Risk Warning and Temporary Mitigation Tool for Windows Server RDL Remote Execution Vulnerability
The original report is in Chinese, and this version is an AI-translated edition.
1. Vulnerability overview
Microsoft in July fixed three Windows Server Remote Desktop Licensing Service (RDL) remote code execution vulnerabilities, identified as CVE-2024-38077, CVE-2024-38074 and CVE-2024-38076. Among them, CVE-2024-38077 has the biggest impact, affecting 17 versions of Windows Server, CVE-2024-38074 affecting 13 versions of Windows Server, and CVE-2024-38076 affecting 7 versions of Windows Server. Windows Server is a server operating system launched by Microsoft Corporation, which is specially designed for server environment and provides rich functions and powerful network management capability. It is suitable to be used in many aspects such as enterprise station building, network application, database management, etc.
The vulnerability found this time only affects the version of Windows Server and does not affect other versions of Windows, which exists in Windows Remote Desktop Authorization Service (RDL). Since this service is widely deployed and a server that opens Windows Remote Desktop (TCP: Port 3389) for managing remote desktop connection permissions, although this service is not opened by default, due to remote management requirements, Manual opening by the administrator is still extensive. The vulnerability was caused by a heap buffer overflow in the Windows Remote Desktop Authorization Service that can cause an attacker to execute arbitrary code remotely without authentication. Through this vulnerability, the attacker only needs to send special data packets to the server that has opened the relevant service, and can completely control the target system and obtain the highest SYSTEM authority.
2.Scope of impact of vulnerability
The three Windows Server Remote Desktop Authorization Service (RDL) remote code execution vulnerabilities that Microsoft fixes affect the version of Windows Server as follows.
| Vulnerability Number | Influence Version |
| Cve-2024-38077 | Windows Server 2012 R2 (Server Core installation) |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | |
| Windows Server 2012 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2012 | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 1 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 1 | |
| Windows Server 2008 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 2 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2008 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 2 | |
| Windows Server 2008 for 32-bit Systems Service Pack 2 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2008 for 32-bit Systems Service Pack 2 | |
| Windows Server 2016 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2016 | |
| Windows Server 2022, 23H2 Edition (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2022 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2022 | |
| Windows Server 2019 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2019 | |
| Cve-2024-38074 | Windows Server 2012 R2 (Server Core installation) |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | |
| Windows Server 2012 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2012 | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 1 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 1 | |
| Windows Server 2016 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2016 | |
| Windows Server 2022, 23H2 Edition (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2022 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2022 | |
| Windows Server 2019 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2019 | |
| Cve-2024-38076 | Windows Server 2016 (Server Core installation) |
| Windows Server 2016 | |
| Windows Server 2022, 23H2 Edition (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2022 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2022 | |
| Windows Server 2019 (Server Core installation) | |
| Windows Server 2019 |
3.Vulnerability response plan
3.1 Official bug fix plan
At present, Microsoft has issued a security patch to repair this vulnerability, it is suggested that the affected users upgrade the protection in time.
- Cve-2024-38077 bug patch download address:
Https: / / msrc.microsoft.com / update-guide / Vulnerability / CVE-2024-38077
| Product | Article | Download | Build Number |
| Windows Server 2008 for 32-bit Systems Service Pack 2 | 5040499 | Monthly Rollup | 6.0.6003.22769 |
| Windows Server 2008 for 32-bit Systems Service Pack 2 | 5040490 | Security Only | 6.0.6003.22769 |
| Windows Server 2008 for 32-bit Systems Service Pack 2 (Server Core installation) | 5040499 | Monthly Rollup | 6.0.6003.22769 |
| Windows Server 2008 for 32-bit Systems Service Pack 2 (Server Core installation) | 5040490 | Security Only | 6.0.6003.22769 |
| Windows Server 2008 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 2 | 5040499 | Monthly Rollup | 6.0.6003.22769 |
| Windows Server 2008 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 2 | 5040490 | Security Only | 6.0.6003.22769 |
| Windows Server 2008 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 2 (Server Core installation) | 5040499 | Monthly Rollup | 6.0.6003.22769 |
| Windows Server 2008 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 2 (Server Core installation) | 5040490 | Security Only | 6.0.6003.22769 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 1 | 5040497 | Monthly Rollup | 6.1.7601.27219 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 1 | 5040498 | Security Only | 6.1.7601.27219 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 1 (Server Core installation) | 5040497 | Monthly Rollup | 6.1.7601.27219 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 1 (Server Core installation) | 5040498 | Security Only | 6.1.7601.27219 |
| Windows Server 2012 | 5040485 | Monthly Rollup | 6.2.9200.24975 |
| Windows Server 2012 (Server Core installation) | 5040485 | Monthly Rollup | 6.2.9200.24975 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 5040456 | Monthly Rollup | 6.3.9600.22074 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 (Server Core installation) | 5040456 | Monthly Rollup | 6.3.9600.22074 |
| Windows Server 2016 | 5040434 | Security Update | 10.0.14393.7159 |
| Windows Server 2016 (Server Core installation) | 5040434 | Security Update | 10.0.14393.7159 |
| Windows Server 2019 | 5040430 | Security Update | 10.0.17763.6054 |
| Windows Server 2019 (Server Core installation) | 5040430 | Security Update | 10.0.17763.6054 |
| Windows Server 2022 | 5040437 | Security Update | 10.0.20348.2582 |
| Windows Server 2022 (Server Core installation) | 5040437 | Security Update | 10.0.20348.2582 |
| Windows Server 2022, 23H2 Edition (Server Core installation) | 5040438 | Security Update | 10.0.25398.1009 |
- Cve-2024-38074 bug patch download address:
Https: / / msrc.microsoft.com / update-guide / en-US / advisory / CVE-2024-38074
| Product | Article | Download | Build Number |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 (Server Core installation) | 5040456 | Monthly Rollup | 6.3.9600.22074 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 5040456 | Monthly Rollup | 6.3.9600.22074 |
| Windows Server 2012 (Server Core installation) | 5040485 | Monthly Rollup | 6.2.9200.24975 |
| Windows Server 2012 | 5040485 | Monthly Rollup | 6.2.9200.24975 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 1 (Server Core installation) | 5040497 5040498 | Monthly Rollup Security Only | 6.1.7601.27219 6.1.7601.27219 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 1 | 5040497 5040498 | Monthly Rollup Security Only | 6.1.7601.27219 6.1.7601.27219 |
| Windows Server 2016 (Server Core installation) | 5040434 | Security Update | 10.0.14393.7159 |
| Windows Server 2016 | 5040434 | Security Update | 10.0.14393.7159 |
| Windows Server 2022, 23H2 Edition (Server Core installation) | 5040438 | Security Update | 10.0.25398.1009 |
| Windows Server 2022 (Server Core installation) | 5040437 | Security Update | 10.0.20348.2582 |
| Windows Server 2022 | 5040437 | Security Update | 10.0.20348.2582 |
| Windows Server 2019 (Server Core installation) | 5040430 | Security Update | 10.0.17763.6054 |
| Windows Server 2019 | 5040430 | Security Update | 10.0.17763.6054 |
- Cve-2024-38076 bug patch download address:
Https: / / msrc.microsoft.com / update-guide / en-US / Vulnerability / CVE-2024-38076
| Product | Article | Download | Build Number |
| Windows Server 2016 (Server Core installation) | 5040434 | Security Update | 10.0.14393.7159 |
| Windows Server 2016 | 5040434 | Security Update | 10.0.14393.7159 |
| Windows Server 2022, 23H2 Edition (Server Core installation) | 5040438 | Security Update | 10.0.25398.1009 |
| Windows Server 2022 (Server Core installation) | 5040437 | Security Update | 10.0.20348.2582 |
| Windows Server 2022 | 5040437 | Security Update | 10.0.20348.2582 |
| Windows Server 2019 (Server Core installation) | 5040430 | Security Update | 10.0.17763.6054 |
| Windows Server 2019 | 5040430 | Security Update | 10.0.17763.6054 |
| Windows Server 2016 (Server Core installation) | 5040434 | Security Update | 10.0.14393.7159 |
| Windows Server 2016 | 5040434 | Security Update | 10.0.14393.7159 |
| Windows Server 2022, 23H2 Edition (Server Core installation) | 5040438 | Security Update | 10.0.25398.1009 |
| Windows Server 2022 (Server Core installation) | 5040437 | Security Update | 10.0.20348.2582 |
3.2 Temporary vulnerability mitigation plan
Currently, Microsoft’s official vulnerability mitigation solution is to disable this service on Windows Server servers that do not require Remote Desktop Licensing. Note: This operation will affect the authorization and authentication of remote desktop, and may cause problems in remote desktop login and affect normal business.
It is important to note that the vulnerability mitigation solution does not fix this vulnerability! Even if you shut down the service, we recommend that you install the official Microsoft patch in due course to completely fix the vulnerability!
3.3 Use safety day vulnerability emergency tools to mitigate vulnerabilities
Antiy CVE-2024-38077 vulnerability emergency handling tool is a special tool for detecting and handling the vulnerability, through which you can check whether your computer will be affected by the vulnerability, and perform emergency handling and download the patch. This tool has been uploaded to Antiy Vertical Response Platform (https: / / vs2.antiy.cn /).
Start program and detect Double-click “ATFixRDLtool.exe” to start program, after program is started, vulnerability detection will be automatically performed; if the current version of computer’s operating system is not affected by the vulnerability or the vulnerability has been repaired, It is not necessary to use this tool for disposal. If that vulnerability exist in the current version of the computer’s operate system, the tool will prompt you and you can use the tool to dispose of it.
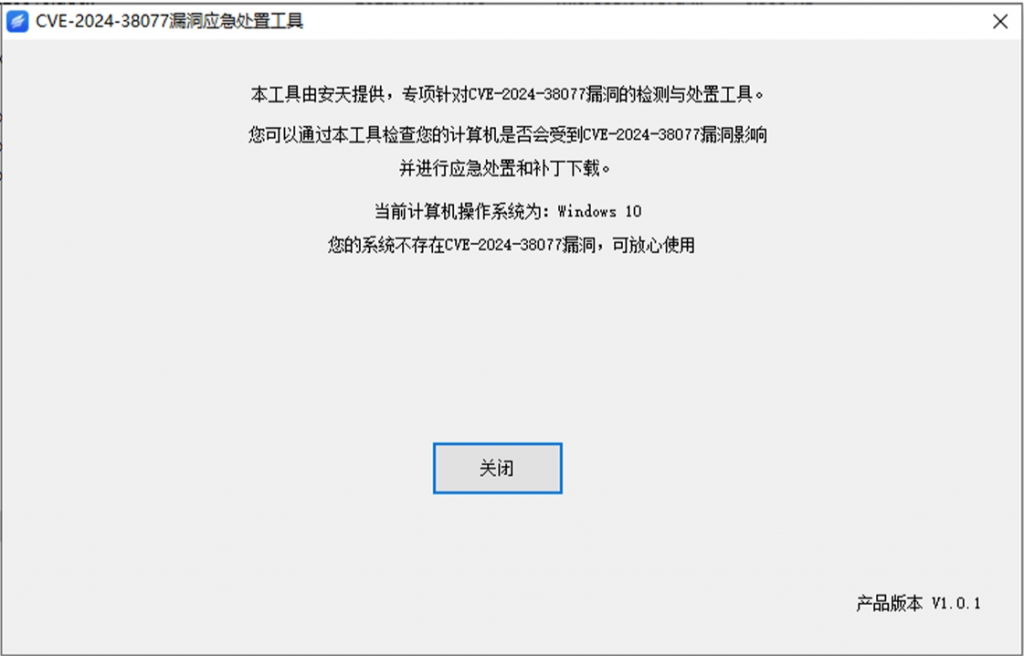
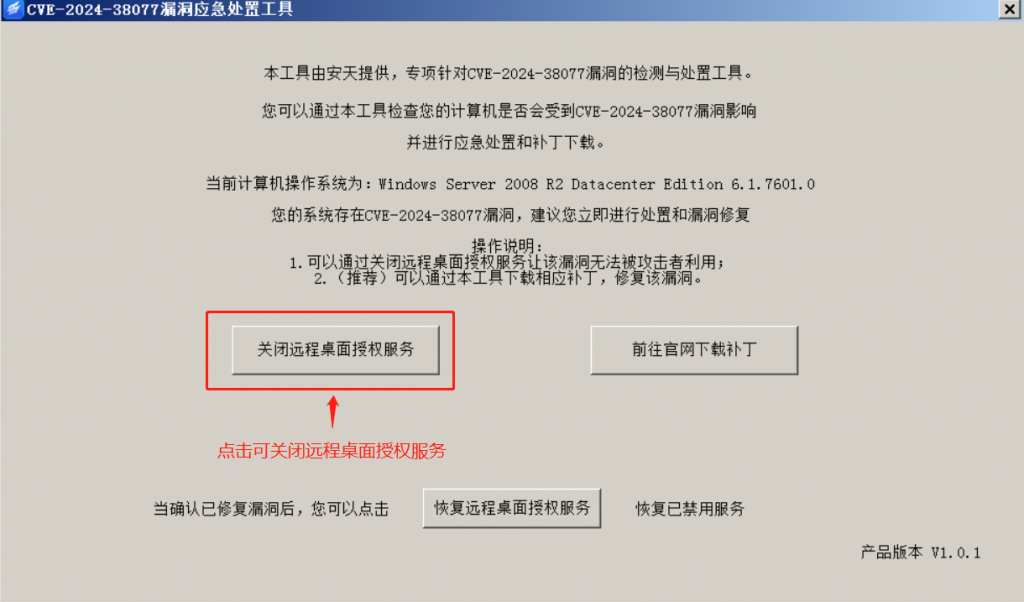
Vulnerability disposal This tool provides two ways to dispose of the vulnerability, including:
Method 1: closes the remote desktop authorization service, after closing the service, the attacker will not be able to use the vulnerability to attack, but when closing the service while using the remote desktop service, only two sessions will be allowed to log in at most. And this method is a mitigation measure, it is recommended that you fix the vulnerability as soon as possible to ensure security.
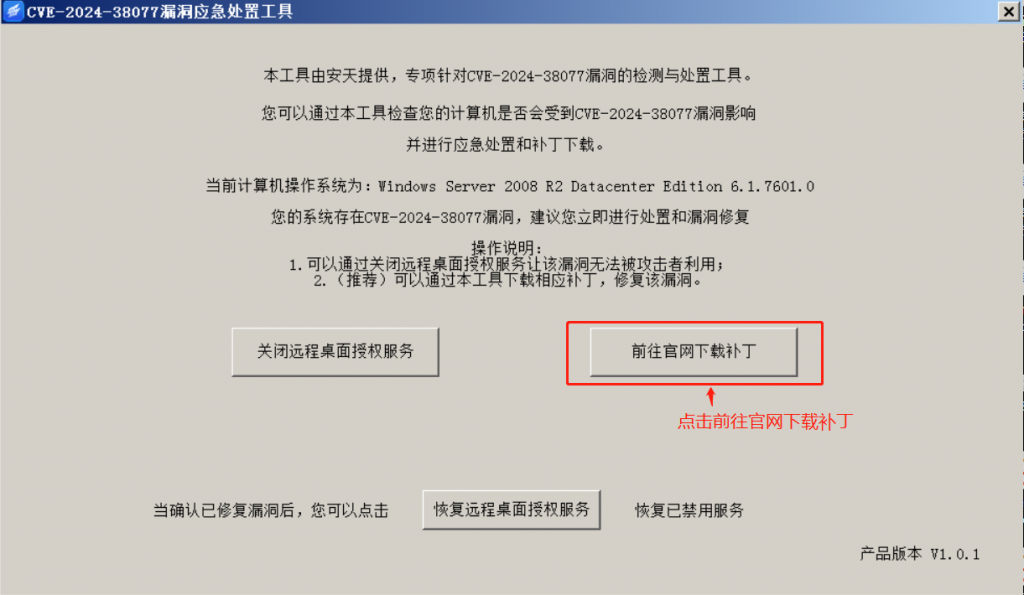
Method 2: Click “Go to the official website to download the patch,” and the tool will automatically jump to the official patch download page for you, download the required patch and run the installation locally. Fixing the vulnerability can fundamentally solve the problem, and it is suggested to fix the vulnerability in time. Note that downloading the patch requires the computer to access the Internet
- Security Statement
This security statement is only intended to describe any safety issues that may exist and shall not be subject to any warranty or commitment by Antiy. The use of this security statement shall comply with relevant laws and regulations. Any direct or indirect consequence and loss caused by the dissemination and use of the information provided in this security statement shall be the responsibility of the user, and the author of this security statement and the security statement shall not be liable for this.
Antiy shall have the right to revise and interpret this security statement. If you wish to reproduce or disseminate this security statement, you must ensure the integrity, including the copyright notice. Without the permission of Antiy the content of this security statement shall not be arbitrarily modified or increased, nor shall it be used for commercial purposes in any way.
Reference
[1] Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2024-38077)
Https: / / msrc.microsoft.com / update-guide / Vulnerability / CVE-2024-38077
[2] Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2024-38074)
Https: / / msrc.microsoft.com / update-guide / en-US / advisory / CVE-2024-38074
[3] Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2024-38076)
Https: / / msrc.microsoft.com / update-guide / en-US / Vulnerability / CVE-2024-38076
Appendix: About Antiy
Antiy is committed to enhancing the network security defense capabilities of its customers and effectively responding to security threats. Through more than 20 years of independent research and development, Antiy has developed technological leadership in areas such as threat detection engines, advanced threat countermeasures, and large-scale threat automation analysis.
Antiy has developed IEP (Intelligent Endpoint Protection System) security product family for PC, server and other system environments, as well as UWP (Unified Workload Protect) security products for cloud hosts, container and other system environments, providing system security capabilities including endpoint antivirus, endpoint protection (EPP), endpoint detection and response (EDR), and Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) , etc. Antiy has established a closed-loop product system of threat countermeasures based on its threat intelligence and threat detection capabilities, achieving perception, retardation, blocking and presentation of the advanced threats through products such as the Persistent Threat Detection System (PTD), Persistent Threat Analysis System (PTA), Attack Capture System (ACS), and TDS. For web and business security scenarios, Antiy has launched the PTF Next-generation Web Application and API Protection System (WAAP) and SCS Code Security Detection System to help customers shift their security capabilities to the left in the DevOps process. At the same time, it has developed four major kinds of security service: network attack and defense logic deduction, in-depth threat hunting, security threat inspection, and regular security operations. Through the Threat Confrontation Operation Platform (XDR), multiple security products and services are integrated to effectively support the upgrade of comprehensive threat confrontation capabilities.
Antiy provides comprehensive security solutions for clients with high security requirements, including network and information authorities, military forces, ministries, confidential industries, and critical information infrastructure. Antiy has participated in the security work of major national political and social events since 2005 and has won honors such as the Outstanding Contribution Award and Advanced Security Group. Since 2015, Antiy’s products and services have provided security support for major spaceflight missions including manned spaceflight, lunar exploration, and space station docking, as well as significant missions such as the maiden flight of large aircraft, escort of main force ships, and Antarctic scientific research. We have received several thank-you letters from relevant departments.
Antiy is a core enabler of the global fundamental security supply chain. Nearly a hundred of the world’s leading security and IT enterprises have chosen Antiy as their partner of detection capability. At present, Antiy’s threat detection engine provides security detection capabilities for over 1.3 million network devices and over 3 billion smart terminal devices worldwide, which has become a “national-level” engine. As of now, Antiy has filed 1,877 patents in the field of cybersecurity and obtained 936 patents. It has been awarded the title of National Intellectual Property Advantage Enterprise and the 17th (2015) China Patent Excellence Award.
Antiy is an important enterprise node in China emergency response system and has provided early warning and comprehensive emergency response in major security threats and virus outbreaks such as “Code Red”, “Dvldr”, “Heartbleed”, “Bash Shellcode” and “WannaCry”. Antiy conducts continuous monitoring and in-depth analysis against dozens of advanced cyberspce threat actors (APT groups) such as “Equation”, “White Elephant”, “Lotus” and “Greenspot” and their attack actions, assisting customers to form effective protection when the enemy situation is accurately predicted.


