Analysis of the InterLock Ransomware Attacking Group’s Situation
The original report is in Chinese, and this version is an AI-translated edition.
1.Overview
The InterLock ransomware attack group was discovered in September 2024. This group penetrates victims’ networks through various means such as phishing, exploiting vulnerabilities, bundling with other malicious software, and illegally obtaining credentials, steals sensitive information and encrypts data, and implements double extortion to exert pressure on victims. So far, no evidence has been found that the group recruits affiliates through the ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) model to expand illegal profits. Currently, it has been detected that the group has developed encryption payloads targeting Windows, Linux, and FreeBSD systems. On Windows systems, the InterLock ransomware uses the “AES+RSA” algorithm to encrypt files. Signs of infection include the addition of the “.interlock” extension to file names and the appearance of a file named “!README.txt”. README! A ransom note with the extension “.txt”. As of now, no tool has been found that can effectively decrypt the data encrypted by the InterLock ransomware.
The InterLock group operates a website named “InterLock Worldwide Secrets Blog” on the dark web, which publicly discloses the information of the victims. This website contains the organization’s introduction, contact details, victim profiles, as well as data stolen from the victims’ systems. For each victim, the attackers create separate information sections, listing the victim’s name, official website link, overview of the information, types and quantities of the stolen files. The attackers use the public information of the victims and some of the stolen files as a threat to force the victims to pay ransoms or meet other illegal demands to prevent their data from being sold or disclosed. As of November 21, 2024, this website has disclosed the information of 7 victims, but the actual number of victims may be higher. The attackers may choose not to disclose or delete certain information for various reasons, such as reaching an agreement with the victims or the victims paying the ransom to have the information removed.
The characteristics of extortion encryption payload and attack tactics used by InterLock reveal the possible connection between InterLock and Rhysida [2]. Since its discovery in May 2023, the Rhysida group has operated in RaaS and dual blackmail models, but its attack activity has declined since October 2024. In the current complex ecology of cybercrime and the continued crackdown by global law enforcement agencies on extortion attack groups, the relationship between InterLock and Rhysida has led to multiple speculations that InterLock could be an affiliate or affiliate of Rhysida, In addition, that Rhysida group may have set up Interlock by inherit its technology and tactics, or by set up Interlock by some members of the Rhysida organization because of internal disagreement or other reasons, or by order to circumvent the crackdown of law enforcement agencies, Continue its illegal activities under the new name of InterLock. The speculations are based on similarities in ransomware operations and tactics between the two groups, as well as common dynamics and evasion strategies within cybercrime groups. Information about the ransomware software and its organization can be found in the Computer Virus Encyclopedia (https://www.virusview.net/RansomwareAttack).
It has been proved that Antiy IEP can effectively detect and kill the InterLock ransomware.
2.Group overview
Table 2-1 Group overview ‑
| Group name | Interlock |
| Time of occurrence | September 2024 |
| Method of intrusion | Phishing, exploit, piggyback on other malware, and illegally obtain credentials |
| Typical Encryption Suffix | .interlock |
| Decryption tools | No public decryption tools have been found |
| Encryption system | Windows, Linux, FreeBSD |
| Attack mode | Undirected and directed attack modes |
| Common industries | Health care, finance, education, manufacturing, public administration |
| Double ransom or not | Yes |
| Ransom note | 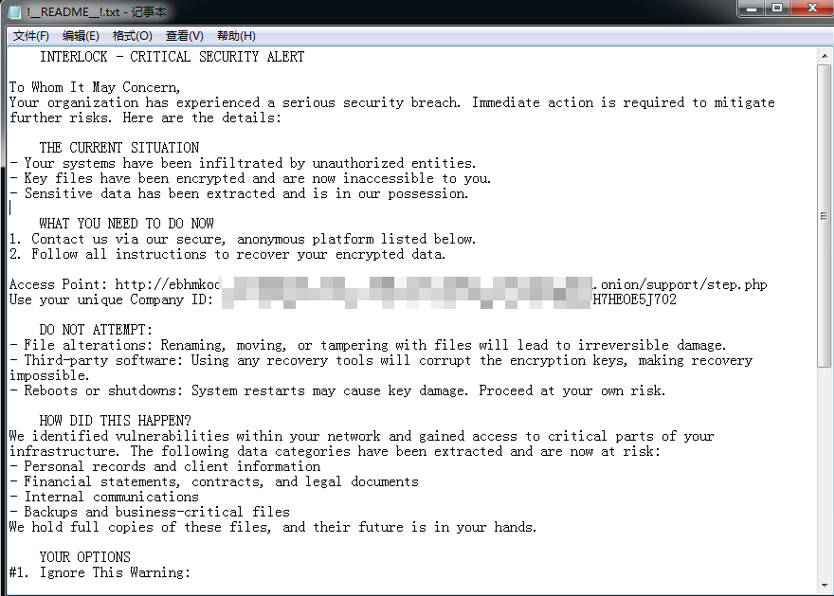 |
Interlock ransomware was discovered by MOXFIVE in September 2024 [1], and it was determined that the ransomware was used by InterLock based on information reserved in the ransomware letter.
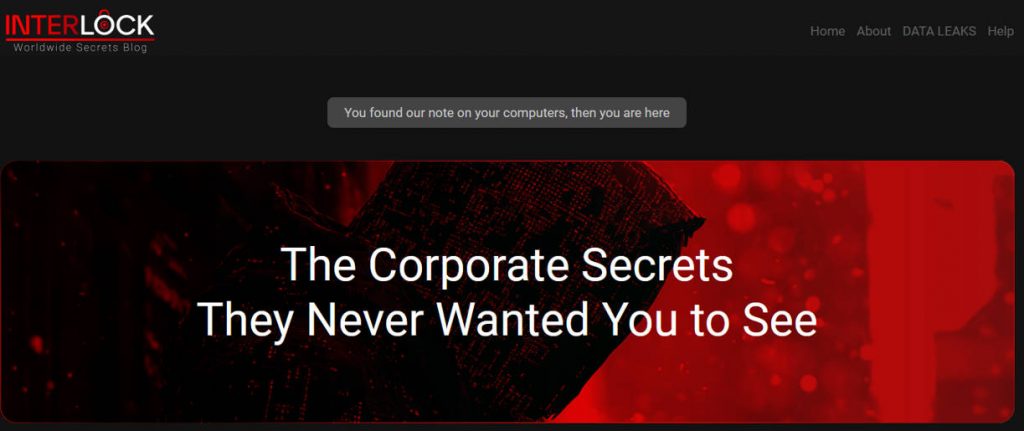
Figure 2-1 Organization of Dark Web Pages ‑
On the websites in the dark web, there is a “self-introduction” information section where the user can provide details such as their identity and the reasons for launching the ransomware attack.
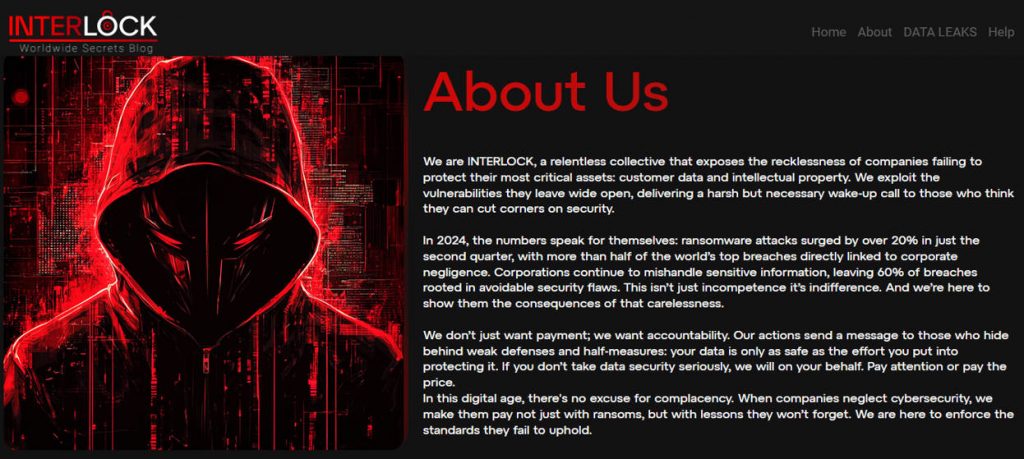
Figure 2-2 Organization of “Self-introduction.
Since the first victim’s information was released by the InterLock group on 13 October 2024, seven victims’ information has been released in succession as of 21 November, and the actual number of victims may be higher.
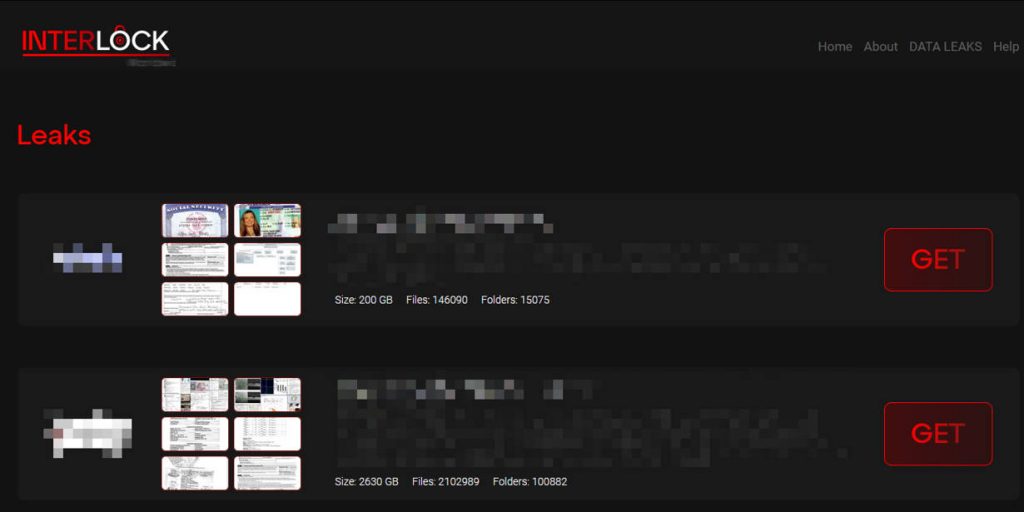
Figure 2-3 Victim Information Column
3.Sorting out the functions and techniques of samples
3.1 Sample labels
Table 3-1: Interlock Ransomware Sample Label
| Virus name | Trojan / Win32.InterLock [Ransom] |
| Original file name | Matrix |
| Md5 | F7f679420671b7e18677831d4d276277 |
| File size | 1.89 MB (1,982,464 bytes) |
| File format | Binexecute / Microsoft.EXE [: X86] |
| Time stamp | 2024-10-11 04: 47: 13 UTC |
| Digital signature | None |
| Shell type | None |
| Compiled Language | Visual C / C + + |
| Vt First Upload Time | 2024-10-13 17: 10: 43 UTC |
| Vt test result | 57 / 73 |
3.2 Sample analysis
The sample execution supports 4 execution parameters, and the specific functions are shown in Table 3-2.
Table 3-2 Function parameters
| Parameters | Functions |
| – Directory | Encrypt the specified folder |
| – file | Encrypt the specified file |
| – DELETE | From Delete |
| – System | Create System Scheduled Tasks |
The sample contains a large number of obfuscated code, and through the code self- decryption to restore the normal code execution, thereby increasing the analysis difficulty and reducing the code static characteristics.

Figure 3-1 Sample code confusion
If a self-delete paramete is specified, aft encryption ends, that file% Temp%\ tmp < random number > .wasd is freed and then execute using rundll32. The file is actually a dll format file, there is an export function run, function to delete the file.
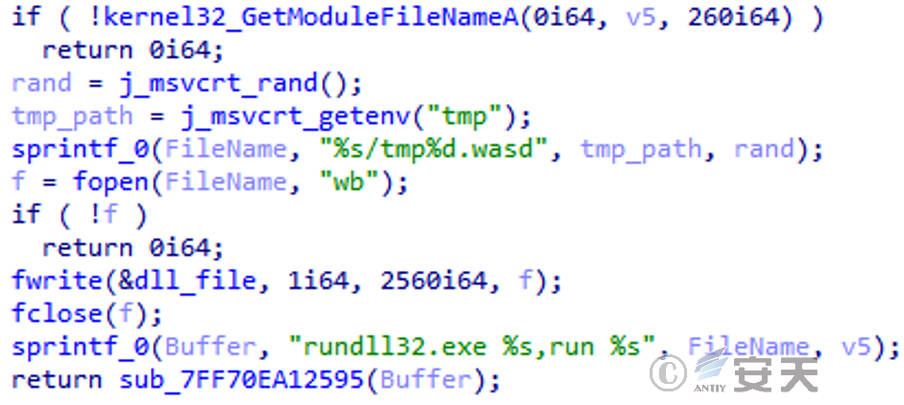
Figure 3-2 Self-deletion function
If you specify the scheduled task parameters, a scheduled task named TaskSystem is created.
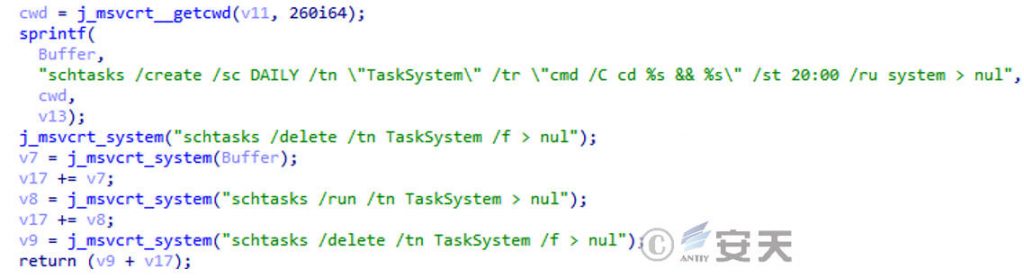
Figure 3-3 Creating Scheduled Tasks
Avoid system crash or encryption to anti-virus software files due to encryption, and do not encrypt specific folders.
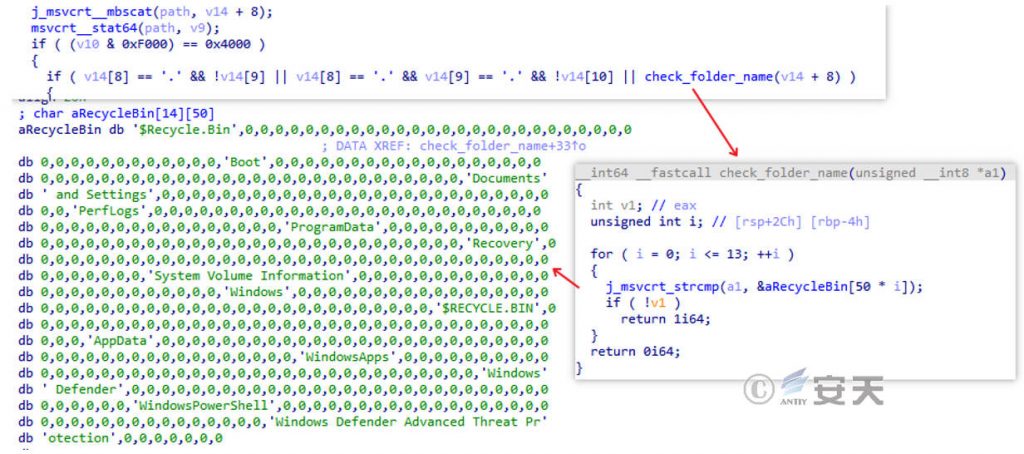
Figure 3-4 Bypass the Encrypted Folder
The folder information which specifically bypasses the encryption is shown in Table 3-3.
Table 3-3 Bypass the encrypted folder
| Bypass encrypted folders | ||||
| $Recycle.Bin | Boot | Documents and Settings | Perflogs | Programdata |
| Recovery | Windows | System Volume Information | Appdata | Windows Apps |
| Windows Defender | Windows PowerShell | Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection | ||
To avoid system crash due to encryption, do not encrypt files with specific suffix and specific file name.
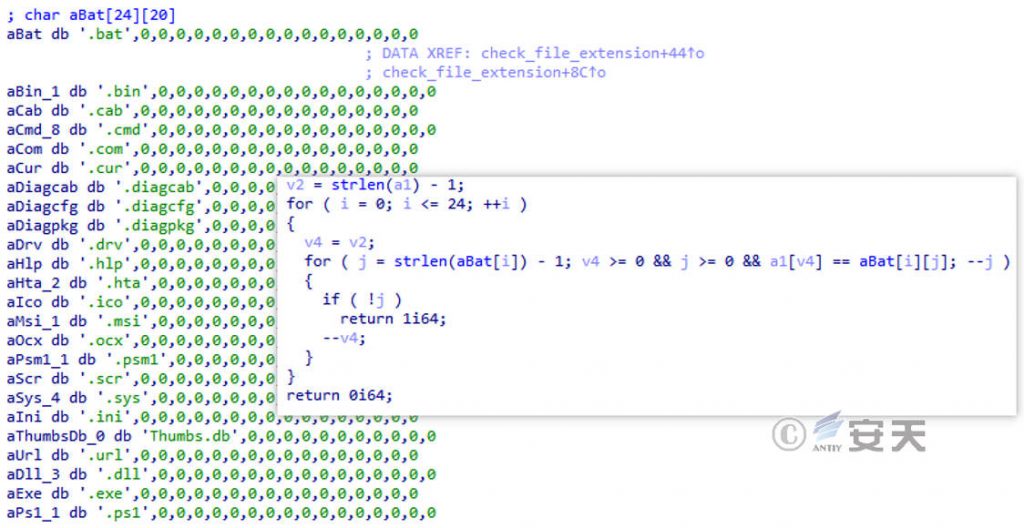
Figure 3-5 Encoder suffix and filename bypassing encryption
The suffix name and file name information for bypassing the encryption are shown in Table 34. ‑
Table 3-4 Bypass encrypted suffixes and file names
| Bypass encrypted suffixes and filenames | ||||
| .bin | .diagcab | .hta | .scr | .dll |
| .cab | .diagcfg | .ico | .sys | .exe |
| .cmd | .diagpkg | .msi | .ini | .ps1 |
| .com | .drv | .ocx | .url | .psm1 |
| .cur | .hlp | Thumbs.db | ||
The sample uses the LibTomCrypt encryption library.
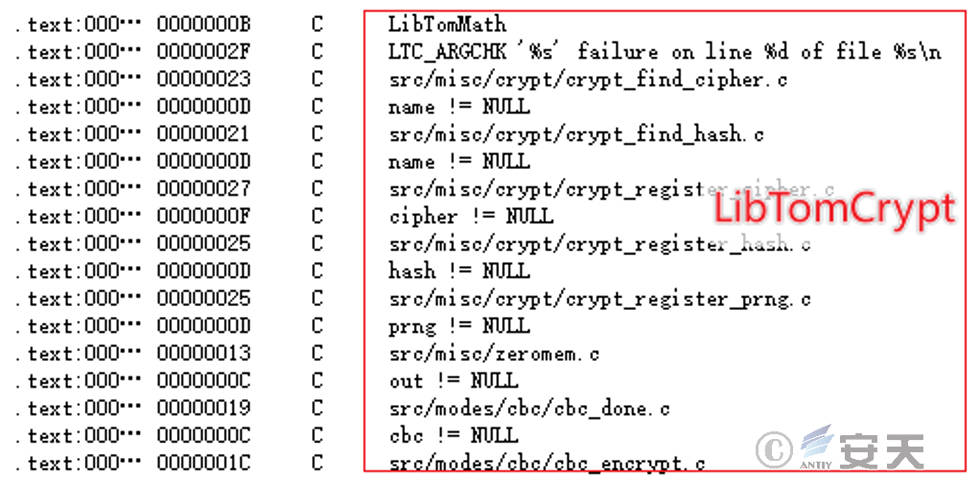
Figure 3-6 LibTomCrypt Encryption Library
The AES encryption packet size is aligned by padding bytes at the end of the target file to be encrypted until the file size is a multiple of 16 bytes.
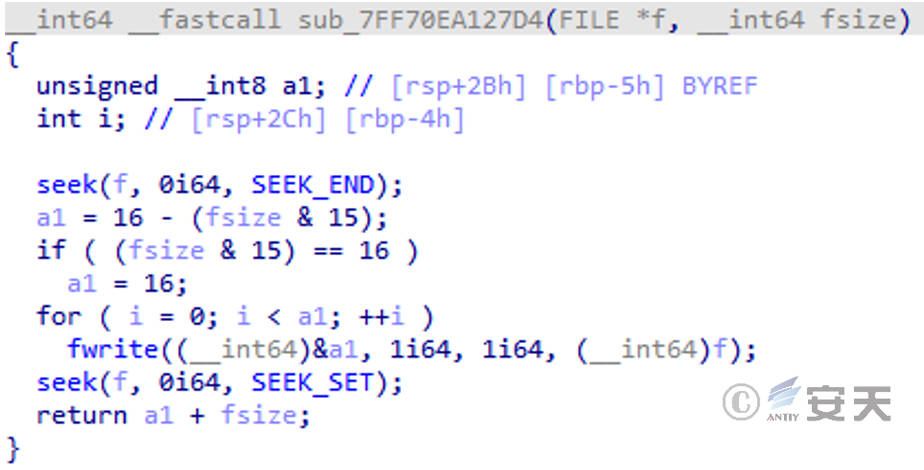
Figure 3-7 Fill the end of the target file
The sample adopts AES-CBC and RSA encryption algorithms, and the sample will generate an independent random number of 48 bytes for each file, and the first 32 bytes of the random number will be used as the AES key to encrypt the entire file. At the same time, the random number of 48 bytes is appended to the end of the encrypted file after asymmetric encryption using RSA. The overall encryption logic is shown in Figure 3-8.

Figure 3-8 Encryption logic
Use AES to encrypt the file code as shown in Figure 3-9, all contents of the file will be encrypted.
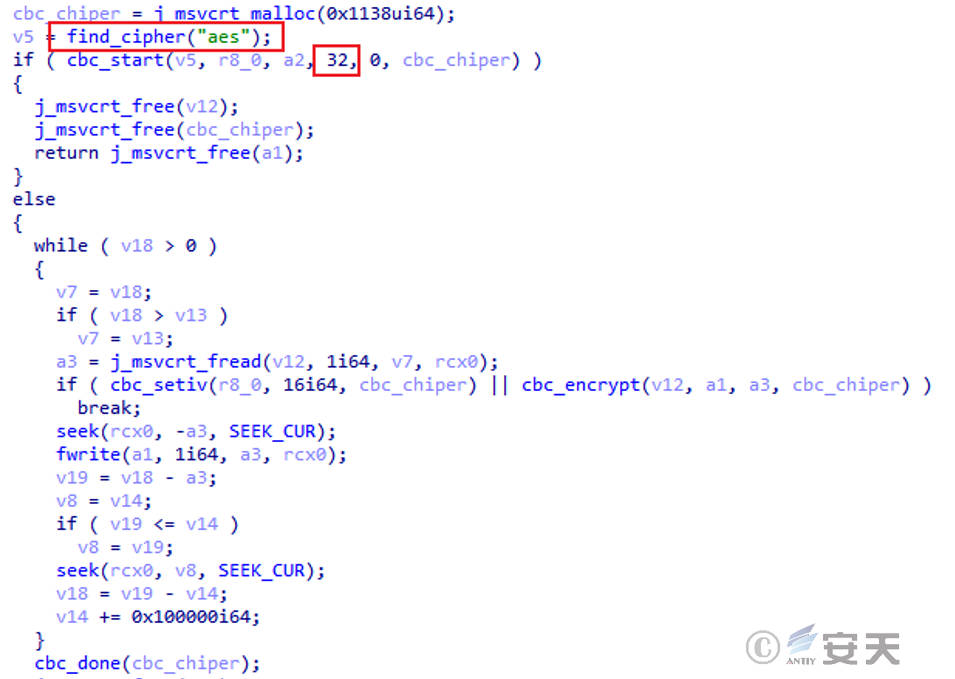
Figure 3-9 Employs an AES encryption algorithm
Relevant contents of the ransom letter.
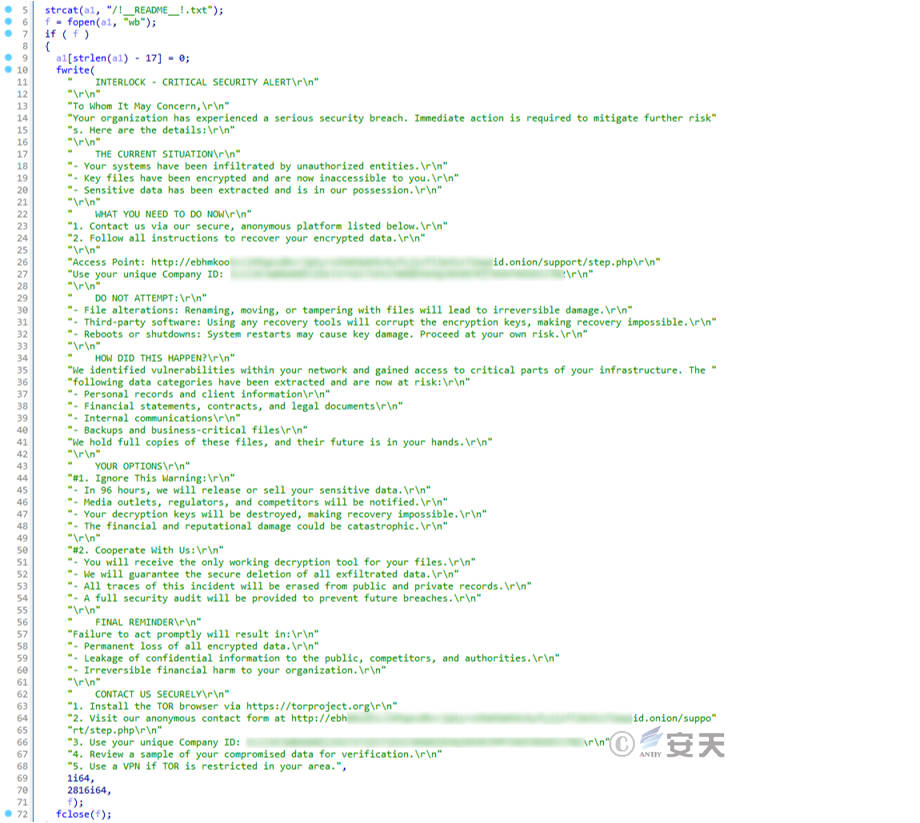
Figure 3-10: Code for creating a ransom letter
Clean the intrusion trace, after the sample execution ends, call the API to clean the related log.
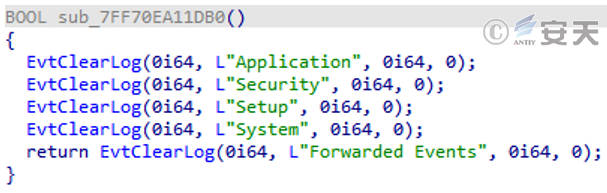
Figure 3-11 Clearing of relevant logs
4.Recommendations for protection
It is suggested that enterprise users deploy professional terminal security protection products, conduct real-time detection of local new and start-up files, and perform periodic virus scanning in the network. The Antiy IEP (hereinafter referred to as “IEP”), relying on Antiy’s self-research threat detection engine and core-level active defense capability, can effectively detect and kill the virus samples found this time.
With core-level protection capability, IEP judges whether there are attack actions such as persistence, power raising and information theft based on the operation behaviors of memory objects such as continuous monitoring of processes by the core driver. Combined with the detection of ransomware behavior characteristic database, it can analyze whether the process behavior is suspected to be a ransomware attack behavior, and can block the discovered ransomware attack at the first time.
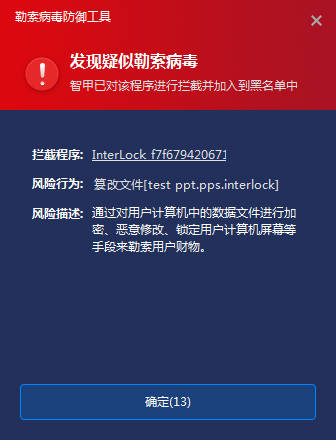
Figure 4-1 When a virus is found, IEP intercepts and sends an alarm at the first time
IEP provides a unified security management center, through which administrators can quickly complete operations such as viewing, analyzing and handling security events in the network, and improve the efficiency of security management.
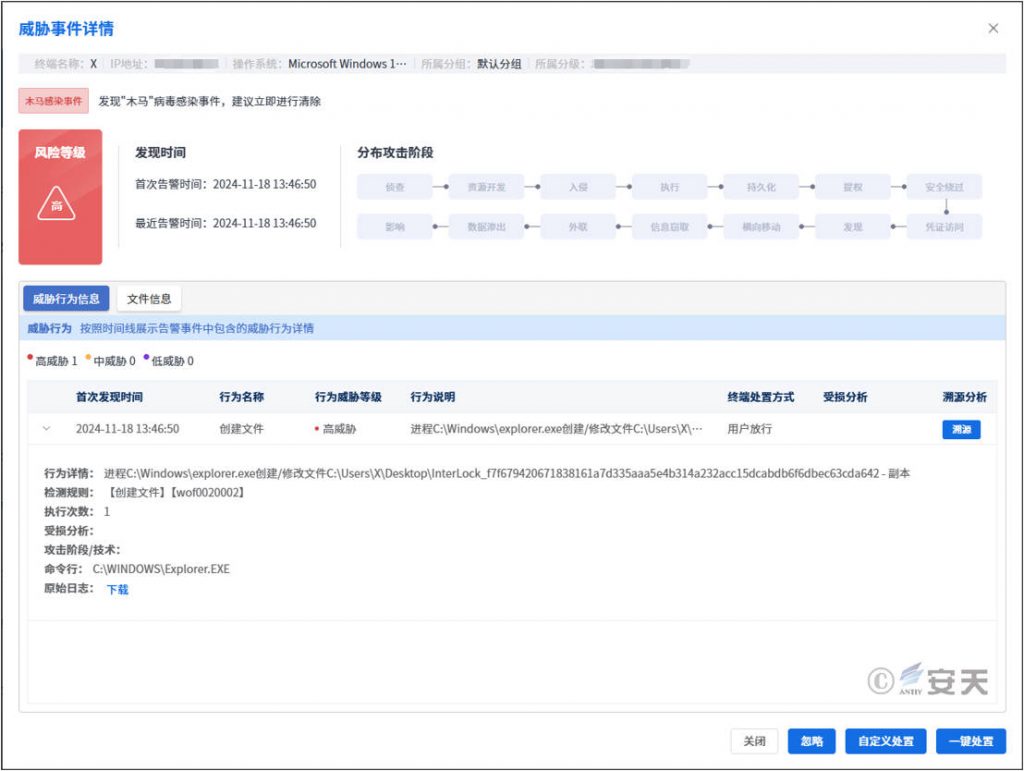
Figure 4-2 One-click handling of threats through the unified management platform of IEP
Appendix I: Reference
[1] Active Racketeer Attack Group Inventory 2023 [R / OL]. (2024-01-25)
Https: / / www.antiy.cn / research / notice & report / research _ report / RansomwareInventory.html
[2] Moxfive Threat Actor Alert-INTERLOCK Ransomware [R / OL]. (2024-09-30)
Https: / / www.mocfive.com / resources / mocfive-threat-actor-spotlight-lock-ransomware
Appendix 2: About Antiy
Antiy is committed to enhancing the network security defense capabilities of its customers and effectively responding to security threats. Through more than 20 years of independent research and development, Antiy has developed technological leadership in areas such as threat detection engines, advanced threat countermeasures, and large-scale threat automation analysis.
Antiy has developed IEP (Intelligent Endpoint Protection System) security product family for PC, server and other system environments, as well as UWP (Unified Workload Protect) security products for cloud hosts, container and other system environments, providing system security capabilities including endpoint antivirus, endpoint protection (EPP), endpoint detection and response (EDR), and Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) , etc. Antiy has established a closed-loop product system of threat countermeasures based on its threat intelligence and threat detection capabilities, achieving perception, retardation, blocking and presentation of the advanced threats through products such as the Persistent Threat Detection System (PTD), Persistent Threat Analysis System (PTA), Attack Capture System (ACS), and TDS. For web and business security scenarios, Antiy has launched the PTF Next-generation Web Application and API Protection System (WAAP) and SCS Code Security Detection System to help customers shift their security capabilities to the left in the DevOps process. At the same time, it has developed four major kinds of security service: network attack and defense logic deduction, in-depth threat hunting, security threat inspection, and regular security operations. Through the Threat Confrontation Operation Platform (XDR), multiple security products and services are integrated to effectively support the upgrade of comprehensive threat confrontation capabilities.
Antiy provides comprehensive security solutions for clients with high security requirements, including network and information authorities, military forces, ministries, confidential industries, and critical information infrastructure. Antiy has participated in the security work of major national political and social events since 2005 and has won honors such as the Outstanding Contribution Award and Advanced Security Group. Since 2015, Antiy’s products and services have provided security support for major spaceflight missions including manned spaceflight, lunar exploration, and space station docking, as well as significant missions such as the maiden flight of large aircraft, escort of main force ships, and Antarctic scientific research. We have received several thank-you letters from relevant departments.
Antiy is a core enabler of the global fundamental security supply chain. Nearly a hundred of the world’s leading security and IT enterprises have chosen Antiy as their partner of detection capability. At present, Antiy’s threat detection engine provides security detection capabilities for over 1.3 million network devices and over 3 billion smart terminal devices worldwide, which has become a “national-level” engine. As of now, Antiy has filed 1,877 patents in the field of cybersecurity and obtained 936 patents. It has been awarded the title of National Intellectual Property Advantage Enterprise and the 17th (2015) China Patent Excellence Award.
Antiy is an important enterprise node in China emergency response system and has provided early warning and comprehensive emergency response in major security threats and virus outbreaks such as “Code Red”, “Dvldr”, “Heartbleed”, “Bash Shellcode” and “WannaCry”. Antiy conducts continuous monitoring and in-depth analysis against dozens of advanced cyberspce threat actors (APT groups) such as “Equation”, “White Elephant”, “Lotus” and “Greenspot” and their attack actions, assisting customers to form effective protection when the enemy situation is accurately predicted.


