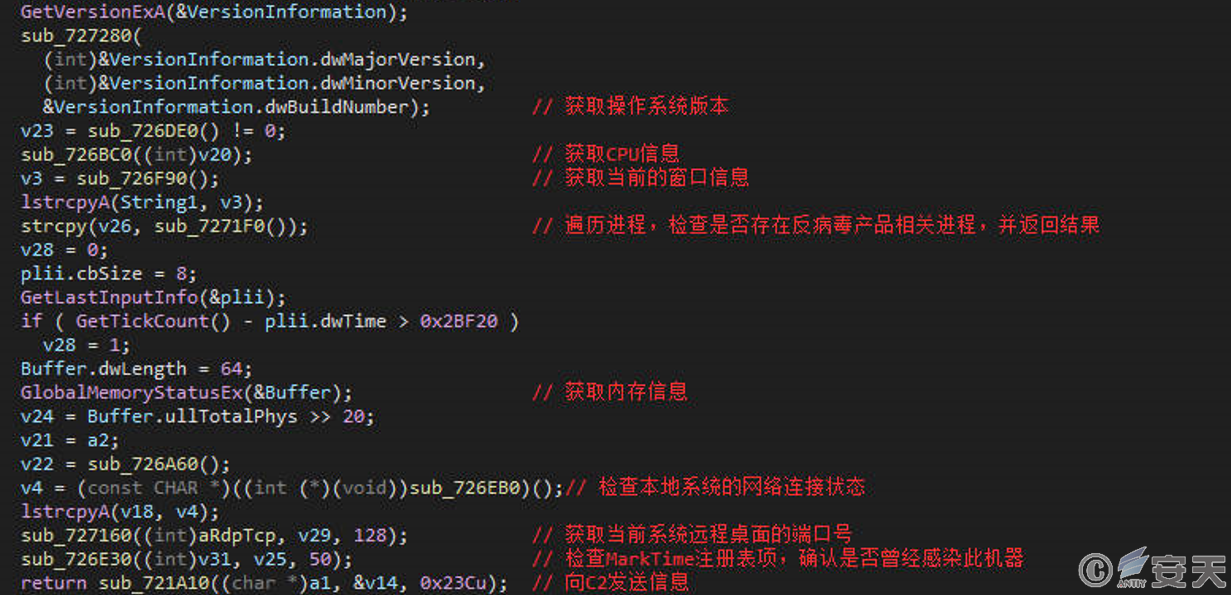
Figure 2-10 Information gathered
The Gh0st remote control Trojan is capable of receiving remote control commands and executing corresponding functions. It supports extending its functionality through the download and execution of plugins. From the captured control-end program, it is evident that this remote control Trojan possesses various features. Its primary functions include displaying controlled-end online information, monitoring the controlled-end screen, managing system files on the controlled end, and remote control.
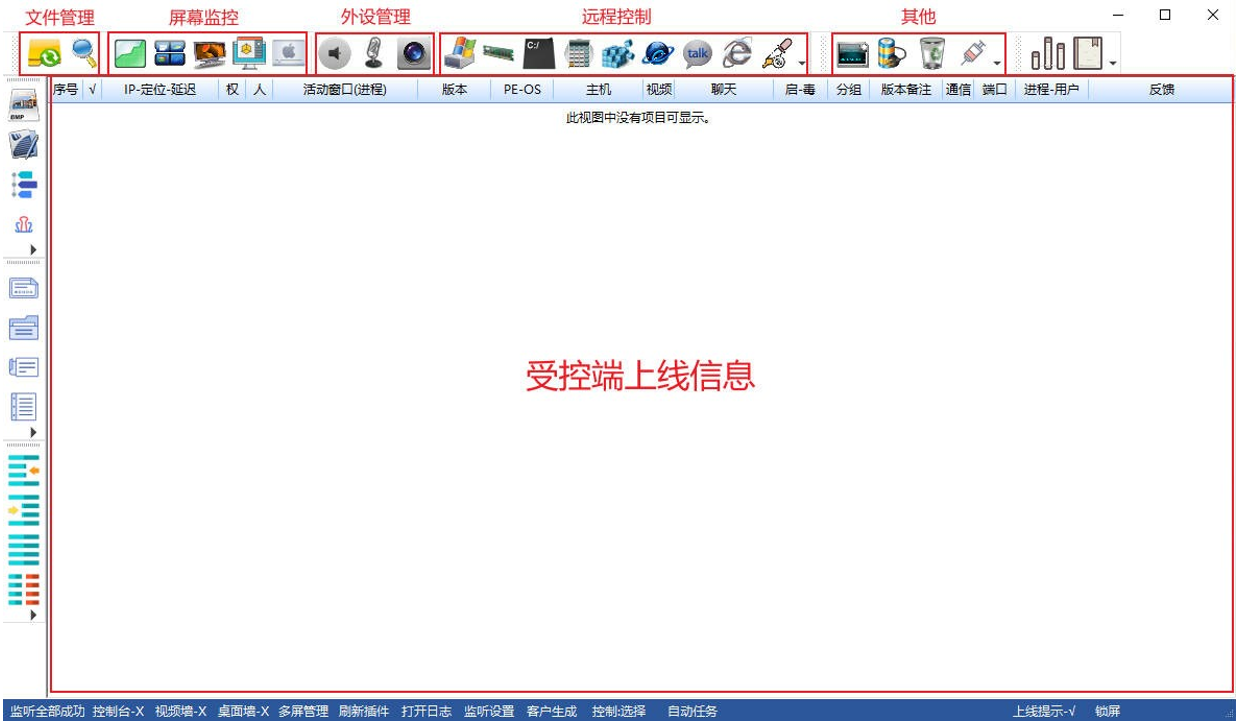
Figure 2-11 Gh0st remote control Trojan console program
Based on observations, although groups use various versions of control-end programs, they generally exhibit a fundamental similarity. Due to the open-source nature of the Gh0st remote control Trojan’s source code for many years, this remote control Trojan, as well as numerous derivative variants, have widely circulated in the underground industry. As a result, groups can rapidly develop control-end programs and their corresponding controlled-end Trojans and employ evasion techniques to avoid detection.
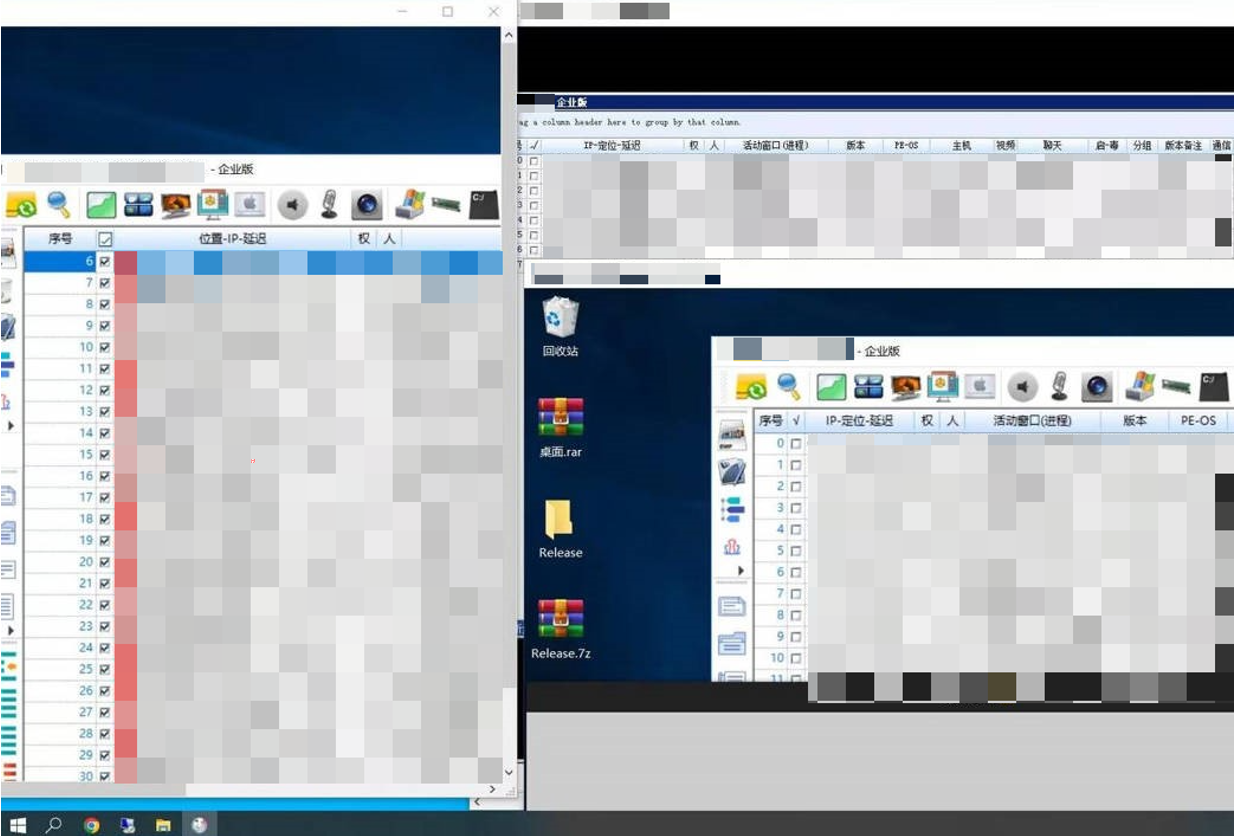
Figure 2-12 groups console program
3、Various Monetization Methods of Groups
3.1 Assuming a False Identity
After implanting the Gh0st remote control Trojan, groups primarily control the victim’s host to conduct subsequent attack activities on WeChat and WeChat for Enterprise (Enterprise WeChat). On one hand, groups use the victim’s WeChat account to disseminate malicious programs to their friends or groups, thereby further expanding the scope of infection. On the other hand, groups control the victim’s WeChat account, assuming a certain identity to engage in fraud against the victim or their friends, or maliciously create group chats with the victim’s friends for fraudulent activities.
3.2 Maliciously Adding to Groups
groups add the victim’s WeChat account to pre-created WeChat groups, control the victim’s WeChat to add their friends to the same group, and then remove the victim’s WeChat account from the group.
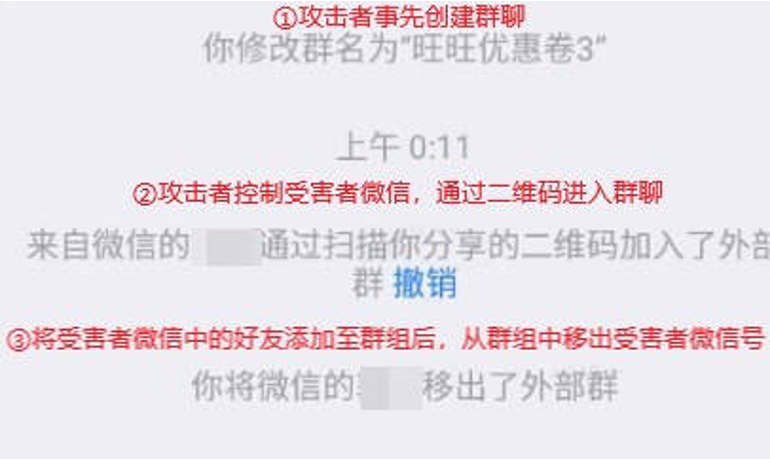
Figure 3-1 1.1 Maliciously Adding to Groups
To avoid detection, these activities typically occur between 0 AM and 6 AM. The created group names often relate to seminars, coupons, benefits, etc., and they are often marked with numbers.
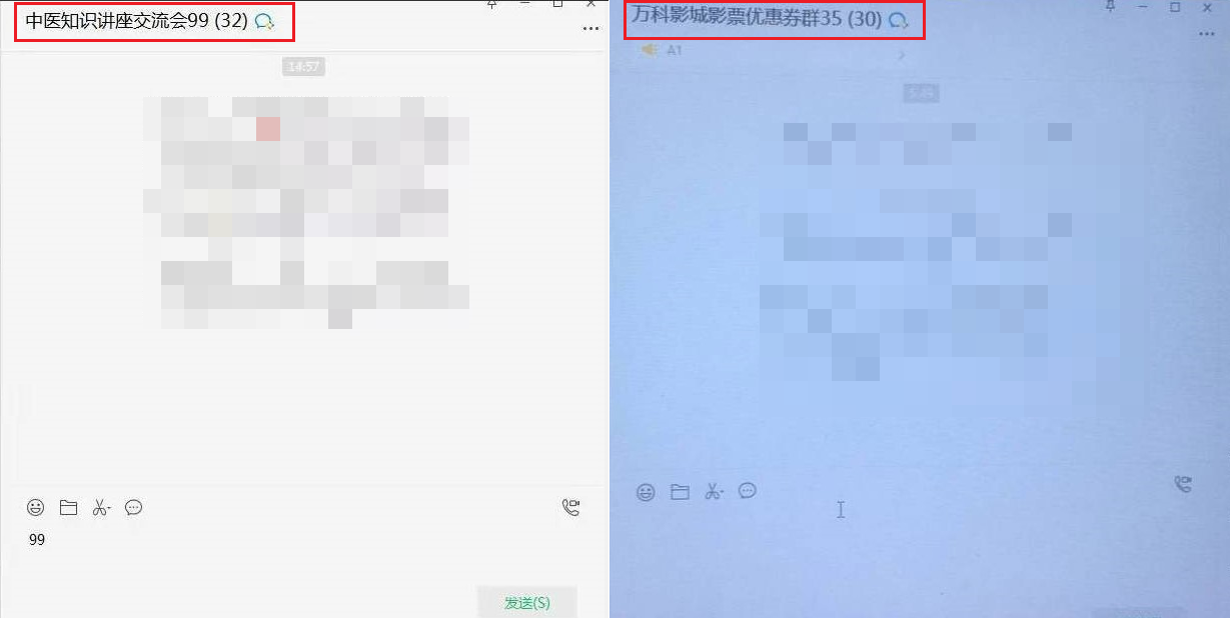
Figure 3-2 Groups created by groups
groups use methods like sending red envelopes within the group to lower users’ guard, entice them to join large groups, add customer service representatives on WeChat, and usually send text messages in the form of images

Figure 3-3 Texts messages in pictures
Finally, groups engage in fraud against selected victims, inducing them to make money transfers. After successfully defrauding the victims, they cease further contact.
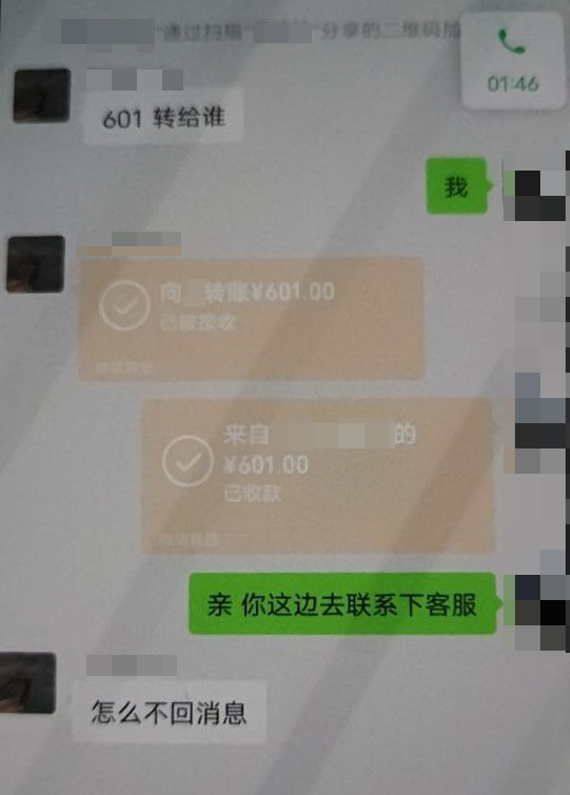
Figure 3-4 induce victims to make money transfer
4、Protection, Detection and Disposal
1.Enhancing Security Awareness of Business Personnel
Enhancing the security awareness of business personnel can reduce the likelihood of the organization being targeted for attacks. When customer service, sales, and other personnel use instant messaging applications like WeChat and Enterprise WeChat on their computer, they should avoid downloading and running various files from unknown sources due to the nature of their work or other interests. Organizations can strengthen their “first line of defense” by choosing security awareness training services.
2.Antiy Security Threat Investigation Tools for Detecting Natrix Payloads
If you suspect or detect an attack by the Natrix Group, particularly their distribution of Gh0st remote control Trojans during their attack activities, you can download Antiy’s Security Threat Investigation Tools from the Antiy Vertical Response Platform (https://vs2.antiy.cn, tool name: Natrix Special Investigation Tool). These tools are useful for rapidly detecting and investigating such threats in cases of unexpected security incidents or special scenarios.
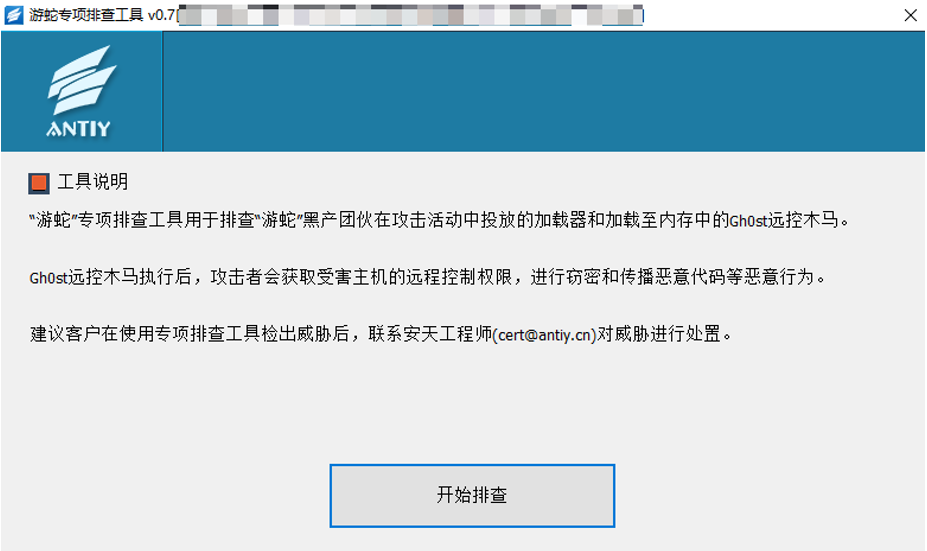
Figure 4-1 Natrix Special Investigation Tool
The Natrix Special Investigation Tool is designed to investigate the loaders and Gh0st remote control Trojans distributed by the Natrix Group during their attack activities. After Gh0st remote control Trojans are executed, attackers gain remote control over the victim’s host, enabling activities such as data theft and malicious code distribution.
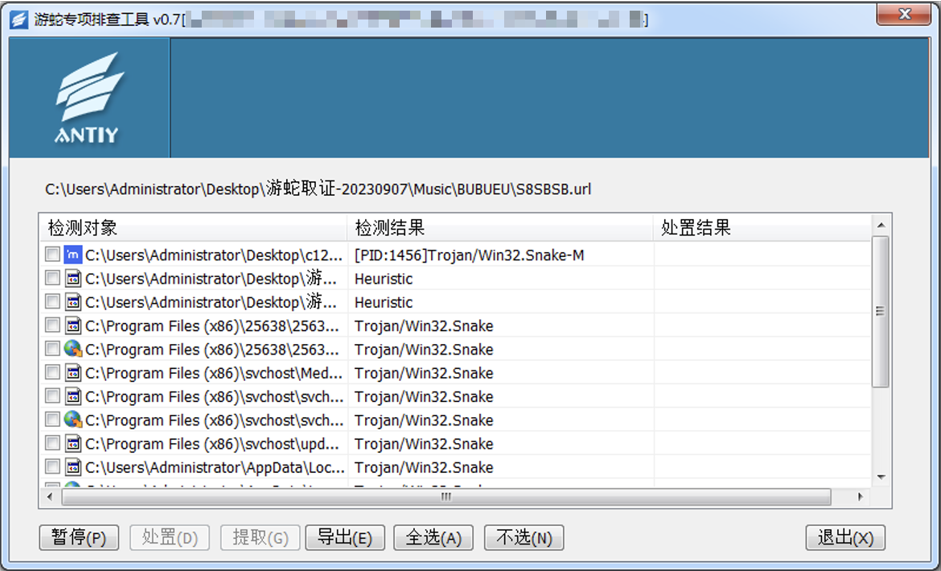
Figure 4-2 Detection of threats related to Natrix
As the attack payloads used by the Natrix Group evolve rapidly and continually update evasion techniques, it is recommended that customers, after using the specialized investigation tool to detect threats, contact Antiy’s Emergency Response Team (cert@antiy.cn) to handle the threats.
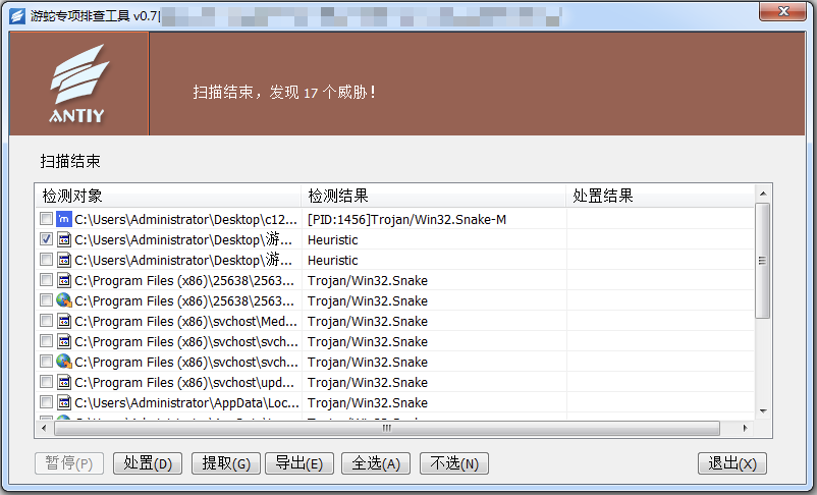
Figure 4-3 Discovery of Natrix Group
You can also call Antiy’s 24/7 service hotline at 400-840-9234 for assistance. In the event of a malware attack, it is advisable to isolate the affected host promptly and secure the scene while awaiting a security engineer’s investigation.
3.Strengthening Endpoint File Reception and Execution Protection
Deploy an enterprise-level endpoint defense and response system to real-time monitor and protect against the reception of unknown files by instant messaging software. Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection system (EDR) uses the Antiy Next-Generation Threat Detection Engine to scan files of unknown origin. It employs kernel-level proactive defense capabilities to prevent these files from executing.
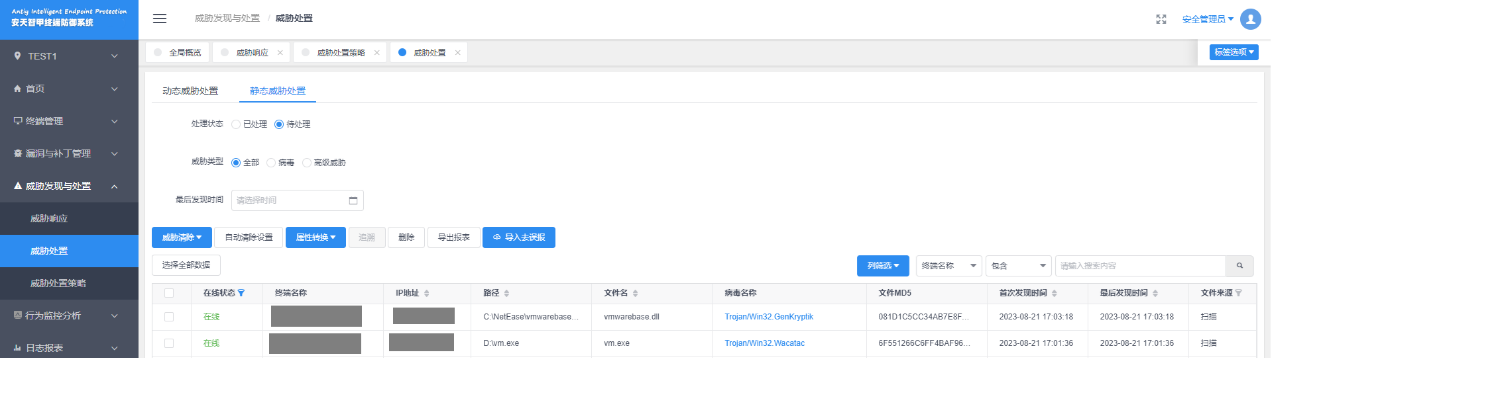
Figure 4-4 Antiy’s EDR effectively defense the attack of Natrix Group
Regarding the attack behavior of the Natrix Group, Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection system (EDR) has enhanced capabilities in the “Infection Environment Detection” and “Scheduled Task Defense” modules. When the Natrix Group distributes malicious programs to target terminals through methods like phishing and induces users to execute them, Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection system (EDR) actively monitors scheduled tasks in the background. Once it identifies a task with the Natrix characteristic, it immediately parses its runtime parameters, concatenates the complete path to the malicious program, terminates the malicious program’s process, and deletes the file, ensuring effective identification and blocking while the malicious code is running. After blocking, it immediately displays a pop-up window to alert the user, ensuring the security of the business environment.

Figure 4-5 Antiy’s EDR blocks abnormally created scheduled tasks
Finally, regarding attack patterns that ultimately target endpoints through inducement and malicious construction, Antiy recommends that customers promptly update the Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection system (EDR), the Antiy Persistent Threat Detection System, and other product feature libraries and rule sets. Configure security controls and alerting policies to continuously address such attacks.
Appendix 1: References
[1] Analysis of the Activities of the Natrix Group Using WeChat to Spread Malicious Code
https://www.antiy.cn/research/notice&report/research_report/SnakeTrojans_Analysis.html
[2] Analysis of Attack Activities Using Cloud Note Platforms for Delivering Remote Control Trojans
https://www.antiy.cn/research/notice&report/research_report/20230324.html
[3] Analysis of Large-Scale Attack Activities Targeting Domestic Users by the Natrix Group
https://www.antiy.cn/research/notice&report/research_report/20230518.html
[4] For more information on the Natrix Group, see the Antiy Virus Encyclopedia.
https://virusview.net/malware/Trojan/Win32/SwimSnake
[5] Antiy security threat investigation tools (Download Natrix Group Special Inspection Tool)
https://vs2.antiy.cn
